Related Research Articles

Liberia is a country in West Africa founded by free people of color from the United States. The emigration of African Americans, both free and recently emancipated, was funded and organized by the American Colonization Society (ACS). The mortality rate of these settlers was the highest in accurately recorded human history. Of the 4,571 emigrants who arrived in Liberia between 1820 and 1843, only 1,819 survived.

Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is geographically situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea to the south in the Atlantic Ocean. It covers an area of 923,769 square kilometres (356,669 sq mi), and with a population of over 218 million. It is the most populous country in Africa, and the world’s seventh-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in the north, Chad in the northeast, Cameroon in the east, and Benin in the west. Nigeria is a federal republic comprising 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, where the capital, Abuja, is located. The largest city in Nigeria is Lagos, one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world and the second-largest in Africa.

The history of Nigeria can be traced to settlers trading across the middle East and Africa as early as 1100 BC. Numerous ancient African civilizations settled in the region that is known today as Nigeria, such as the Kingdom of Nri, the Benin Empire, and the Oyo Empire. Islam reached Nigeria through the Bornu Empire between and Hausa States around during the 11th century, while Christianity came to Nigeria in the 15th century through Augustinian and Capuchin monks from Portugal. The Songhai Empire also occupied part of the region. From the 15th century, European slave traders arrived in the region to purchase enslaved Africans as part of the Atlantic slave trade, which started in the region of modern-day Nigeria; the first Nigerian port used by European slave traders was Badagry, a coastal harbour. Local merchants provided them with slaves, escalating conflicts among the ethnic groups in the region and disrupting older trade patterns through the Trans-Saharan route.

The Federal government of Nigeria is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive, and judicial, whose powers are vested by the constitution of Nigeria in the national assembly, the president, and the federal courts, including the supreme court, respectively. The constitution provides a separation and balance of powers among the three branches and aims to prevent the repetition of past mistakes made by the government.

The Peoples Democratic Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in Nigeria, along with its main rival, the All Progressives Congress.

The Nigerian Civil War was a civil war fought between the government of Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state which had declared its independence from Nigeria in 1967. Nigeria was led by General Yakubu Gowon, while Biafra was led by Lt. Colonel Odumegwu Ojukwu. Biafra represented the nationalist aspirations of the Igbo ethnic group, whose leadership felt they could no longer coexist with the federal government dominated by the interests of the Muslim Hausa-Fulanis of northern Nigeria. The conflict resulted from political, economic, ethnic, cultural and religious tensions which preceded Britain's formal decolonization of Nigeria from 1960 to 1963. Immediate causes of the war in 1966 included ethno-religious violence and anti-Igbo pogroms in Northern Nigeria, a military coup, a counter-coup and persecution of Igbo living in Northern Nigeria. Control over the lucrative oil production in the Niger Delta also played a vital strategic role.
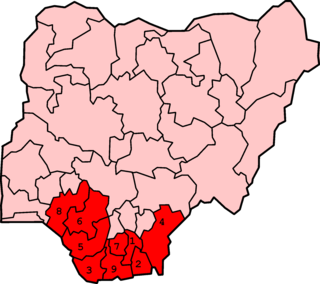
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is typically considered to be located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitical zone, one state (Ondo) from South West geopolitical zone and two states from South East geopolitical zone.

The National Assembly of the Federal Republic of Nigeria is a bicameral legislature established under section 4 of the Nigerian Constitution. It consists of a Senate with 109 members and a 360-member House of Representatives. The body, modeled after the federal Congress of the United States, is supposed to guarantee equal representation with 3 Senators to each 36 states irrespective of size in the Senate plus 1 senator representing the FCT and single-member district, plurality voting in the House of Representatives. The National Assembly, like many other organs of the Nigerian federal government, is based in Abuja in the Federal Capital Territory.
The National Council of Nigeria and the Cameroons (NCNC) later changed to the National Convention of Nigerian Citizens, was a Nigerian nationalist political party from 1944 to 1966, during the period leading up to independence and immediately following independence.

Nigeria is the largest oil and gas producer in Africa. Crude oil from the Niger delta basin comes in two types: light, and comparatively heavy – the lighter around 36 gravity and the heavier, 20–25 gravity. Both types are paraffinic and low in sulfur. Nigeria's economy and budget has been largely supported from income and revenues generated from the petroleum industry since 1960. Statistics as of February 2021 shows that the Nigeria's oil sector contributes to about 9% of the entire country's GDP. Nigeria as the largest oil and gas producer in Africa, is a major exporter of Crude oil and petroleum products to the United States of America. In 2010, Nigeria exported over one million barrels per day to the United States of America representing 9% of the U.S total crude oil and petroleum products imports and over 40% of Nigeria exports.
The Action Group (AG) was a Nigerian nationalist political party established in Ibadan on 21st March 1951, by Chief Obafemi Awolowo. The party was founded to serve as the platform for realizing his preliminary objective of mobilizing Western Nigerians to forestall the NCNC control of the Western Region and the subsequent aim of cooperating with other nationalist parties to win independence for Nigeria. It benefited immensely from the relationships developed in the Egbe Omo Oduduwa formed in Awolowo's days in London as a student.

The Action Congress of Nigeria (ACN), formerly known as Action Congress (AC), was a Nigerian political party formed via the merger of a faction of Alliance for Democracy, the Justice Party, the Advance Congress of Democrats, and several other minor political parties in September 2006. The party controlled Lagos. It was regarded as a natural successor to the progressive politics more closely associated with the Action Group and Unity Party of Nigeria (UPN) led by Chief Obafemi Awolowo in the First and Second Republics respectively. However, criticism of the party's more pragmatic and less ideological political outlook associated with AG and UPN, has made many argue it was less of a worthy political heir. The Party had strong presence in the South West, Mid-West and North Central Regions. Lagos, Edo, Ekiti, Kogi, Ondo, Bauchi, Plateau, Niger, Adamawa, Oyo and Osun states by far accounts for majority of the party's presence and discernible power base.

Colonial Nigeria was ruled by the British Empire from the mid-nineteenth century until 1960 when Nigeria achieved independence. British influence in the region began with the prohibition of slave trade to British subjects in 1807. Britain annexed Lagos in 1861 and established the Oil River Protectorate in 1884. British influence in the Niger area increased gradually over the 19th century, but Britain did not effectively occupy the area until 1885. Other European powers acknowledged Britain's dominance over the area in the 1885 Berlin Conference.

Corruption is an anti-social attitude awarding improper privileges contrary to legal and moral norms and impairs the authorities' capacity to secure the welfare of all citizens. Corruption in Nigeria is a constant phenomenon. In 2012, Nigeria was estimated to have lost over $400 billion to corruption since its independence. In 2021, the country ranked 154th in the 180 countries listed in Transparency International's Corruption Index.

The Second Nigerian Republic was a brief formation of the Nigerian state which succeeded the military governments formed after the overthrow of the first republic.
Stephen Oluwole Awokoya (1913–1985) was a former minister of education in the old Western Region of Nigeria. He was one of the leading architects of a nationalistic policy to promote formal schooling in Nigeria during the 1950s. He is credited for the creation of the universal primary education in Western Nigeria.

Olusegun Mimiko, was the senatorial candidate of the Zenith Labour Party for Ondo Central District in the 2019 election. He is a Nigerian politician who served as the 16th, and fifth civilian, Governor of Ondo State, Nigeria, from February 2009, to February 2017. The first two-term governor of Ondo state and the first Labour Party governor in Nigeria. Mimiko was previously a federal minister for housing and urban development, a secretary to the Ondo State Government, and a two-time Ondo State Commissioner for Health.

Michael Adekunle Ajasin was a Nigerian politician who was elected Governor of Ondo State on the Unity Party of Nigeria (UPN) platform during the Nigerian Second Republic.
Melford Obiene Okilo had a long and distinguished career as a politician in Nigeria from the start of independence in 1960 until shortly before his death in 2008. He was a member of parliament (1956–1964) and a Minister in the Nigerian First Republic. He was the first elected Governor of Rivers State, Nigeria (1979–1983) during the Nigerian Second Republic. Later he was Senator for Bayelsa East, in Bayelsa State (1999–2003) during the Nigerian Fourth Republic.
Mazi Samuel Goomsu Ikoku was a Nigerian trade unionist and politician. As a student at University of Southampton, Ikoku supported Nigeria's independence movement, writing articles printed by the West African Pilot. After his degree, he joined the radical arm of the independence movement, working as an adviser to the Nigerian Federation of Labour led Michael Imoudu and later co-founding the United Working People's Party in 1952. A year later, the party was officially disbanded, the government did so after branding the organization as subversive and communist. Ikoku later began a relationship with the Action Group (AG) that span majority of the First Republic.
References
- Larry Diamond, Cleavage, Conflict, and Anxiety in the Second Nigerian Republic, The Journal of Modern African Studies > Vol. 20, No. 4 Dec. 1982
- C. S. Whitaker Jr, Second Beginnings: The New Political Framework, Issue: A Journal of Opinion > Vol. 11, No. 1/2 (Spring, 1981)
- Rotimi T. Suberu, The Struggle for New States in Nigeria, 1976-1990, African Affairs > Vol. 90, No. 361 (Oct., 1991), pp. 499–522