Baroque chess is a chess variant invented in 1962 by Robert Abbott. In 1963, at the suggestion of his publisher, he changed the name to Ultima, by which name it is also known. Abbott later considered his invention flawed and suggested amendments to the rules, but these suggestions have been substantially ignored by the gaming community, which continues to play by the 1962 rules. Since the rules for Baroque were first laid down in 1962, some regional variation has arisen, causing the game to diverge from Ultima.

ChessV is a free computer program designed to play many chess variants. ChessV is an open-source, universal chess variant program with a graphical user-interface, sophisticated AI, support for opening books and other features of traditional chess programs. The developer of this program, Gregory Strong, has been adding more variants with each release of ChessV. Over 100 chess variants are supported, including the developer's few own variants and other exotic variants, and can be programmed to play additional variants. ChessV is designed to be able to play any game that is reasonably similar to chess. ChessV is one of only a few such programs that exist. The source code of this program is freely available for download as well as the executable program.
Extinction chess is a chess variant invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger, editor of Games magazine, in 1985. Instead of checkmate as the winning condition, the object of the game is the elimination of all of a particular type of piece of the opponent. In other words, the objective is any of the following:
Transcendental chess (TC) also known as pre-chess, is a chess variant invented in 1978 by Maxwell Lawrence. Chess960 (Fischer random chess) is similar but has fewer starting positions. In transcendental chess the beginning positions of the pieces on the back row are randomly determined, with the one restriction that the bishops be on opposite-colored squares. There are 8,294,400 such positions in total. In Chess960 there are 960 possible starting positions, but that is because the king must be located between the rooks and both sides must have the same starting position. In transcendental chess there is no such rule so the position of one side can be any of 42×6!÷22 = 2,880. There is no castling. On the first turn a player, instead of making a move, can transpose any two pieces on the back row.

Hasami shogi is a variant of shogi. The game has two main variants, and all Hasami variants, unlike other shogi variants, use only one type of piece, and the winning objective is not checkmate. One main variant involves capturing all but one of the opponent's men; the other involves building an unbroken vertical or horizontal chain of five-in-a-row.
Chess with different armies is a chess variant invented by Ralph Betza in 1979. Two sides use different sets of fairy pieces. There are several armies of equal strength to choose from, including the standard FIDE army. In all armies, kings and pawns are the same as in FIDE chess, but the four other pieces are different.

Minichess is a family of chess variants played with regular chess pieces and standard rules, but on a smaller board. The motivation for these variants is to make the game simpler and shorter than standard chess. The first chess-like game implemented on a computer was the 6×6 chess variant Los Alamos chess. The low memory capacity of early computers meant that a reduced board size and a smaller number of pieces were required for the game to be implementable on a computer.
Modern chess is a chess variant played on a 9×9 board. The game was invented by Gabriel Vicente Maura in 1968. Besides the usual set of chess pieces, each player has a prime minister and an additional pawn:

Fortress chess is a four-player chess variant played in Russia in the 18th and 19th centuries. The board contains 192 squares including the fortresses at its corners. The fortresses contain 16 squares and various pieces are placed inside.
Courier chess is a chess variant that dates from the 12th century and was popular for at least 600 years. It was a part of the slow evolution towards modern chess from Medieval Chess.

Tri-chess is the name of a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. The game is played on a board comprising 150 triangular cells. The standard chess pieces are present, minus the queens, and plus the chancellor and cardinal compound fairy pieces per side.
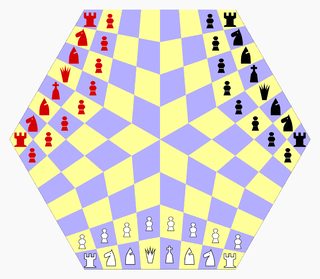
Three-man chess is a chess variant for three players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1984. The game is played on a hexagonal board comprising 96 quadrilateral cells. Each player controls a standard army of chess pieces.

Quatrochess is a chess variant for four players invented by George R. Dekle Sr. in 1986. It is played on a square 14×14 board that excludes the four central squares. Each player controls a standard set of sixteen chess pieces, and additionally nine fairy pieces. The game can be played in partnership or all-versus-all.
Stratomic is a chess variant invented by Robert Montay-Marsais in 1972. The game is played on a 10×10 board with all the standard chess pieces present, and in addition, two nuclea pieces and two extra pawns per side. The game brings the concept of modern warfare weaponry to chess.

Falcon–hunter chess is a chess variant invented by Karl Schultz in 1943, employing the two fairy chess pieces falcon and hunter. The game takes several forms, including variations hunter chess and decimal falcon–hunter chess added in the 1950s.
The Chess Variant Pages is a non-commercial website devoted to chess variants. It was created by Hans Bodlaender in 1995. The site is "run by hobbyists for hobbyists" and is "the most wide-ranging and authoritative web site on chess variants".

Game of the Seven Kingdoms is a seven-player variant of the game xiangqi. It is traditionally ascribed to Sima Guang, although he died well before the 13th century, to which this game is traditionally dated. The rules of the game can be found in his book, 古局象棋圖. There is skepticism regarding the game's 13th-century formulation.

A chess variant is a game related to, derived from, or inspired by chess. Such variants can differ from chess in many different ways.
Duchess is a chess variant for 2+ players, created by Alan Blair and John Kramer in 1985 with the help of Mike Blair and Warwick Hooke. It supports 2-6 players in either free-for-all, 2v2, or 3v3 formats, and has largely the same rules as standard chess. Notable inclusions are three fairy chess pieces and a central "vortex" space being used for promotion rather than the back rank.










