
The second USS Ohio was a ship of the line of the United States Navy, rated at 74 guns, although her total number of guns was 104. She was designed by Henry Eckford, laid down at Brooklyn Navy Yard in 1817, and launched on 30 May 1820. She went into ordinary and in the ensuing years decayed badly. Refitted for service in 1838, Ohio sailed on 16 October 1838 to join the Mediterranean Squadron under Commodore Isaac Hull. Acting as flagship for two years, she protected commerce and suppressed the slave trade off the African coast. Ohio proved to have excellent performance under sail, repeatedly making more than 12 kn. One of her officers stated, "I never supposed such a ship could be built—a ship possessing in so great a degree all the qualifications of a perfect vessel." In 1840, Ohio returned to Boston, where she again went into ordinary. From 1841 to 1846, Ohio served as receiving ship.

USS Dale was a sloop-of-war in the United States Navy commissioned on 11 December 1839. Dale was involved in the Mexican–American War, the American Civil War, operations along Africa to suppress slave trade, and was used by the U.S. Revenue Cutter Service and later the U.S. Coast Guard, among other activities. Dale was placed into ordinary numerous times.

The first John Adams was originally built in 1799 as a frigate for the United States Navy, converted to a corvette in 1809, and later converted back to a frigate in 1830. Named for American Founding Father and president John Adams, she fought in the Quasi-War, the First and Second Barbary Wars, the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.
USS Germantown was a United States Navy sloop-of-war in commission for various periods between 1847 and 1860. She saw service in the Mexican–American War in 1847–1848 and during peacetime operated in the Caribbean, in the Atlantic Ocean off Africa and South America, and in East Asia. Scuttled at the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, she was captured and refloated by the Confederate States of America and placed in service with the Confederate States Navy as the floating battery CSS Germantown before again being scuttled in 1862.

The first USS Supply was a ship-rigged sailing vessel which served as a stores ship in the United States Navy. She saw service in the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War.

The third USS Vixen was a steamboat in the United States Navy during the Mexican–American War.

USS Scourge was a steamer warship in service during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). She was the third United States Navy ship of that name.

The First Battle of Tabasco was fought during the Mexican–American War, in October 1846, in an attempt to capture cities along the Tabasco coast.
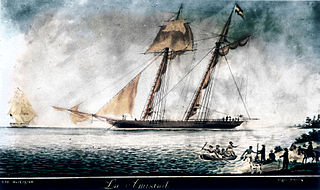
Washington was a revenue cutter that served in the United States Revenue Cutter Service and in the United States Navy. She discovered, boarded, and captured La Amistad after the slaves onboard had seized control of that schooner in an 1839 mutiny.

The United States Revenue Cutter Wolcott was one of 13 revenue cutters of the Morris-Taney Class to be launched. Named after Secretaries of the Treasury and Presidents of the United States, these cutters were the backbone of the United States Revenue-Marine for more than a decade. Samuel Humphreys designed these cutters for roles as diverse as fighting pirates, privateers, combating smugglers and operating with naval forces. He designed the vessels on a naval schooner concept. They had Baltimore Clipper lines. The vessels built by Webb and Allen, designed by Isaac Webb, resembled Humphreys' but had one less port.
USRC Walter Forward was a schooner constructed for service with the United States Revenue Marine. She was more commonly known as USRC Forward. Forward served with the U.S. Army and U.S. Navy in Mexican waters during the Mexican–American War and was commended for her actions during the Tabasco River landings by Commodore Matthew C. Perry, U.S. Navy. After the war, she was transferred to the U.S. Coast Survey for a short time as USCS Walter Forward before being returned to the Revenue Marine for service during the 1850s and the American Civil War.
Karl Jack Bauer, was one of the founders of the North American Society for Oceanic History (NASOH) and a well-known naval historian. NASOH's K. Jack Bauer Award is named in his memory.
The third USS Morris was a schooner in the United States Navy in commission in 1846. She was named for Robert Morris, a Founding Father, Continental Congressman, and major financier of the American Revolutionary War.

The Bombardment of Punta Sombrero was an American naval bombardment in response to a Mexican attack on a United States Navy warship during the Mexican–American War, on October 31, 1847.
USS Boxer of the United States Navy was a 10-gun schooner, launched on 22 November 1831 by the Boston Navy Yard, and commissioned sometime in 1832, with Lt. Benjamin Payne in command; this was the second U.S. Navy ship to be named for the original HMS Boxer, which had been captured from the British during the War of 1812.

Lieutenant Benjamin Fitz-Bourne Hunter, USN (Ret.), was a sailor and officer of the United States Sailing Navy. Born November 11, 1821, in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, he held positions of increasing responsibility and commanded many groups of sailors. He died April 9, 1884, age 62, in Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and was buried in Natchez, Mississippi.
The second USS Union was a schooner that served in the United States Navy briefly during the Mexican War.
USS Reefer, was a pilot schooner purchased by the United States Navy at New York City on May 25, 1846 from shipbuilders Brown & Bell for service as a dispatch boat in Commodore David Conner's Home Squadron during the Mexican–American War.

Libertad, meaning "liberty" in Spanish, was a merchant schooner built on the west coast of Mexico for service between Mexico and the Baja California peninsula and along the coast of Mexico. During the Mexican–American War, she was captured at Loreto, Mexico, along with the schooner Fortuna on 1 October 1846 by the United States Navy sloop-of-war USS Cyane under the command of Commander Samuel Francis Du Pont.










