
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), Mycobacterium avium complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires’ disease. It is almost always used together with other antibiotics with two notable exceptions: when given as a "preferred treatment that is strongly recommended" for latent TB infection; and when used as post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent Haemophilus influenzae type b and meningococcal disease in people who have been exposed to those bacteria. Before treating a person for a long period of time, measurements of liver enzymes and blood counts are recommended. Rifampicin may be given either by mouth or intravenously.

Tuberculosis is diagnosed by finding Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria in a clinical specimen taken from the patient. While other investigations may strongly suggest tuberculosis as the diagnosis, they cannot confirm it.

Tuberculosis management describes the techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB).

QIAGEN is a provider of sample and assay technologies for molecular diagnostics, applied testing, academic and pharmaceutical research. The company operates in more than 35 offices in over 25 countries. QIAGEN N.V., the global corporate headquarter of the QIAGEN group, is located in Venlo, The Netherlands. European, American, and Asian regional headquarters are located in respectively Hilden, Germany; Germantown, Maryland United States; and Shanghai, China. QIAGEN's shares are listed at the NYSE and at the Frankfurt Stock Exchange in the Prime Standard. Thierry Bernard is the company's Chief Executive Officer(CEO). The main operative headquarters are located in Hilden, Germany.

Tuberculous meningitis, also known as TB meningitis or tubercular meningitis, is a specific type of bacterial meningitis caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of the meninges—the system of membranes which envelop the central nervous system.
Point-of-care testing (POCT), also called near-patient testing or bedside testing, is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or mostly confined to the medical laboratory, which entailed sending off specimens away from the point of care and then waiting hours or days to learn the results, during which time care must continue without the desired information.
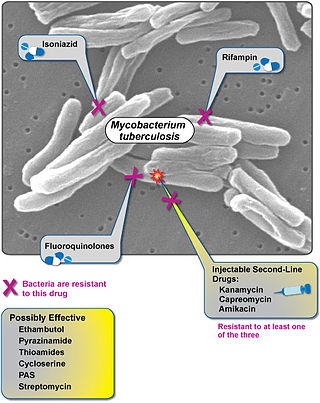
Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis caused by bacteria that are resistant to some of the most effective anti-TB drugs. XDR-TB strains have arisen after the mismanagement of individuals with multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
The National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP), earlier known as the Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programme (RNTCP), is the Public Health initiative of the Government of India that organizes its anti-Tuberculosis efforts. It functions as a flagship component of the National Health Mission (NHM) and provides technical and managerial leadership to anti-tuberculosis activities in the country. As per the National Strategic Plan 2017–25, the program has a vision of achieving a "TB free India",with a strategies under the broad themes of "Prevent, Detect,Treat and Build pillars for universal coverage and social protection". The program provides, various free of cost, quality tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment services across the country through the government health system.
Interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) are diagnostic tools for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). They are surrogate markers of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and indicate a cellular immune response to M. tuberculosis if the latter is present.

FIND is a global health non-profit based in Geneva, Switzerland. FIND functions as a product development partnership, engaging in active collaboration with over 150 partners to facilitate the development, evaluation, and implementation of diagnostic tests for poverty-related diseases. The organisation's Geneva headquarters are in Campus Biotech. Country offices are located in New Delhi, India; Cape Town, South Africa; and Hanoi, Viet Nam.
The Xpert MTB/RIF is a cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) for simultaneous rapid tuberculosis diagnosis and rapid antibiotic sensitivity test. It is an automated diagnostic test that can identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) DNA and resistance to rifampicin (RIF). It was co-developed by the laboratory of Professor David Alland at the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey (UMDNJ), Cepheid Inc. and Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics, with additional financial support from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH).

Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical testing. In medicine the technique is used to diagnose and monitor disease, detect risk, and decide which therapies will work best for individual patients, and in agricultural biosecurity similarly to monitor crop- and livestock disease, estimate risk, and decide what quarantine measures must be taken.

DiaSorin is an Italian multinational biotechnology company that produces and markets in vitro diagnostics reagent kits used in immunodiagnostics and molecular diagnostics and since July 2021, it is also active in the Life Science business. The group was founded in 2000 and is headquartered in Saluggia, Italy. Its production is at several plants located in Europe and the United States: Saluggia and Gerenzano (Italy), Dietzenbach (Germany), Stillwater, Minnesota (US), Dartford (UK). Following the acquisition of Luminex, the company acquired five additional production plants located in the United States and in Canada (Toronto). The company is a constituent of the FTSE MIB index.

Cepheid is an American molecular diagnostics company. Its systems automate traditional nucleic acid tests. The tests can be used to identify and analyze pathogens and genetic disorders. Cepheid sells clinical tests for healthcare-associated infections, infectious diseases, sexual health, oncology and genetics.

The National Tuberculosis Institute (NTIB) is a Government of India institute, under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, dedicated to advanced research on Tuberculosis. The Institute is located along Bellary Road, in Bengaluru, Karnataka state, India.

COVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2. The two main types of tests detect either the presence of the virus or antibodies produced in response to infection. Molecular tests for viral presence through its molecular components are used to diagnose individual cases and to allow public health authorities to trace and contain outbreaks. Antibody tests instead show whether someone once had the disease. They are less useful for diagnosing current infections because antibodies may not develop for weeks after infection. It is used to assess disease prevalence, which aids the estimation of the infection fatality rate.

A coronavirus breathalyzer is a diagnostic medical device enabling the user to test with 90% or greater accuracy the presence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in an exhaled breath. As of the first half of 2020, the idea of a practical coronavirus breathalyzer was concomitantly developed by unrelated research groups in Australia, Canada, Finland, Germany, Indonesia, Israel, Netherlands, Poland, Singapore, United Kingdom and USA.
DnaNudge is a British company specializing in DNA testing. In late 2020, during the COVID-19 pandemic, it introduced COVID Nudge, a rapid RT-PCR test for COVID-19. The device uses a disposable sample capsule that is placed into a sample processor box, and gives results in 90 minutes. As of August 2020, the British government had ordered 5000 of the sample processor boxes.
Seegene, Inc is a Korean manufacturer of in vitro diagnostic (IVD) products, particularly molecular diagnostics. Its portfolio includes a range of assays and screening products for sepsis, respiratory diseases such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, as well as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It was founded in 2000. In early 2020, it began developing and distributing a range of tests for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.











