Uganda is a country in East-Central Africa, west of Kenya, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Contents
Uganda or Ugandan may also refer to:
Uganda is a country in East-Central Africa, west of Kenya, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Uganda or Ugandan may also refer to:

Kampala is the capital and largest city of Uganda. The city proper has a population of 1,680,000 and is divided into the five political divisions of Kampala Central Division, Kawempe Division, Makindye Division, Nakawa Division, and Rubaga Division.
The history of Uganda comprises the history of the people who inhabited the territory of present-day Uganda before the establishment of the Republic of Uganda, and the history of that country once it was established. Evidence from the Paleolithic era shows humans have inhabited Uganda for at least 50,000 years. The forests of Uganda were gradually cleared for agriculture by people who probably spoke Central Sudanic languages.
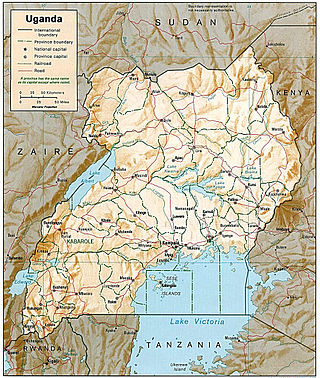
Transport in Uganda refers to the transportation structure in Uganda. The country has an extensive network of paved and unpaved roads.
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:

Port Bell is a small industrial centre in the greater metropolitan Kampala area, in Uganda. Port Bell has a rail link and a railroad ferry wharf used for International traffic across Lake Victoria to Tanzania and Kenya.

The Uganda Railway was a metre-gauge railway system and former British state-owned railway company. The line linked the interiors of Uganda and Kenya with the Indian Ocean port of Mombasa in Kenya. After a series of mergers and splits, the line is now in the hands of the Kenya Railways Corporation and the Uganda Railways Corporation.

Lake Victoria ferries are motor ships for ferry services carrying freight and/or vehicles and/or passengers between Uganda, Tanzania, and Kenya on Lake Victoria.

The Imperial British East Africa Company (IBEAC) was a commercial association founded to develop African trade in the areas controlled by the British Empire. The company was incorporated in London on 18 April 1888 and granted a royal charter by Queen Victoria on 6 September 1888. It was led by William Mackinnon and built upon his company's trading activities in the region, with the encouragement of the British government through the granting of an imperial charter, although it remained unclear what that actually meant.

Entebbe International Airport is the only international airport in Uganda. It is located about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) southwest of the town of Entebbe, on the northern shores of Lake Victoria. This is approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) by road south-west of the central business district of Kampala, the capital city of Uganda.

Uganda Airlines was the flag carrier of Uganda. The airline was established in May 1976, and started operations in 1977. It was headquartered in Entebbe, Wakiso District, Uganda, and operated from its hub in Entebbe International Airport.

British India Steam Navigation Company ("BI") was formed in 1856 as the Calcutta and Burmah Steam Navigation Company.

The Uganda Railways Corporation (URC) is the parastatal railway of Uganda. It was formed after the breakup of the East African Railways Corporation (EARC) in 1977 when it took over the Ugandan part of the East African railways.
Articles related to Uganda include:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Zambia:
Uganda Air Cargo Corporation (UACC),, is an airline based in Kampala, Uganda. It operates scheduled and charter services for both passengers and cargo.
Kenya and Uganda Railways and Harbours (KURH) ran harbours, railways and lake and river ferries in Kenya Colony and the Uganda Protectorate from 26. February 1926 until 1. May 1948. It included the Uganda Railway, which it extended from Nakuru to Kampala in 1931. In the same year it built a branch line to Mount Kenya.

Football is the national sport in Uganda. The Uganda national football team, nicknamed The Cranes, is the national team of Uganda and is controlled by the Federation of Uganda Football Associations. They have never qualified for the FIFA World Cup; their best finish in the African Nations Cup was second in 1978.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Kampala, Buganda, Uganda.

Uganda Airlines is the flag carrier of Uganda. The company is a revival of the older Uganda Airlines which operated from 1977 until 2001. The current carrier began flying in August 2019.
The Uganda Volunteer Reserve was a military unit of the Uganda Protectorate. The UVR was established in March 1903 with support from the British government's Colonial Defence Committee (CDC). The CDC promoted the establishment of such forces in the self-governing parts of the British Empire from which regular British Army troops had been withdrawn. The UVR was organised around "rifle corps" of a minimum of 15 men. Initially only one corps was established, at Entebbe, but a second, at Kampala, was established in June 1914. The members of the UVR were required to attend rifle practice annually and were unpaid, except for a bonus for meeting a minimum marksmanship standard.