In mathematics, the truncated power function [1] with exponent is defined as
Contents
In particular,
and interpret the exponent as conventional power.
In mathematics, the truncated power function [1] with exponent is defined as
In particular,
and interpret the exponent as conventional power.
In number theory, an arithmetic, arithmetical, or number-theoretic function is generally any function f(n) whose domain is the positive integers and whose range is a subset of the complex numbers. Hardy & Wright include in their definition the requirement that an arithmetical function "expresses some arithmetical property of n". There is a larger class of number-theoretic functions that do not fit this definition, for example, the prime-counting functions. This article provides links to functions of both classes.

In the mathematical subfield of numerical analysis, a B-spline or basis spline is a spline function that has minimal support with respect to a given degree, smoothness, and domain partition. Any spline function of given degree can be expressed as a linear combination of B-splines of that degree. Cardinal B-splines have knots that are equidistant from each other. B-splines can be used for curve-fitting and numerical differentiation of experimental data.

In mathematics, mathematical physics and the theory of stochastic processes, a harmonic function is a twice continuously differentiable function where U is an open subset of that satisfies Laplace's equation, that is, everywhere on U. This is usually written as or

In probability theory and statistics, the chi-squared distribution with degrees of freedom is the distribution of a sum of the squares of independent standard normal random variables.
In analytic number theory and related branches of mathematics, a complex-valued arithmetic function is a Dirichlet character of modulus if for all integers and :

In mathematics, the symmetric difference of two sets, also known as the disjunctive union and set sum, is the set of elements which are in either of the sets, but not in their intersection. For example, the symmetric difference of the sets and is .
In mathematics, the Sierpiński space is a finite topological space with two points, only one of which is closed. It is the smallest example of a topological space which is neither trivial nor discrete. It is named after Wacław Sierpiński.
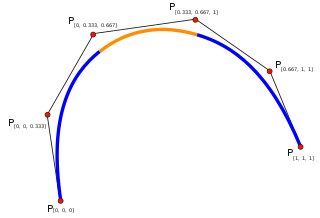
In mathematics, a spline is a function defined piecewise by polynomials. In interpolating problems, spline interpolation is often preferred to polynomial interpolation because it yields similar results, even when using low degree polynomials, while avoiding Runge's phenomenon for higher degrees.
In mathematics, the Vitali–Hahn–Saks theorem, introduced by Vitali, Hahn, and Saks, proves that under some conditions a sequence of measures converging point-wise does so uniformly and the limit is also a measure.

In physics, the ARGUS distribution, named after the particle physics experiment ARGUS, is the probability distribution of the reconstructed invariant mass of a decayed particle candidate in continuum background.

A triangular function is a function whose graph takes the shape of a triangle. Often this is an isosceles triangle of height 1 and base 2 in which case it is referred to as the triangular function. Triangular functions are useful in signal processing and communication systems engineering as representations of idealized signals, and the triangular function specifically as an integral transform kernel function from which more realistic signals can be derived, for example in kernel density estimation. It also has applications in pulse-code modulation as a pulse shape for transmitting digital signals and as a matched filter for receiving the signals. It is also used to define the triangular window sometimes called the Bartlett window.
The hidden subgroup problem (HSP) is a topic of research in mathematics and theoretical computer science. The framework captures problems such as factoring, discrete logarithm, graph isomorphism, and the shortest vector problem. This makes it especially important in the theory of quantum computing because Shor's algorithms for factoring and finding discrete logarithms in quantum computing are instances of the hidden subgroup problem for finite abelian groups, while the other problems correspond to finite groups that are not abelian.
In mathematics, the Schur orthogonality relations, which were proven by Issai Schur through Schur's lemma, express a central fact about representations of finite groups. They admit a generalization to the case of compact groups in general, and in particular compact Lie groups, such as the rotation group SO(3).
In mathematics, a Caccioppoli set is a set whose boundary is measurable and has a finite measure. A synonym is set of (locally) finite perimeter. Basically, a set is a Caccioppoli set if its characteristic function is a function of bounded variation.

Anatoly Alexeyevich Karatsuba was a Russian mathematician working in the field of analytic number theory, p-adic numbers and Dirichlet series.

In mathematics, the McKay graph of a finite-dimensional representation V of a finite group G is a weighted quiver encoding the structure of the representation theory of G. Each node represents an irreducible representation of G. If χ i, χ j are irreducible representations of G, then there is an arrow from χ i to χ j if and only if χ j is a constituent of the tensor product Then the weight nij of the arrow is the number of times this constituent appears in For finite subgroups H of the McKay graph of H is the McKay graph of the defining 2-dimensional representation of H.
In mathematics, singular integral operators of convolution type are the singular integral operators that arise on Rn and Tn through convolution by distributions; equivalently they are the singular integral operators that commute with translations. The classical examples in harmonic analysis are the harmonic conjugation operator on the circle, the Hilbert transform on the circle and the real line, the Beurling transform in the complex plane and the Riesz transforms in Euclidean space. The continuity of these operators on L2 is evident because the Fourier transform converts them into multiplication operators. Continuity on Lp spaces was first established by Marcel Riesz. The classical techniques include the use of Poisson integrals, interpolation theory and the Hardy–Littlewood maximal function. For more general operators, fundamental new techniques, introduced by Alberto Calderón and Antoni Zygmund in 1952, were developed by a number of authors to give general criteria for continuity on Lp spaces. This article explains the theory for the classical operators and sketches the subsequent general theory.
In mathematics, the Christ–Kiselev maximal inequality is a maximal inequality for filtrations, named for mathematicians Michael Christ and Alexander Kiselev.
The graph coloring game is a mathematical game related to graph theory. Coloring game problems arose as game-theoretic versions of well-known graph coloring problems. In a coloring game, two players use a given set of colors to construct a coloring of a graph, following specific rules depending on the game we consider. One player tries to successfully complete the coloring of the graph, when the other one tries to prevent him from achieving it.
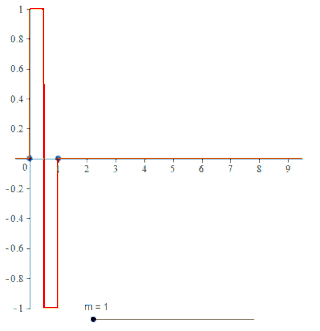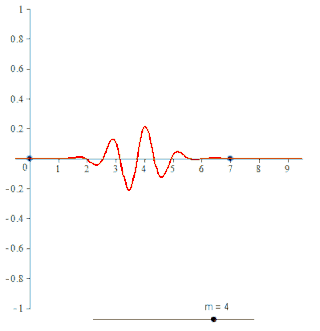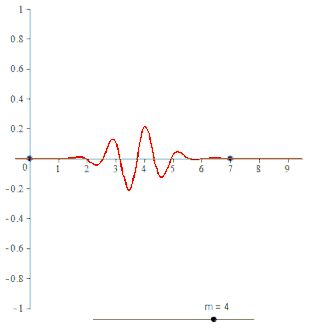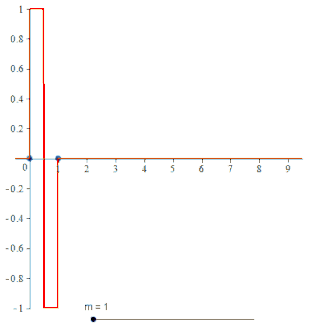
In the mathematical theory of wavelets, a spline wavelet is a wavelet constructed using a spline function. There are different types of spline wavelets. The interpolatory spline wavelets introduced by C.K. Chui and J.Z. Wang are based on a certain spline interpolation formula. Though these wavelets are orthogonal, they do not have compact supports. There is a certain class of wavelets, unique in some sense, constructed using B-splines and having compact supports. Even though these wavelets are not orthogonal they have some special properties that have made them quite popular. The terminology spline wavelet is sometimes used to refer to the wavelets in this class of spline wavelets. These special wavelets are also called B-spline wavelets and cardinal B-spline wavelets. The Battle-Lemarie wavelets are also wavelets constructed using spline functions.