Related Research Articles
Arizona has been the name of three ships of the United States Navy and will be the name of a future submarine.

Eight ships of the United States Navy have been named USS Hornet, after the stinging insect:
USS Enterprise may refer to the following ships and other vessels:
USS Merrimack, or variant spelling USS Merrimac, may be any one of several ships commissioned in the United States Navy and named after the Merrimack River.
Four ships of the United States Navy have borne the name USS Maine, named for the 23rd state:
Four ships of the United States Navy have been named USS Missouri in honor of the state of Missouri:
At least seven United States Navy ships have been named Alabama, after the southern state of Alabama.
USS Iowa may refer to several vessels:
Five ships of the United States Navy have been named USS Kearsarge. The first was named for Mount Kearsarge, and the later ones were named in honor of the first.
USS America may refer to:
USS Alexander Hamilton may refer to the following ships operated by the United States government:
USS Morris may refer to the following ships of the United States Navy:
The first USS Tunxis was launched on 4 June 1864 at Chester, Pennsylvania, by Reaney, Son & Archbold; and commissioned at the Philadelphia Navy Yard on 12 July 1864. On 21 September 1864, the light-draft monitor departed the sheltered waters of the navy yard on her maiden voyage. However, she soon began taking on water at such an alarming rate that she came about and returned to Philadelphia where she was decommissioned later in the month.
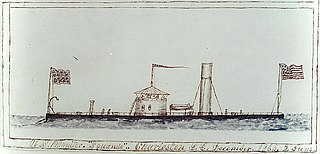
USS Squando was a Casco-class light draft monitor built during the American Civil War. Designed for service in rivers, the class required design changes due to the lack of seaworthiness of the first Casco-class vessel. Squando required her deck to be raised 22 inches (56 cm) before completion in order to provide more freeboard. Launched in late December 1864 or early January 1865, she was commissioned on June 6, 1865. Completed after the American Civil War had wound down, she served in the North Atlantic Squadron in 1865 and 1866 before being decommissioned in May of the latter year. After being renamed twice in 1869, she was sold in 1874 and then broken up.
USS Hydra may refer to the following ships of the United States Navy:
USS Otsego may refer to the following ships of the United States Navy:
USS Tunxis (YN-119/AN-90) was a Cohoes-class net laying ship which was assigned to protect United States Navy ships and harbors during World War II with her anti-submarine nets. Her World War II career was cut short due to the war coming to an end, but, post-war, she was reactivated and served the Navy until she was put into reserve and eventually transferred to Venezuela as Puerto Nutrias.
Reaney, Son & Archbold was a 19th-century American iron shipbuilding company located on the Delaware River at Chester, Pennsylvania. The company was established in 1859 by Thomas Reaney but it was undercapitalized from the outset, and like many other American shipbuilding companies, fell victim to the shipbuilding slump that followed the American Civil War.
The Tunxis were a Native American tribe.
References
This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships .