
The Type 23 frigate or Duke class is a class of frigates built for the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. The ships are named after British Dukes, thus leading to the class being commonly known as the Duke class. The first Type 23, HMS Norfolk, was commissioned in 1989, and the sixteenth, HMS St Albans was commissioned in June 2002. They form the core of the Royal Navy's destroyer and frigate fleet and serve alongside the Type 45 destroyers. Originally designed for anti-submarine warfare in the North Atlantic, the Royal Navy's Type 23 frigates have proven their versatility in warfighting, peacekeeping and maritime security operations around the globe. Thirteen Type 23 frigates remain in service with the Royal Navy, with three vessels having been sold to the Chilean Navy.

HMS Invincible was the Royal Navy's lead ship of her class of three light aircraft carriers. She was launched on 3 May 1977 as the seventh ship to carry the name. She was originally designated as an anti-submarine warfare carrier, but was used as an aircraft carrier during the Falklands War, when she was deployed with HMS Hermes. She took over as flagship of the British fleet when Hermes was sold to India. Invincible was also deployed in the Yugoslav Wars and the Second Gulf War. In 2005, she was decommissioned, and was eventually sold for scrap in February 2011.

The Type 42 or Sheffield class, was a class of fourteen guided missile destroyers that served in the Royal Navy. A further two ships of this class were built for and served with the Argentine Navy.

The Type 45 destroyer, also known as the D or Daring class, is a class of six guided missile destroyers built for the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. The class is primarily designed for anti-aircraft and anti-missile warfare and is built around the PAAMS air-defence system utilizing the SAMPSON AESA and the S1850M long-range radars. The first three destroyers were assembled by BAE Systems Surface Fleet Solutions from partially prefabricated "blocks" built at different shipyards; the remaining three were built by BAE Systems Maritime – Naval Ships. The first ship in the Daring class, HMS Daring, was launched on 1 February 2006 and commissioned on 23 July 2009.

The County class was a class of British guided missile destroyers, the first such warships built by the Royal Navy. Designed specifically around the Seaslug anti-aircraft missile system, the primary role of these ships was area air defence around the aircraft carrier task force in the nuclear-war environment.

The Type 21 frigate, or Amazon-class frigate, was a British Royal Navy general-purpose escort that was designed in the late 1960s, built in the 1970s and served throughout the 1980s into the 1990s.

HMS Sheffield was a Type 42 guided missile destroyer and the second Royal Navy ship to be named after the city of Sheffield in Yorkshire. Commissioned on 16 February 1975 the Sheffield was part of the Task Force 317 sent to the Falkland Islands during the Falklands War. She was struck by an Exocet air-launched anti-ship missile from an Argentinian Super Étendard aircraft on 4 May 1982 and foundered while under tow on 10 May 1982.

HMS Glamorgan was a County-class destroyer of the Royal Navy with a displacement of 5,440 tonnes. The ship was built by Vickers-Armstrongs in Newcastle Upon Tyne and named after the Welsh county of Glamorgan.

HMS Kent was a batch-1 County-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She and her sisters were equipped with the Sea Slug Mk-1 medium-range surface-to-air missile SAM system, along with the short-range Sea Cat SAM, two twin 4.5-inch gun turrets, two single 20mm cannon, ASW torpedo tubes, and a platform and hangar that allowed her to operate one Wessex helicopter. The County class were large ships, with good seakeeping abilities and long range, and were ideal blue-water ships for their time.

HMS Bristol (D23) was a Type 82 destroyer, the only vessel of her class to be built for the Royal Navy. Bristol was intended to be the first of a class of large destroyers to escort the CVA-01 aircraft carriers projected to come into service in the early 1970s but the rest of the class and the CVA-01 carriers were cancelled as a result of the 1966 Defence White Paper which cut defence spending.

The Leander-class, or Type 12I (Improved) frigates, comprising twenty-six vessels, was among the most numerous and long-lived classes of frigate in the Royal Navy's modern history. The class was built in three batches between 1959 and 1973. It had an unusually high public profile, due to the popular BBC television drama series Warship. The Leander silhouette became synonymous with the Royal Navy through the 1960s until the 1980s.

HMS Andromeda was a Leander-class frigate of the Royal Navy. She was built at HM Dockyard Portsmouth. She was launched on 24 May 1967 and commissioned into the Royal Navy on 2 December 1968. She took part in the Falklands War and was sold to India in 1995, for use as a training ship, being renamed INS Krishna. She was finally decommissioned in May 2012.

Sea Wolf is a naval surface-to-air missile system designed and built by BAC, later to become British Aerospace (BAe) Dynamics. It is an automated point-defence weapon system designed as a short-range defence against both sea-skimming and high angle anti-ship missiles and aircraft. The Royal Navy has fielded two versions, the GWS-25 Conventionally Launched Sea Wolf (CLSW) and the GWS-26 Vertically Launched Sea Wolf (VLSW) forms. In Royal Navy service Sea Wolf is being replaced by Sea Ceptor.

HMS Sirius (F40) was a Leander-class frigate of the Royal Navy (RN) built by H.M. Dockyard Portsmouth, and was the penultimate RN warship to be built there for a period of forty years, until Vosper Thornycroft built HMS Clyde. Sirius was launched on 22 September 1964 and commissioned on 15 June 1966. The ship continued in front line service until February 1992.

The Type 82 or Bristol-class destroyer was to have been a class of eight Royal Navy guided missile destroyers mounting the Sea Dart missile, intended to replace the Seaslug-armed County-class destroyers. They would provide area air-defence over carrier task forces and could serve, independently in the a modern cruiser role East of Suez in the Med with significant surveillance, communication, target processing and selection role and long range air, surface and anti submarine missile capability and would also serve in a group of 4/T82 and 4 Broad Beam Leander as outer and inner escorts to the planned CVA-01 aircraft carriers.
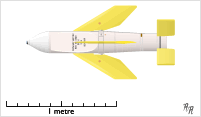
Seacat was a British short-range surface-to-air missile system intended to replace the ubiquitous Bofors 40 mm gun aboard warships of all sizes. It was the world's first operational shipboard point-defence missile system, and was designed so that the Bofors guns could be replaced with minimum modification to the recipient vessel and (originally) using existing fire-control systems. A mobile land-based version of the system was known as Tigercat.

Sea Dart or GWS30 was a British naval surface-to-air missile system designed by Hawker Siddeley Dynamics in the 1960s, entering service in 1973. It was fitted to the Type 42 destroyers, Type 82 destroyer and Invincible-class aircraft carriers of the Royal Navy. Originally developed by Hawker Siddeley, the missile was built by British Aerospace after 1977, and was withdrawn from service in 2012.

The Type 61 Salisbury class was a class of the Royal Navy aircraft direction (AD) frigate, built in the 1950s. The purpose of the aircraft direction ships was to provide radar picket duties at some distance from a carrier task force and offer interception guidance to aircraft operating in their area.

HMS Lowestoft was a Rothesay or Type 12 class anti-submarine frigate of the British Royal Navy. Lowestoft was reconstructed in the late 1960s to largely the same pattern as the third group of Leander frigates, with new radar and fire control and a hangar and pad for a Wasp helicopter for longer range, anti submarine, engagement. In the late 1970s it was converted as the prototype towed array frigate for the Royal Navy, but retained its full armament. Lowestoft was sunk as a target on 8 June 1986 by HMS Conqueror using a Tigerfish torpedo. She was the last Royal Naval target to be sunk still displaying her pennant number.

The Type 965 radar was VHF long-range aircraft warning radar used by warships of the Royal Navy from the 1960s onwards. The Type 965M, Type 965P, Type 965Q and Type 965R were improved versions; the Type 960, 965M and 965Q used the single bedstead AKE(1) aerial, whilst the Type 965P and 965R used the double bedstead AKE(2) aerial.



















