Tulare County is a county located in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 473,117. The county seat is Visalia. The county is named for Tulare Lake, once the largest freshwater lake west of the Great Lakes. Drained for agricultural development, the site is now in Kings County, which was created in 1893 from the western portion of the formerly larger Tulare County.

Visalia is a city in the agricultural San Joaquin Valley of California. The population was 141,384 as per the 2020 census. Visalia is the fifth-largest city in the San Joaquin Valley, the 42nd most populous in California, and 192nd in the United States. As the county seat of Tulare County, Visalia serves as the economic and governmental center to one of the most productive agricultural counties in the country.

General Sherman is a giant sequoia tree located at an elevation of 2,109 m (6,919 ft) above sea level in the Giant Forest of Sequoia National Park in Tulare County, in the U.S. state of California. By volume, it is the largest known living single-stem tree on Earth. It is estimated to be around 2,200 to 2,700 years old.

Central California is generally thought of as the middle third of the U.S. state, of California, north of Southern California, which includes Los Angeles, and south of Northern California, which includes San Francisco. It includes the northern portion of the San Joaquin Valley, part of the Central Coast, the central hills of the California Coast Ranges and the foothills and mountain areas of the central Sierra Nevada.
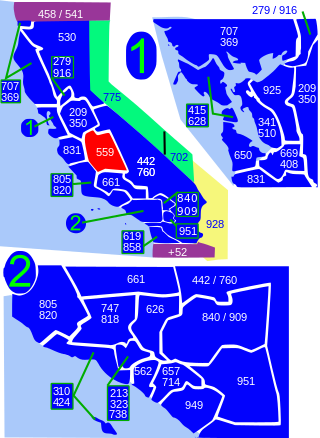
Area code 559 is a telephone area code in the North American Numbering Plan for the central San Joaquin Valley in central California. The numbering plan area includes the counties of Fresno, Madera, Kings, and Tulare, an area largely coextensive with the Fresno and Visalia-Porterville metropolitan areas. The area code was placed in service in 1998, when its services area was split from that of area code 209.
The Mariposa War, also known as the Yosemite Indian War, was a conflict between the United States and the indigenous people of California's Sierra Nevada in the 1850s. The war was fought primarily in Mariposa County and surrounding areas, and was sparked by the discovery of gold in the region. As a result of the military expedition, the Mariposa Battalion became the first non-indigenous group to enter Yosemite Valley and the Nelder Grove.
James D. Savage (1823–1852) was a California pioneer. He was a 49er, businessman, American soldier in the Mexican–American War, and commander of the California Militia, Mariposa Battalion in the Mariposa War and the first alleged non-Native American visitor to the Yosemite Valley.

The Kaweah River is a river draining the southern Sierra Nevada in Tulare County, California in the United States. Fed primarily by high elevation snowmelt along the Great Western Divide, the Kaweah begins as four forks in Sequoia National Park, where the watershed is noted for its alpine scenery and its dense concentrations of giant sequoias, the largest trees on Earth. It then flows in a southwest direction to Lake Kaweah – the only major reservoir on the river – and into the San Joaquin Valley, where it diverges into multiple channels across an alluvial plain around Visalia. With its Middle Fork headwaters starting at almost 13,000 feet (4,000 m) above sea level, the river has a vertical drop of nearly two and a half miles (4.0 km) on its short run to the San Joaquin Valley, making it one of the steepest river drainages in the United States. Although the main stem of the Kaweah is only 33.6 miles (54.1 km) long, its total length including headwaters and lower branches is nearly 100 miles (160 km).

Rancho San Francisco was a land grant in present-day northwestern Los Angeles County and eastern Ventura County, California. It was a grant of 48,612 acres (19,673 ha) by Governor Juan B. Alvarado to Antonio del Valle, a Mexican army officer, in recognition for his service to Alta California. It is not related to the city of San Francisco.

The Visalia Unified School District is located in Tulare County, California. The school district covers an area of 214 miles, and includes 27 elementary schools, a newcomer language assessment center, five middle schools, four comprehensive high schools, a continuation high school, an adult school, a charter alternative academy, a charter independent study school, a K-8 charter home school, and a school that serves orthopedic handicapped students. The VUSD area has a population base of over 135,000 people, over 32,000 of which are served by the school district.

Visalia, California, commonly known in the 1850s as Four Creeks, is the oldest continuously inhabited inland European settlement between Stockton and Los Angeles. The city played an important role in the American colonization of the San Joaquin Valley as the county seat of Old Tulare County, an expansive region comprising most if not all of modern-day Fresno, Kings, and Kern counties.
There are 45 routes assigned to the "J" zone of the California Route Marker Program, which designates county routes in California. The "J" zone includes county highways in Alameda, Calaveras, Contra Costa, Fresno, Kern, Inyo, Mariposa, Merced, Sacramento, San Benito, San Joaquin, Stanislaus, and Tulare counties.

Tree Hill near Richmond, Virginia, in Henrico County, Virginia, is a Greek Revival style plantation house overlooking the James River about two miles east of downtown Richmond near the intersection of the historic Osborne Turnpike and New Market Road. Currently still a private farm, but expected to become partly a park after housing and commercial development, it was once owned by Richmond distiller and landowner Franklin Stearns, a prominent Unionist during the American Civil War. Centuries earlier, it had been a Native American camp site, and the birthplace of powerful chief Powhatan (d.1618).
Cutler Park is a large municipal park at the eastern end of Visalia, California near Venice Hills. The park covers 70 acres of land. It is one of the largest Valley Oak Woodlands in Central California.
The Stockton–Los Angeles Road, also known as the Millerton Road, Stockton–Mariposa Road, Stockton–Fort Miller Road or the Stockton–Visalia Road, was established about 1853 following the discovery of gold on the Kern River in Old Tulare County. This route between Stockton and Los Angeles followed by the Stockton–Los Angeles Road is described in "Itinerary XXI. From Fort Yuma to Benicia, California", in The Prairie Traveler: A Hand-book for Overland Expeditions by Randolph Barnes Marcy. The Itinerary was derived from the report of Lieutenant R. S. Williamson on his topographical survey party in 1853, that was in search of a railroad route through the interior of California.
The Tule River War of 1856 was a conflict where American settlers, and later, California State Militia, and a detachment of the U. S. Army from Fort Miller, fought a six-week war against the Yokuts in the southern San Joaquin Valley.
Second Garrotte,, California is a ghost town located near Groveland in Tuolumne County, California originally settled during the California Gold Rush. The site of the Second Garrote is a California Historical Landmark No. 438 listed on May 9, 1950. It lies at an elevation of 2,894 feet in Second Garrotte Basin.

Battle of Bishop Creek was one of the early engagements of the Owens Valley Indian War fought on April 6, 1862 along Bishop Creek, in what is now Inyo County, California.
Savage Trading Post is California Historical Landmark No. 527 in El Portal, California on California State Route 140 in Mariposa County. James D. Savage was 49er California Gold Rush miner and trader, in 1849 he built a Log cabin. In the Log cabin, he started a general store and trading post along the Merced River. After just one year the Mariposa War started. In the spring of 1850 James (Jim) Savage started trading at Mariposa Creek in the San Joaquin Valley and he had employees run his Trading Post. In December 1850 the war came to Savage Trading Post and it was set on fire. James Savage was the leader of the California Militia's Mariposa Battalion that traveled to the Yosemite Valley in 1851 to hunt down the Ahwaneechees and their leader Chief Tenaya. The Mariposa Battalion won the battle and thus ended the war. The Mariposa Battalion also became the first non-Native American to see the beauty of Yosemite Valley. Lafayette Bunnell wrote about his visit to the Yosemite Valley. A copy of Savage Trading Post was built at the site of the original and is California Historical Landmark No. 527.