
SAS is a statistical software suite developed by SAS Institute for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, criminal investigation, and predictive analytics.

JMP is a suite of computer programs for statistical analysis developed by the JMP business unit of SAS Institute. It was launched in 1989 to take advantage of the graphical user interface introduced by the Macintosh. It has since been significantly rewritten and made available for the Windows operating system. JMP is used in applications such as Six Sigma, quality control, and engineering, design of experiments, as well as for research in science, engineering, and social sciences.
Angelino Dulcert, probably also the same person known as Angelino de Dalorto, and whose real name was probably Angelino de Dulceto or Dulceti or possibly Angelí Dolcet, was an Italian-Majorcan cartographer.

Abraham Cresques, whose real name was Cresques (son of) Abraham, was a 14th-century Jewish cartographer from Palma, Majorca. In collaboration with his son, Jehuda Cresques, Cresques is credited with the authorship of the celebrated Catalan Atlas of 1375.

The Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World is a large-format English language atlas of ancient Europe, Asia, and North Africa, edited by Richard J. A. Talbert. The time period depicted is roughly from archaic Greek civilization through Late Antiquity. The atlas was published by Princeton University Press in 2000. The book was the winner of the 2000 Association of American Publishers Award for Best Professional/Scholarly Multivolume Reference Work in the Humanities.

Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions, which have been noted for their high cartographic accuracy. The word portolan comes from the Italian portulano, meaning "related to ports or harbors", and which since at least the 17th century designates "a collection of sailing directions".

The National Atlas of the United States was an atlas published by the United States Department of the Interior from 1874 to 1997.

Web mapping or online mapping is the process of using the maps delivered by geographic information systems (GIS) on the Internet, more specifically in the World Wide Web (WWW). A web map or online map is both served and consumed, thus web mapping is more than just web cartography, it is a service by which consumers may choose what the map will show. Web GIS emphasizes geodata processing aspects more involved with design aspects such as data acquisition and server software architecture such as data storage and algorithms, than it does the end-user reports themselves.
The Malaria Atlas Project, abbreviated as MAP, is a non-profit academic group led by Professor Peter Gething, Kerry M Stokes Chair in Child Health, at the Telethon Kids Institute, Perth, Western Australia. The group is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, with previous funding also coming from the Medical Research Council and the Wellcome Trust. MAP aims to disseminate free, accurate and up-to-date information on malaria and associated topics, organised on a geographical basis. The work of MAP falls into three areas:
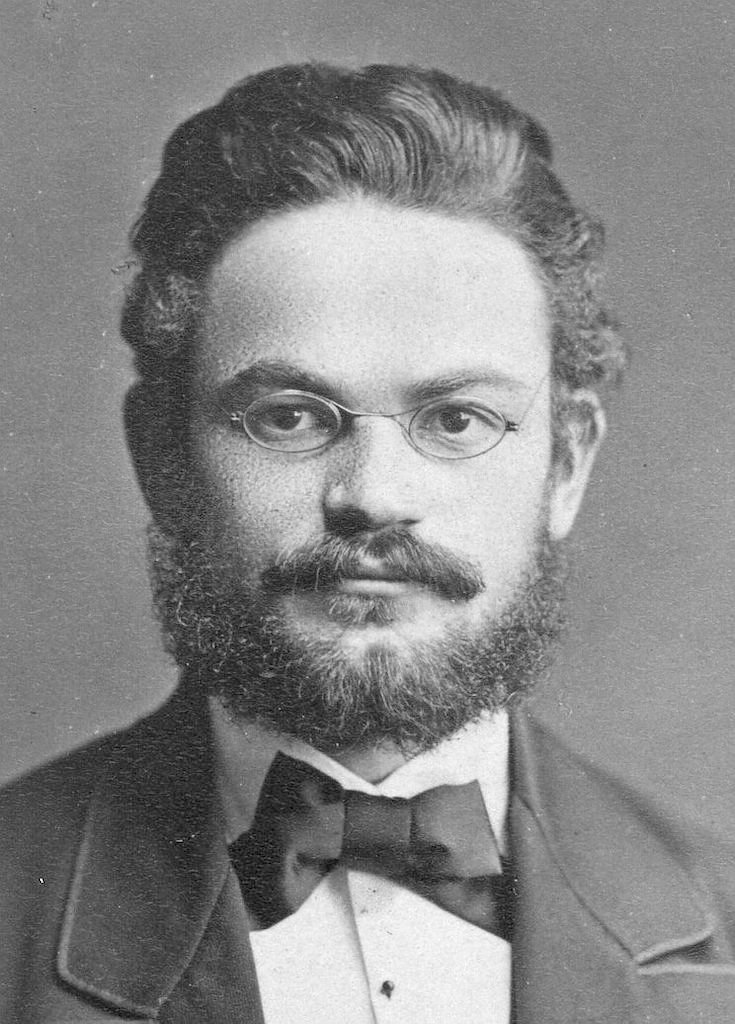

Georg Wenker was a German linguist who began documenting German dialect geography during the late nineteenth century. He is considered a pioneer in this field and contributed several groundbreaking publications, most notably, the Deutscher Sprachatlas.
A bird atlas is an ornithological work that attempts to provide information on the distribution, abundance, long-term change as well as seasonal patterns of bird occurrence and make extensive use of maps. They often involve a large numbers of volunteers to cover a wide geographic area and the methods used are standardized so that the studies can be continued in the future and the results remain comparable. In some cases the species covered may be restricted to those that breed or are resident. Migration atlases on the other hand cover migratory birds depict maps showing summaries of ringing and recoveries.

"Majorcan cartographic school" is the term coined by historians to refer to the collection of predominantly Jewish cartographers, cosmographers and navigational instrument-makers and some Christian associates that flourished in Majorca in the 13th, 14th and 15th centuries until the expulsion of the Jews. The label is usually inclusive of those who worked in Catalonia. The Majorcan school is frequently contrasted with the contemporary Italian cartography school.
The geologic map of Georgia is a special-purpose map made to show geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by colors or symbols to indicate where they are exposed at the surface. Structural features such as faults and shear zones are also shown. Since the first national geological map, in 1809, there have been numerous maps which included the geology of Georgia. The first Georgia specific geologic map was created in 1825. The most recent state-produced geologic map of Georgia, by the Georgia Department of Natural Resources is 1:500,000 scale, and was created in 1976 by the department's Georgia Geological Survey. It was generated from a base map produced by the United States Geological Survey. The state geologist and Director of the Geological Survey of Georgia was Sam M. Pickering, Jr. Since 1976, several geological maps of Georgia, featuring the state's five distinct geologic regions, have been produced by the federal government.

Pietro Vesconte was a Genoese cartographer and geographer. A pioneer of the field of the portolan chart, he influenced Italian and Catalan mapmaking throughout the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. He appears to have been the first professional mapmaker to sign and date his works regularly.
Catalan charts, Catalan maps or Catalan portolans are a subtype of the medieval period (1300–1500) portolan chart. Portolan charts are a type of map generated by using a mariner's compass and direct observation to determine the shape and location of coastlines and ports. The term "portolan" means "pertaining to ports and harbors" and should not be confused with "relating to Portugal". Sometimes they are referred to as "Catalan type" portolans or simply Catalan portolans. Two primary subgroups of medieval period portolan maps exist, the Italian, and the Catalan. While both the Italian and Catalan maps derive from the same common source, there are several differences, both in terms of style and in content.

A map collection or map library is a storage facility for maps, usually in a library, archive, or museum, or at a map publisher or public-benefit corporation, and the maps and other cartographic items stored within that facility.
Mitchell Beazley Publishers Limited is a British book publisher which is particularly specialised in atlases, reference books, natural history books, cook books, garden books, and wine books.

A rhumbline network, more properly called, a windrose network, or sometimes also called harbour-finding chart, compass chart, or rhumb chart, is a navigational aid drawn on early portolan charts dating from the medieval to early modern period. This network is like a web forming a grid on the map.
Alvin Jewett Johnson (1827-1884), also known as A.J. Johnson, led the New York City publishing company which published Johnson's Family Atlases from 1860 to 1887. These atlases were published under his name alone or with Browning (1860–62) and Ward (1862-1866). These atlases are fascinating because sequence of atlas maps documented the growth of the United States during this quarter of century, showing the step-by-step expansion of railroads and the development of new states, counties and towns. As the years went along, the maps were updated creating for each map a set of map states or variations. These atlases and loose maps taken from them have become of increasing value to collectors and historians. In order for these loose maps to be of full use to historians for study loose maps from these atlases need to be definitively dated. Collectors also need to know the true date of the maps; while some of the states/variations were utilized for up to two years, many changes occurred sometimes within one year, thus making some versions more plentiful than others.

The Vallard Atlas is a world atlas, one of the Dieppe school of maps, produced in 1547. It is believed to have been owned by Nicolas Vallard, its authorship being unknown.













