Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of two official languages, alongside English.

"Lupang Hinirang", originally titled in Spanish as "Marcha Nacional Filipina", and commonly and informally known by its incipit "Bayang Magiliw", is the national anthem of the Philippines. Its music was composed in 1898 by Julián Felipe, and the lyrics were adopted from the Spanish poem "Filipinas", written by José Palma in 1899.

The University of the Philippines is a state university system in the Philippines. It is the country's national university, as mandated by Republic Act No. 9500, giving it institutional autonomy.

The University of the Philippines Diliman, also referred to as UP Diliman or simply University of the Philippines (UP), is a public, coeducational, research university located in Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines. It was established on February 12, 1949, as the flagship campus and seat of administration of the University of the Philippines System, the premier and national university of the Philippines.

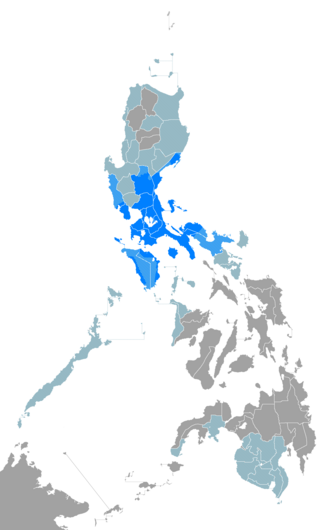
Filipino is a language under the Austronesian language family. It is the national language of the Philippines, and one of the two official languages of the country, with English. It is a standardized variety of Tagalog based on the native dialect, spoken and written, in Metro Manila, the National Capital Region, and in other urban centers of the archipelago. The 1987 Constitution mandates that Filipino be further enriched and developed by the other languages of the Philippines.
Filipinoorthography specifies the correct use of the writing system of the Filipino language, the national and co-official language of the Philippines.

The Commission on the Filipino Language (CFL), also referred to as the Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino (KWF), is the official regulating body of the Filipino language and the official government institution tasked with developing, preserving, and promoting the various local Philippine languages. The commission was established in accordance with the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines.
The Abakada alphabet was an "indigenized" Latin alphabet adopted for the Tagalog-based Wikang Pambansa in 1939.

The National Commission for Culture and the Arts of the Philippines is the official government agency for culture in the Philippines. It is the overall policy making body, coordinating, and grants giving agency for the preservation, development and promotion of Philippine arts and culture; an executing agency for the policies it formulates; and task to administering the National Endowment Fund for Culture and the Arts (NEFCA) – fund exclusively for the implementation of culture and arts programs and projects.

Virgilio Senadren Almario, better known by his pen name Rio Alma, is a Filipino author, poet, critic, translator, editor, teacher, and cultural manager. He is a National Artist of the Philippines. He formerly served as the chairman of the Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino (KWF), the government agency mandated to promote and standardize the use of the Filipino language. On January 5, 2017, Almario was also elected as the chairman of the National Commission for Culture and the Arts (NCCA).

The University of the Philippines Visayas is a public research university in the Philippines with campuses and facilities throughout the Visayas. A constituent university of the University of the Philippines system, it teaches management, accountancy, marketing, economics, chemistry, applied mathematics and physics, marine science education and research, fisheries, and aquaculture. It offers regional studies programs on the preservation and enrichment of the Visayan cultural heritage.

The Philippine Carabao Center an attached agency of the Department of Agriculture, was established at Science City of Muñoz in Nueva Ecija province in 1992 to breed and cross carabao based on high-yield Murrah buffalo in the Philippines as a multi-purpose animal that can be raised for milk, meat, hide, and draft.

Louie Mar Gangcuangco is a Filipino physician, HIV researcher and novelist. He is the author of the novel Orosa-Nakpil, Malate and is working as Assistant Professor of Medicine for the Hawaii Center for AIDS-University of Hawai'i at Manoa.
The Diliman Commune was an uprising led by the students, faculty members, and residents of the University of the Philippines Diliman, together with transport workers, on February 1–9, 1971, in protest of the three centavo increase in oil prices midway through the second term of the Marcos administration—about a year after the events of the First Quarter Storm and about a year before Marcos' eventual declaration of Martial Law.

Isang Bansa, Isang Diwa was the national motto of the Philippines from 1978 to 1986, during the presidency of President Ferdinand Marcos. It was adopted on June 9, 1978 by virtue of Presidential Decree No. 1413. The motto has been criticized and has been denounced as "the slogan of a fascist regime".
The Sentro ng Wikang Filipino, also known the Sentro, is a language academy, research center, and university-based publishing house that is part of the University of the Philippines System (UP). It has offices in various autonomous universities of UP System, the most notable of which is the one housed at the University of the Philippines Diliman that won the Philippine National Book Award for Publisher of the Year by the Manila Critics' Circle. The Sentro is active not just within the UP system due to its mission of "developing and disseminating" the Filipino language according to the provisions of the 1987 Philippine Constitution.

Zeus Atayza Salazar is a Filipino historian, anthropologist, and philosopher of history, best known for pioneering an emic perspective in Philippine history called Pantayong Pananaw, earning him the title "Father of New Philippine Historiography." He is a major player in the indigenization campaign in the Philippines. Salazar spent 30 years teaching at University of the Philippines Diliman and held both history department chair and college dean positions.
Pamana is a Filipino educational television series developed by the Sky Foundation and broadcast on Knowledge Channel beginning in 2001. Both this series and Kasaysayan TV were the first original programs to be created by the foundation.
Consuelo Morales Joaquin Paz was a Filipino linguist and ethnologist, and a retired professor at the University of the Philippines Diliman. Widely considered as the first female diachronic linguist from the Philippines, she is regarded as a pillar of modern Philippine linguistics and an important figure in the establishment and advancement of Filipino as the national language of the country.












