
A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.
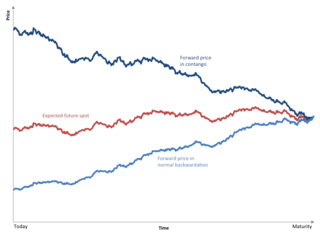
Contango is a situation in which the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market or carrying-cost market.
An index fund is a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) designed to follow certain preset rules so that it can replicate the performance ("track") of a specified basket of underlying investments. While index providers often emphasize that they are for-profit organizations, index providers have the ability to act as "reluctant regulators" when determining which companies are suitable for an index. Those rules may include tracking prominent indices like the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average or implementation rules, such as tax-management, tracking error minimization, large block trading or patient/flexible trading strategies that allow for greater tracking error but lower market impact costs. Index funds may also have rules that screen for social and sustainable criteria.
A closed-end fund, also known as a closed-end mutual fund, is an investment vehicle fund that raises capital by issuing a fixed number of shares at its inception, and then invests that capital in financial assets such as stocks and bonds. After inception it is closed to new capital, although fund managers sometimes employ leverage. Investors can buy and sell the existing shares in secondary markets.
A mutual fund is an investment fund that pools money from many investors to purchase securities. The term is typically used in the United States, Canada, and India, while similar structures across the globe include the SICAV in Europe, and the open-ended investment company (OEIC) in the UK.
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund that is also an exchange-traded product, i.e., it is traded on stock exchanges. ETFs own financial assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, debts, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars. Many ETFs provide some level of diversification compared to owning an individual stock.
A unit trust is a form of collective investment constituted under a trust deed. A unit trust pools investors' money into a single fund, which is managed by a fund manager. Unit trusts offer access to a wide range of investments, and depending on the trust, it may invest in securities such as shares, bonds, gilts, and also properties, mortgage and cash equivalents. Those investing in the trust own "units", whose price is called the "net asset value" (NAV). The number of these units is not fixed and when more is invested in a unit trust, more units are created.
An investment company is a financial institution principally engaged in holding, managing and investing securities. These companies in the United States are regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and must be registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940. Investment companies invest money on behalf of their clients who, in return, share in the profits and losses.
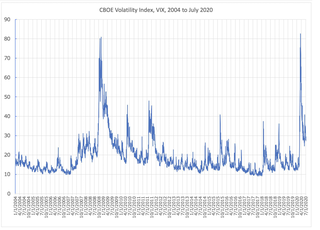
VIX is the ticker symbol and the popular name for the Chicago Board Options Exchange's CBOE Volatility Index, a popular measure of the stock market's expectation of volatility based on S&P 500 index options. It is calculated and disseminated on a real-time basis by the CBOE, and is often referred to as the fear index or fear gauge.
Gold exchange-traded products are exchange-traded funds (ETFs), closed-end funds (CEFs) and exchange-traded notes (ETNs) that are used to own gold as an investment. Gold exchange-traded products are traded on the major stock exchanges including the SIX Swiss Exchange, the Bombay Stock Exchange, the London Stock Exchange, the Paris Bourse, and the New York Stock Exchange. Each gold ETF, ETN, and CEF has a different structure outlined in its prospectus. Some such instruments do not necessarily hold physical gold. For example, gold ETNs generally track the price of gold using derivatives.
An inverse exchange-traded fund is an exchange-traded fund (ETF), traded on a public stock market, which is designed to perform as the inverse of whatever index or benchmark it is designed to track. These funds work by using short selling, trading derivatives such as futures contracts, and other leveraged investment techniques.

Platinum as an investment is often compared in financial history to gold and silver, which were both known to be used as money in ancient civilizations. Experts posit that platinum is about 15–20 times scarcer than gold and approximately 60–100 times scarcer than silver, on the basis of annual mine production. Since 2014, platinum prices have fallen lower than gold. Approximately 75% of global platinum is mined in South Africa.
A portfolio manager (PM) is a professional responsible for making investment decisions and carrying out investment activities on behalf of vested individuals or institutions. Clients invest their money into the PM's investment policy for future growth, such as a retirement fund, endowment fund, or education fund. PMs work with a team of analysts and researchers and are responsible for establishing an investment strategy, selecting appropriate investments, and allocating each investment properly towards an investment fund or asset management vehicle.
Silver exchange-traded products are exchange-traded funds (ETFs), exchange-traded notes (ETNs) and closed-end funds (CEFs) that aim to track the price of silver. Silver exchange-traded products are traded on the major stock exchanges including the London and New York Stock Exchanges. The U.S Geological Survey cites the emergence of silver ETFs as a significant factor in the 2007-2011 price rise of silver. As of September 2011, the largest of these funds holds the equivalent of over one third of the world's total annual silver production.

SPDR Gold Shares is part of the SPDR family of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) managed and marketed by State Street Global Advisors. For a few years, the fund was the second-largest exchange-traded fund in the world, and it was briefly the largest. As of the close of 2014, it dropped out of the top ten.
United States Commodity Funds LLC (USCF) is a US company based in Oakland, CA, specializing in managing exchange-traded commodity funds, which are often referred to as commodity-based exchange-traded funds (ETFs). USCF was one of the earliest issuers of exchange-traded commodity funds in the United States. It is best known for launching in 2006 the first crude oil based exchange traded commodity fund in the United States, United States Oil Fund, LP, as well as launching in 2007 the first natural gas exchange traded commodity fund, United States Natural Gas Fund, LP. USO and UNG are two of the most actively traded ETFs in the United States. As of June 30, 2016, USCF managed eleven different exchange traded commodity funds with total assets of approximately $5 billion.

An investment fund is a way of investing money alongside other investors in order to benefit from the inherent advantages of working as part of a group such as reducing the risks of the investment by a significant percentage. These advantages include an ability to:

Securities market participants in the United States include corporations and governments issuing securities, persons and corporations buying and selling a security, the broker-dealers and exchanges which facilitate such trading, banks which safe keep assets, and regulators who monitor the markets' activities. Investors buy and sell through broker-dealers and have their assets retained by either their executing broker-dealer, a custodian bank or a prime broker. These transactions take place in the environment of equity and equity options exchanges, regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), or derivative exchanges, regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). For transactions involving stocks and bonds, transfer agents assure that the ownership in each transaction is properly assigned to and held on behalf of each investor.






