Related Research Articles

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

A building code is a set of rules that specify the standards for construction objects such as buildings and non-building structures. Buildings must conform to the code to obtain planning permission, usually from a local council. The main purpose of building codes is to protect public health, safety and general welfare as they relate to the construction and occupancy of buildings and structures — for example, the building codes in many countries require engineers to consider the effects of soil liquefaction in the design of new buildings. The building code becomes law of a particular jurisdiction when formally enacted by the appropriate governmental or private authority.

A composting toilet is a type of dry toilet that treats human waste by a biological process called composting. This process leads to the decomposition of organic matter and turns human waste into compost-like material. Composting is carried out by microorganisms under controlled aerobic conditions. Most composting toilets use no water for flushing and are therefore called "dry toilets".

A hot tub is a large tub full of water used for hydrotherapy, relaxation or pleasure. Some have powerful jets for massage purposes. Hot tubs are sometimes also known as "spas" or by the trade name Jacuzzi. Hot tubs may be located outdoors or indoors.

Hydronics is the use of liquid water or gaseous water (steam) or a water solution as a heat-transfer medium in heating and cooling systems. The name differentiates such systems from oil and refrigerant systems.
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes.
The International Code Council (ICC), also known as the Code Council, is an American nonprofit standards organization sponsored by the building trades, which was founded in 1994 through the merger of three regional model code organizations in the American construction industry. The organization creates the International Building Code (IBC), a model building code, which has been adopted for use as a base code standard by most jurisdictions in the United States. Despite its name, the International Code Council is not an international organization, its codes are rarely used outside the United States, and its regulations don't follow consistently international best practices.
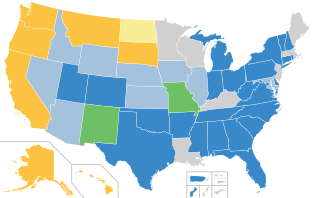
Designated as an American National Standard, the Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to govern the installation and inspection of plumbing systems as a means of promoting the public's health, safety and welfare.

Underfloor heating and cooling is a form of central heating and cooling that achieves indoor climate control for thermal comfort using hydronic or electrical heating elements embedded in a floor. Heating is achieved by conduction, radiation and convection. Use of underfloor heating dates back to the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods.
Building officials of developed countries are generally the jurisdictional administrator of building and construction codes, engineering calculation supervision, permits, facilities management, and accepted construction procedures.

Architectural Engineer (PE) is a professional engineering designation in the United States. The architectural engineer applies the knowledge and skills of broader engineering disciplines to the design, construction, operation, maintenance, and renovation of buildings and their component systems while paying careful attention to their effects on the surrounding environment.
Designated as an American National Standard, the Uniform Swimming Pool, Spa and Hot Tub Code (USPSHTC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to govern the installation and inspection of plumbing systems associated with swimming pools, spas and hot tubs as a means of promoting the public's health, safety and welfare.
Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory is the term used by the United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration to identify third-party organizations that have the necessary qualifications to perform safety testing and certification of products covered within OSHA and each organization's scopes. The testing and certification are conducted in accordance with U.S. consensus-based product safety test standards developed or issued by U.S. standards organizations
IAPMO Standards are the plumbing and mechanical standards of the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO). For more than thirty years, IAPMO’s standards-developing efforts have primarily focused on plumbing product standards. This concentration was primarily due to IAPMO members’ expertise from more than 50 years of writing and updating the Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC). IAPMO is an American National Standards Institute (ANSI)-recognized Standards Development Organization (SDO).
IAPMO R&T was started in 1936 as a third-party listing agency specializing in plumbing and mechanical products. IAPMO R&T is accredited to certify products that meet the criteria of the Uniform Plumbing Code, Uniform Mechanical Code, Uniform Solar Energy Code, Uniform Swimming Pool, Spa and Hot Tub Code and other nationally recognized codes and standards in North America.
A plumbing code is a code that provides regulations for the design, installation and inspection of building plumbing and sanitary systems. In the United States, jurisdictions enact their own codes, some of which are based upon model plumbing codes. The most widely adopted plumbing code in the United States is the International Plumbing Code published by the International Code Council (ICC). This code is also used as the basis for the plumbing codes of some other countries. Another model plumbing code published and utilized widely across the United States is the Uniform Plumbing Code, published by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO), a multinational operation with offices in 13 nations. IAPMO codes are developed using ANSI consensus development procedures. This code serves as the basis for the national plumbing codes in India and Indonesia.
The California Building Standards Code is the building code for California, and Title 24 of the California Code of Regulations (CCR). It is maintained by the California Building Standards Commission which is granted the authority to oversee processes related to the California building codes by California Building Standards Law. Code amendments are proposed by the California Department of Housing and Community Development. The California building codes under Title 24 are established based on several criteria: standards adopted by states based on national model codes, national model codes adapted to meet California conditions, and standards passed by the California legislature that address concerns specific to California.
The International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) coordinates the development and adaptation of plumbing, mechanical, swimming pool and solar energy codes to meet the specific needs of individual jurisdictions both in the United States and abroad.
The Uniform Mechanical Code (UMC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to govern the installation, inspection and maintenance of HVAC and refrigeration systems. It is designated as an American National Standard.
Designated as an American National Standard, the Uniform Solar, Hydronics and Geothermal Code (USHGC) is a model code developed by the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) to govern the installation and inspection of solar energy, hydronic heating/cooling systems, and geothermal energy systems as a means of promoting the public's health, safety and welfare.
References
- ↑ "Plumbing Innovations: Latest Trends And Technologies". 2024-04-10. Retrieved 2025-01-15.
- ↑ Pipe & sewer cleaning using the approved tools and techniques. Retrieved 15 March 2023