
The Union of Evangelical Churches (German: Union Evangelischer Kirchen, UEK) is an organisation of 10 United and 2 Reformed evangelical churches in Germany, which are all member churches of the Evangelical Church in Germany.

The Union of Evangelical Churches (German: Union Evangelischer Kirchen, UEK) is an organisation of 10 United and 2 Reformed evangelical churches in Germany, which are all member churches of the Evangelical Church in Germany.
Guests are
The UEK was founded on July 1, 2003. The organisation succeeded the former organisation Evangelical Church of the Union (German : Evangelische Kirche der Union, EKU). The seat of the organisation used to be Berlin. For structural reasons, it was moved to the seat of the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD) in Hanover though. On November 9, 2019, Union of Evangelical Churches allowed blessings of same-sex marriages. [1]
The parliament (=Vollkonferenz) of the organisation is an elected group of 47 members, which are elected for six years each term. The 47 members elect a "Präsidium".

The Evangelical Church in Germany is a federation of twenty one Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United Protestant regional churches and denominations in Germany, which collectively encompasses the vast majority of Protestants in that country. In 2020, the EKD had a membership of 20,236,000 members, or 24.3% of the German population. It constitutes one of the largest national Protestant bodies in the world. Church offices managing the federation are located in Hannover-Herrenhausen, Lower Saxony. Many of its members consider themselves Lutherans.
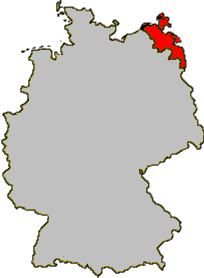
The Pomeranian Evangelical Church was a Protestant regional church in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, serving the citizens living in Hither Pomerania. The Pomeranian Evangelical Church was based on the teachings brought forward by Martin Luther and other Reformators during the Reformation. It combined Lutheran and Reformed traditions. The seat of the church was Greifswald, the bishop's preaching venue was the former Collegiate Church of St. Nicholas in Greifswald.

A united church, also called a uniting church, is a church formed from the merger or other form of church union of two or more different Protestant Christian denominations.

The Independent Evangelical-Lutheran Church is a confessional Lutheran church body of Germany. It is a member of the European Lutheran Conference and of the International Lutheran Council (ILC). The SELK has about 33,000 members in 174 congregations. The seat of SELK is in Hanover.

The Prussian Union of Churches was a major Protestant church body which emerged in 1817 from a series of decrees by Frederick William III of Prussia that united both Lutheran and Reformed denominations in Prussia. Although not the first of its kind, the Prussian Union was the first to occur in a major German state.

Lutheranism is present on all inhabited continents with an estimated 81 million adherents, out of which 74.2 million are affiliated with the Lutheran World Federation. A major movement that first began the Reformation, it constitutes one of the largest Protestant branches, claiming about 80 million of 920 million Protestants, The Lutheran World Federation brings together the vast majority of Lutherans, the second largest grouping being the International Lutheran Council with 7.15 million in 46 countries. Apart from it, there are also other organisations such as the Confessional Evangelical Lutheran Conference, as well as multiple independent Lutheran denominations.

Evangelical Lutheran Church in Oldenburg is a Lutheran church in the German state of Lower Saxony.

The Protestant Church in Hesse and Nassau is a United Protestant church body in the German states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate. There is no bishop and therefore no cathedral. One of its most prominent churches is Katharinenkirche in Frankfurt am Main.
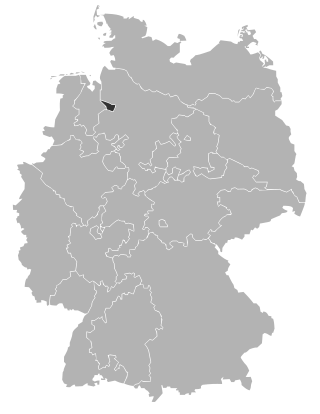
The Evangelical Church of Bremen is a United Protestant member church of the Evangelical Church in Germany in the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen.

Protestant Church in the Rhineland is a United Protestant church body in parts of the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia, Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland and Hesse (Wetzlar). This is actually the area covered by the former Prussian Rhine Province until 1920.
The Evangelical Church Berlin-Brandenburg-Silesian Upper Lusatia is a United Protestant church body in the German states of Brandenburg, Berlin and a part of Saxony.

Evangelical Church of the Palatinate is a United Protestant church in parts of the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland, endorsing both Lutheran and Calvinist orientations.
Lutheran viewpoints concerning homosexuality are diverse because there is no one worldwide body which represents all Lutherans. The Lutheran World Federation, a worldwide 'communion of churches' and the largest global body of Lutherans, contains member churches on both sides of the issue. However, other Lutherans, including the Confessional Evangelical Lutheran Conference and International Lutheran Council, completely reject homosexuality.
The Communion of Protestant Churches in Europe is a fellowship of over 100 Protestant churches which have signed the Leuenberg Agreement. Together they strive for realizing church communion, especially by cooperation in witness and service to the world. Prior to 2003 the CPCE was known as the "Leuenberg Church Fellowship".
Buß- und Bettag was a public holiday in Germany, and is still a public holiday in Saxony. In Germany, Protestant church bodies of Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United denominations celebrate a day of repentance and prayer. It is now celebrated on the penultimate Wednesday before the beginning of the Protestant liturgical year on the first Sunday of Advent; in other words, it is the Wednesday that falls between 16 and 22 November. However, it is not a statutory non-working holiday any more, except in the Free State of Saxony. In the Free State of Bavaria, it is a school holiday only.

The Evangelical-Lutheran Church in Württemberg is a Lutheran member church of the Evangelical Church in Germany in the German former state of Württemberg, now part of the state of Baden-Württemberg.
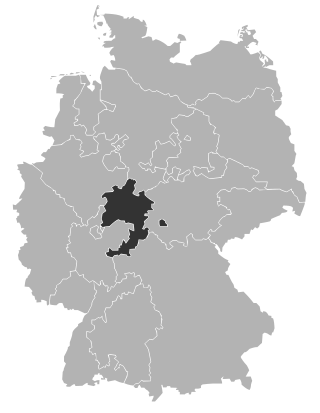
The Evangelical Church of Hesse Electorate-Waldeck is a United Protestant church body in former Hesse-Cassel and the Waldeck part of the former Free State of Waldeck-Pyrmont.
The German Evangelical Church Confederation was a formal federation of 28 regional Protestant churches (Landeskirchen) of Lutheran, Reformed or United Protestant administration or confession. It existed during the Weimar Republic from 1922 until being replaced by the German Evangelical Church in 1933. It was a predecessor body to the Evangelical Church in Germany.
More than 60 percent of Berlin residents have no registered religious affiliation. As of 2010, at least 30 percent of the population identified with some form of Christianity, approximately 8.1 percent were Muslim, 1 percent were Jewish, and 1 percent belonged to other religions. As of 2018, the number of registered church members has shrunk to 14.9 percent for EKD Protestants and 8.5 percent for Catholics.

In Protestant usage, a consistory designates certain ruling bodies in various churches. The meaning and the scope of functions varies strongly, also along the separating lines of the Protestant denominations and church bodies.