
The prehistory of Papua New Guinea can be traced to about 50,000–60,000 years ago, when people first migrated towards the Australian continent. The written history began when European navigators first sighted New Guinea in the early part of the 17th century.

Dutch New Guinea or Netherlands New Guinea was the western half of the island of New Guinea that was a part of the Dutch East Indies until 1949, later an overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. It contained what are now Indonesia's six easternmost provinces, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name Irian Jaya, and now comprise the Papua region of the country.

The Free Papua Movement or Free Papua Organization is a name given to a separatist movement that aims to separate West Papua from Indonesia and establish an independent state in the region. The territory is currently divided into six Indonesian provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, also formerly known as Papua, Irian Jaya and West Irian.

The Republic of West Papua, alternatively known as the Federal Republic of West Papua is a quasi-state consisting of the Western New Guinea region, which is currently part of Indonesia on the continent of Oceania. The region has been part of Indonesia since 1 May 1963 under several names in the following order, West Irian, Irian Jaya, and Papua. Today the region comprises six Indonesian provinces: Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, West Papua, and Southwest Papua.

The New York Agreement is an agreement signed by the Kingdom of the Netherlands and Indonesia regarding the administration of the territory of Western New Guinea. The first part of the agreement proposes that the United Nations assume administration of the territory, and a second part proposes a set of social conditions that will be provided if the United Nations exercises a discretion proposed in article 12 of the agreement to allow Indonesian occupation and administration of the territory. Negotiated during meetings hosted by the United States, the agreement was signed on 15 August 1962 at the United Nations Headquarters in New York City, United States.

The Act of Free Choice was a controversial plebiscite held between 14 July and 2 August 1969 in which 1,025 people selected by the Indonesian military in Western New Guinea voted unanimously in favor of Indonesian control.

The United Nations Regional Groups are the geopolitical regional groups of member states of the United Nations. Originally, the UN member states were unofficially organized into five groups as an informal means of sharing the distribution of posts for General Assembly committees. Now this grouping has taken on a much more expansive and official role. Many UN bodies are allocated on the basis of geographical representation. Top leadership positions, including Secretary-General and President of the General Assembly, are rotated among the regional groups. The groups also coordinate substantive policy and form common fronts for negotiations and bloc voting.

Pakistan has served in 46 United Nations peacekeeping missions in 29 countries around the world. As of 2023, United Nations (UN) statistics show that 168 Pakistani UN peacekeepers have been killed since 1948. The biggest Pakistani loss occurred on 5 June 1993 in Mogadishu. Pakistan joined the United Nations on 30 September 1947, despite opposition from Afghanistan because of the Durand Line issue. The Pakistan Armed Forces are the fifth largest contributor of troops towards UN peacekeeping efforts, behind India and Rwanda.

United Nations Administered West New Guinea refers to the period between 1 October 1962 and 1 May 1963 when Western New Guinea was administered by the United Nations Temporary Executive Authority (UNTEA) in accordance with in article two of the New York Agreement reached between the governments of the Netherlands and Indonesia in August 1962.

Papua New Guinea–United States relations refers to the diplomatic relations between Papua New Guinea and the United States of America. The two countries established diplomatic relations following Papua New Guinea's independence on September 16, 1975. The two nations belong to a variety of regional organizations, including the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum; the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF); the Pacific Community (SPC); and the South Pacific Regional Environmental Program (SPREP).
Robert Guba Aisi is a Papua New Guinean diplomat. He is the former Permanent Representative (ambassador) of Papua New Guinea to the United Nations in New York. He presented his credentials to the Secretary General on June 25, 2002. Prior to being appointed to the United Nations, Aisi was Councillor of Papua New Guinea’s Legal Training Institute.

The Papua conflict is an ongoing conflict in Western New Guinea (Papua) between Indonesia and the Free Papua Movement. Subsequent to the withdrawal of the Dutch administration from the Netherlands New Guinea in 1962 and implementation of Indonesian administration in 1963, the Free Papua Movement has conducted a low-intensity guerrilla war against Indonesia by targeting its military and police, along with ordinary Indonesian civilians.

The New Guinea Council was a unicameral representative body formed in the Dutch overseas territory of Netherlands New Guinea in 1961.
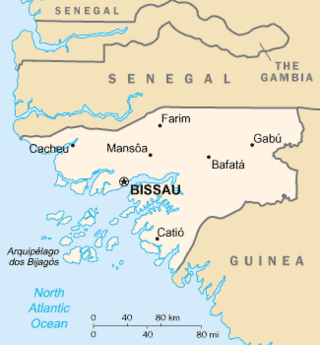
United Nations Security Council resolution 1216 was adopted unanimously on 21 December 1998. After expressing concern at the crisis and humanitarian situation in Guinea-Bissau, the Council called for the immediate establishment of a government of national unity in the National People's Assembly and the holding of elections by the end of March 1999.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1233, adopted unanimously on 6 April 1999, after reaffirming Resolution 1216 (1998) on the situation in Guinea-Bissau, the council established the United Nations Peacebuilding Support Office in Guinea-Bissau (UNOGBIS) to facilitate the implementation of the Abuja Accord.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1580, adopted unanimously on 22 December 2004, after reaffirming resolutions 1216 (1998) and 1233 (1999) on the situation in Guinea-Bissau, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacebuilding Support Office in Guinea-Bissau (UNOGBIS) for a further period of one year and revised its operations. It was the final Security Council resolution adopted in 2004.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1949, adopted unanimously on 23 November 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Guinea-Bissau, particularly Resolution 1876 (2009), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Integrated Peacebuilding Office in Guinea-Bissau (UNIOGBIS) for a further period of one year until 31 December 2011.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1876 was unanimously adopted on 26 June 2009.
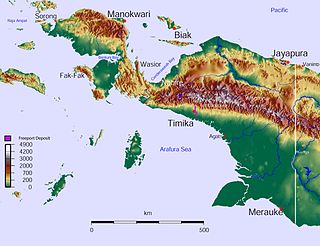
The West New Guinea dispute (1950–1962), also known as the West Irian dispute, was a diplomatic and political conflict between the Netherlands and Indonesia over the territory of Dutch New Guinea. While the Netherlands had ceded sovereignty over most of the Dutch East Indies to Indonesia on 27 December 1949 following an independence struggle, it retained control over its colony on the western half of New Guinea. The Indonesian government claimed this territory as well, on the basis that it had belonged to the Dutch East Indies and that the new Republic of Indonesia was the legitimate successor to the former Dutch colony.
The Declaration on the Rights of Peasants is a United Nations General Assembly resolution on human rights with "universal understanding", adopted by the United Nations in 2018. The resolution was passed by a vote of 121-8, with 54 members abstaining.















