
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A relational database organizes data into one or more data tables in which data may be related to each other; these relations help structure the data. SQL is a language that programmers use to create, modify and extract data from the relational database, as well as control user access to the database. In addition to relational databases and SQL, an RDBMS like MySQL works with an operating system to implement a relational database in a computer's storage system, manages users, allows for network access and facilitates testing database integrity and creation of backups.
Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Co-founded in 1977 by Larry Ellison, who remains executive chairman, Oracle was the third-largest software company in the world in 2020 by revenue and market capitalization. The company's 2023 ranking in the Forbes Global 2000 was 80.

Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California, on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center.

Oracle Solaris is a proprietary Unix operating system offered by Oracle for SPARC and x86-64 based workstations and servers. Originally developed by Sun Microsystems as Solaris, it superseded the company's earlier SunOS in 1993 and became known for its scalability, especially on SPARC systems, and for originating many innovative features such as DTrace, ZFS and Time Slider. After the Sun acquisition by Oracle in 2010, it was renamed Oracle Solaris.

OpenOffice.org (OOo), commonly known as OpenOffice, is a discontinued open-source office suite. Active successor projects include LibreOffice and Collabora Online, with Apache OpenOffice being considered mostly dormant since at least 2015.

StarOffice is a discontinued proprietary office suite. Its source code continues today in derived open-source office suites Collabora Online and LibreOffice. StarOffice supported the OpenOffice.org XML file format, as well as the OpenDocument standard, and could generate PDF and Flash formats. It included templates, a macro recorder, and a software development kit (SDK).
MySQL AB was a Swedish software company founded in 1995. It was acquired by Sun Microsystems in 2008, Sun was in turn acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2010. MySQL AB is the creator of MySQL, a relational database management system, as well as related products such as MySQL Cluster. The company was dually headquartered in Uppsala, Sweden, and Cupertino, California, with offices in other countries.
The Sun Industry Standards Source License (SISSL) is now a retired free and open source license, recognized as such by the Free Software Foundation and the Open Source Initiative (OSI). Under SISSL, developers could modify and distribute source code and derived binaries freely. Furthermore, developers could choose to keep their modifications private or make them public. However, the SISSL is unique among OSI-approved licenses in requiring that "The Modifications which You create must comply with all requirements set out by the Standards body in effect one hundred twenty (120) days before You ship the Contributor Version." If the Modifications do not comply, SISSL becomes a copyleft license, and source must be published "under the same terms as this license [SISSL] on a royalty-free basis within thirty (30) days."
Oracle Grid Engine, previously known as Sun Grid Engine (SGE), CODINE or GRD, was a grid computing computer cluster software system, acquired as part of a purchase of Gridware, then improved and supported by Sun Microsystems and later Oracle. There have been open source versions and multiple commercial versions of this technology, initially from Sun, later from Oracle, then from Univa Corporation, and later from HPC Gridware as Gridware Cluster Scheduler. The open source version is still under active development under the SISSL license as Open Cluster Scheduler.

OpenSolaris is a discontinued open-source computer operating system for SPARC and x86 based systems, created by Sun Microsystems and based on Solaris. Its development began in the mid 2000s and ended in 2010.
IBM Spectrum LSF is a workload management platform, job scheduler, for distributed high performance computing (HPC) by IBM.

Platform Computing was a privately held software company primarily known for its job scheduling product, Load Sharing Facility (LSF). It was founded in 1992 in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and headquartered in Markham, Ontario with 11 branch offices across the United States, Europe and Asia.
The Terascale Open-source Resource and Queue Manager (TORQUE) is a distributed resource manager designed to oversee batch jobs and distributed compute nodes. It offers control and management capabilities for clusters, aiding in utilization, scheduling, and administration tasks.
Distributed Resource Management Application API (DRMAA) is a high-level Open Grid Forum (OGF) API specification for the submission and control of jobs to a distributed resource management (DRM) system, such as a cluster or grid computing infrastructure. The scope of the API covers all the high level functionality required for applications to submit, control, and monitor jobs on execution resources in the DRM system.

Univa was a software company that developed workload management and cloud management products for compute-intensive applications in the data center and across public, private, and hybrid clouds, before being acquired by Altair Engineering in September 2020.

The acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle Corporation was completed on January 27, 2010. After the acquisition was completed, Oracle, only a software vendor prior to the merger, owned Sun's hardware product lines, such as SPARC Enterprise, as well as Sun's software product lines, including the Java programming language.
The Techila Distributed Computing Engine is a commercial grid computing software product. Techila Distributed Computing Engine is developed and licensed by Techila Technologies Ltd, a privately held company headquartered in Tampere, Finland. The product is also available as an on-demand solution in Google Cloud Launcher, the online marketplace created and operated by Google.
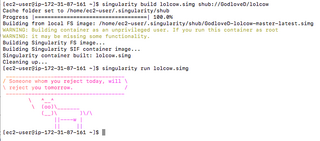
Singularity is a free and open-source computer program that performs operating-system-level virtualization also known as containerization.









