Related Research Articles

Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology.
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials.

The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function.
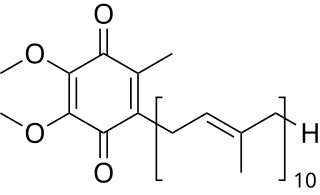
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), also known as ubiquinone, is a naturally occurring biochemical cofactor (coenzyme) and an antioxidant produced by the human body. It can also be obtained from dietary sources, such as meat, fish, seed oils, vegetables, and dietary supplements. CoQ10 is found in many organisms, including animals and bacteria.

A micelle or micella is an aggregate of surfactant amphipathic lipid molecules dispersed in a liquid, forming a colloidal suspension. A typical micelle in water forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single-tail regions in the micelle centre.

A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. While the term originally was specific to metabolite compounds that had toxic effects on other organisms, it has developed to encompass any constituents, secretions, and metabolites of plants or animals. In context of molecular biology, biogenic substances are referred to as biomolecules. They are generally isolated and measured through the use of chromatography and mass spectrometry techniques. Additionally, the transformation and exchange of biogenic substances can by modelled in the environment, particularly their transport in waterways.

A liposome is a small artificial vesicle, spherical in shape, having at least one lipid bilayer. Due to their hydrophobicity and/or hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, particle size and many other properties, liposomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles for administration of pharmaceutical drugs and nutrients, such as lipid nanoparticles in mRNA vaccines, and DNA vaccines. Liposomes can be prepared by disrupting biological membranes.

In chemistry, an ionophore is a chemical species that reversibly binds ions. Many ionophores are lipid-soluble entities that transport ions across the cell membrane. Ionophores catalyze ion transport across hydrophobic membranes, such as liquid polymeric membranes or lipid bilayers found in the living cells or synthetic vesicles (liposomes). Structurally, an ionophore contains a hydrophilic center and a hydrophobic portion that interacts with the membrane.

Nanobiotechnology, bionanotechnology, and nanobiology are terms that refer to the intersection of nanotechnology and biology. Given that the subject is one that has only emerged very recently, bionanotechnology and nanobiotechnology serve as blanket terms for various related technologies.
An efflux pump is an active transporter in cells that moves out unwanted material. Efflux pumps are an important component in bacteria in their ability to remove antibiotics. The efflux could also be the movement of heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that encode efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species - the most concerning being antibiotic resistance because microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media.

Drug delivery refers to approaches, formulations, manufacturing techniques, storage systems, and technologies involved in transporting a pharmaceutical compound to its target site to achieve a desired therapeutic effect. Principles related to drug preparation, route of administration, site-specific targeting, metabolism, and toxicity are used to optimize efficacy and safety, and to improve patient convenience and compliance. Drug delivery is aimed at altering a drug's pharmacokinetics and specificity by formulating it with different excipients, drug carriers, and medical devices. There is additional emphasis on increasing the bioavailability and duration of action of a drug to improve therapeutic outcomes. Some research has also been focused on improving safety for the person administering the medication. For example, several types of microneedle patches have been developed for administering vaccines and other medications to reduce the risk of needlestick injury.

The fatty-acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are a family of transport proteins for fatty acids and other lipophilic substances such as eicosanoids and retinoids. These proteins are thought to facilitate the transfer of fatty acids between extra- and intracellular membranes. Some family members are also believed to transport lipophilic molecules from outer cell membrane to certain intracellular receptors such as PPAR. The FABPs are intracellular carriers that “solubilize” the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA), transporting AEA to the breakdown by FAAH, and compounds that bind to FABPs block AEA breakdown, raising its level. The cannabinoids are also discovered to bind human FABPs that function as intracellular carriers, as THC and CBD inhibit the cellular uptake and catabolism of AEA by targeting FABPs. Competition for FABPs may in part or wholly explain the increased circulating levels of endocannabinoids reported after consumption of cannabinoids. Levels of fatty-acid-binding protein have been shown to decline with ageing in the mouse brain, possibly contributing to age-associated decline in synaptic activity.

Lipid-based nanoparticles are very small spherical particles composed of lipids. They are a novel pharmaceutical drug delivery system, and a novel pharmaceutical formulation. There are many subclasses of lipid-based nanoparticles such as: lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs).

A nanoparticle–biomolecule conjugate is a nanoparticle with biomolecules attached to its surface. Nanoparticles are minuscule particles, typically measured in nanometers (nm), that are used in nanobiotechnology to explore the functions of biomolecules. Properties of the ultrafine particles are characterized by the components on their surfaces more so than larger structures, such as cells, due to large surface area-to-volume ratios. Large surface area-to-volume-ratios of nanoparticles optimize the potential for interactions with biomolecules.
Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the brain is a method for transporting drug molecules across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) using nanoparticles. These drugs cross the BBB and deliver pharmaceuticals to the brain for therapeutic treatment of neurological disorders. These disorders include Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, depression, and brain tumors. Part of the difficulty in finding cures for these central nervous system (CNS) disorders is that there is yet no truly efficient delivery method for drugs to cross the BBB. Antibiotics, antineoplastic agents, and a variety of CNS-active drugs, especially neuropeptides, are a few examples of molecules that cannot pass the BBB alone. With the aid of nanoparticle delivery systems, however, studies have shown that some drugs can now cross the BBB, and even exhibit lower toxicity and decrease adverse effects throughout the body. Toxicity is an important concept for pharmacology because high toxicity levels in the body could be detrimental to the patient by affecting other organs and disrupting their function. Further, the BBB is not the only physiological barrier for drug delivery to the brain. Other biological factors influence how drugs are transported throughout the body and how they target specific locations for action. Some of these pathophysiological factors include blood flow alterations, edema and increased intracranial pressure, metabolic perturbations, and altered gene expression and protein synthesis. Though there exist many obstacles that make developing a robust delivery system difficult, nanoparticles provide a promising mechanism for drug transport to the CNS.
Members of the Organic Anion Transporter (OAT) Family are membrane transport proteins or 'transporters' that mediate the transport of mainly organic anions across the cell membrane. Therefore, OATPs are present in the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane, acting as the cell's gatekeepers. OATPs belong to the Solute Carrier Family (SLC) and the major facilitator superfamily.
Nanoparticle drug delivery systems are engineered technologies that use nanoparticles for the targeted delivery and controlled release of therapeutic agents. The modern form of a drug delivery system should minimize side-effects and reduce both dosage and dosage frequency. Recently, nanoparticles have aroused attention due to their potential application for effective drug delivery.
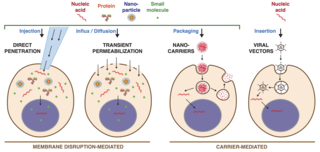
Intracellular delivery is the process of introducing external materials into living cells. Materials that are delivered into cells include nucleic acids, proteins, peptides, impermeable small molecules, synthetic nanomaterials, organelles, and micron-scale tracers, devices and objects. Such molecules and materials can be used to investigate cellular behavior, engineer cell operations or correct a pathological function.
Intranasal drug delivery occurs when particles are inhaled into the nasal cavity and transported directly into the nervous system. Though pharmaceuticals can be injected into the nose, some concerns include injuries, infection, and safe disposal. Studies demonstrate improved patient compliance with inhalation. Treating brain diseases has been a challenge due to the blood brain barrier. Previous studies evaluated the efficacy of delivery therapeutics through intranasal route for brain diseases and mental health conditions. Intranasal administration is a potential route associated with high drug transfer from nose to brain and drug bioavailability.
Immunoliposome therapy is a targeted drug delivery method that involves the use of liposomes coupled with monoclonal antibodies to deliver therapeutic agents to specific sites or tissues in the body. The antibody modified liposomes target tissue through cell-specific antibodies with the release of drugs contained within the assimilated liposomes. Immunoliposome aims to improve drug stability, personalize treatments, and increased drug efficacy. This form of therapy has been used to target specific cells, protecting the encapsulated drugs from degradation in order to enhance their stability, to facilitate sustained drug release and hence to advance current traditional cancer treatment.
References
- ↑ Zhang, Ming; Xu, Liheng (4 March 2022). "Transport of micro- and nanoplastics in the environment: Trojan-Horse effect for organic contaminants". Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 52 (5): 810–846. Bibcode:2022CREST..52..810Z. doi:10.1080/10643389.2020.1845531. S2CID 228865980.
- ↑ Pardridge, William M. (May 2023). "Brain gene therapy with Trojan horse lipid nanoparticles". Trends in Molecular Medicine. 29 (5): 343–353. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2023.02.004. PMC 10005896 . PMID 36907687.
- ↑ Travin, Dmitrii Y.; Severinov, Konstantin; Dubiley, Svetlana (2021). "Natural Trojan horse inhibitors of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases". RSC Chemical Biology. 2 (2): 468–485. doi:10.1039/d0cb00208a. PMC 8323819 . PMID 34382000.