Unionist may refer to:
Contents
- A member or supporter of a trade union
Unionist may refer to:
A Tory is an individual who supports a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalist conservatism which upholds the established social order as it has evolved through the history of Great Britain. The Tory ethos has been summed up with the phrase "God, King, and Country". Tories are monarchists, were historically of a high church Anglican religious heritage, and were opposed to the liberalism of the Whig party.
Republican can refer to:
The Liberal Unionist Party was a British political party that was formed in 1886 by a faction that broke away from the Liberal Party. Led by Lord Hartington and Joseph Chamberlain, the party established a political alliance with the Conservative Party in opposition to Irish Home Rule. The two parties formed the ten-year-long coalition Unionist Government 1895–1905 but kept separate political funds and their own party organisations until a complete merger between the Liberal Unionist and the Conservative parties was agreed to in May 1912.
Social conservatism is a political philosophy and a variety of conservatism which places emphasis on traditional social structures over social pluralism. Social conservatives organize in favor of duty, traditional values and social institutions, such as traditional family structures, gender roles, sexual relations, national patriotism, and religious traditions. Social conservatism is usually skeptical of social change, instead tending to support the status quo concerning social issues.

Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Crown, notably with the loyalists opponents of the American Revolution, and United Empire Loyalists who moved to other colonies in British North America after the revolution.
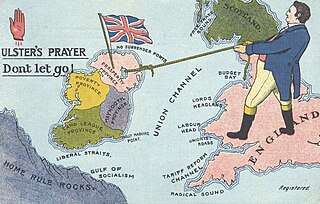
Unionism in Ireland is a political tradition that professes loyalty to the crown of the United Kingdom and to the union it represents with England, Scotland and Wales. The overwhelming sentiment of Ireland's Protestant minority, unionism mobilised in the decades following Catholic Emancipation in 1829 to oppose restoration of a separate Irish parliament. Since Partition in 1921, as Ulster unionism its goal has been to retain Northern Ireland as a devolved region within the United Kingdom and to resist the prospect of an all-Ireland republic. Within the framework of the 1998 Belfast Agreement, which concluded three decades of political violence, unionists have shared office with Irish nationalists in a reformed Northern Ireland Assembly. As of February 2024, they no longer do so as the larger faction: they serve in an executive with an Irish republican First Minister.

The Unionist Party was the main centre-right political party in Scotland between 1912 and 1965.
Unionist Party may refer to:
Unionism may refer to:

Unionism in Scotland is a political movement which favours the continuation of the political union between Scotland and the other countries of the United Kingdom, and hence is opposed to Scottish independence. Scotland is one of four countries of the United Kingdom which has its own devolved government and Scottish Parliament, as well as representation in the UK Parliament. There are many strands of political Unionism in Scotland, some of which have ties to Unionism and Loyalism in Northern Ireland. The two main political parties in the UK — the Conservatives and Labour — both support Scotland remaining part of the UK.

The Irish Unionist Alliance (IUA), also known as the Irish Unionist Party, Irish Unionists or simply the Unionists, was a unionist political party founded in Ireland in 1891 from a merger of the Irish Conservative Party and the Irish Loyal and Patriotic Union (ILPU) to oppose plans for home rule for Ireland within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The party was led for much of its existence by Colonel Edward James Saunderson and later by St John Brodrick, 1st Earl of Midleton. In total, eighty-six members of the House of Lords affiliated themselves with the Irish Unionist Alliance, although its broader membership among Irish voters outside Ulster was relatively small.
Scottish Unionist Party may refer to:
Milne is a surname of Scottish origin, from the same source as Miller.

In the United Kingdom, unionism is a political stance favouring the continued unity of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as one sovereign state, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Those who support the union are referred to as Unionists. Though not all unionists are nationalists, UK or British unionism is associated with British nationalism, which asserts that the British are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of the Britons, which may include people of English, Scottish, Welsh, Irish, Cornish, Jersey, Manx and Guernsey descent.

British nationalism asserts that the British are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Britons, in a definition of Britishness that may include people of English, Scottish, Welsh, and Irish descent. British nationalism is closely associated with British unionism, which seeks to uphold the political union that is the United Kingdom, or strengthen the links between the countries of the United Kingdom.
Junta may refer to:
The Civic Party is a liberal democratic political party in Hong Kong.
The Tory Party was a British political party between 1678 and 1834.

In England, Unionism is a political ideology which favours the continuation of some form of political union between England and the other Countries of the United Kingdom,. As well as the current state of the United Kingdom, It is part of the wider British unionist movement and is closely linked to the notion of Britishness. Unionism in England is characterised by both opposition to England's independence as a separate state and the belief that Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland should continue to be constituent countries of the Union.
Unionist Movement may refer to: