Related Research Articles

The Morrill Land-Grant Acts are United States statutes that allowed for the creation of land-grant colleges in U.S. states using the proceeds from sales of federally owned land, often obtained from Native American tribes through treaty, cession, or seizure. The Morrill Act of 1862 was enacted during the American Civil War, and the Morrill Act of 1890 expanded this model.

Cheyney University of Pennsylvania is a public historically black university in Cheyney, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1837 as the Institute for Colored Youth, it is the oldest of all historically black colleges and universities (HBCUs) in the United States. It is a member of the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education and the Thurgood Marshall College Fund. The university offers bachelor's degrees and is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

A land-grant university is an institution of higher education in the United States designated by a state to receive the benefits of the Morrill Acts of 1862 and 1890.

A normal school or normal college is an institution created to train teachers by educating them in the norms of pedagogy and curriculum. Many such schools are now called teacher training colleges or teachers' colleges, but in Mexico, continue to be called normal schools, with student-teachers being known as normalistas. Many schools currently require a high school diploma for entry, and may be part of a comprehensive university. Normal schools in the United States, Canada, and Argentina trained teachers for primary schools, while in Europe, the equivalent colleges typically educated teachers for primary schools and later extended their curricula to also cover secondary schools.
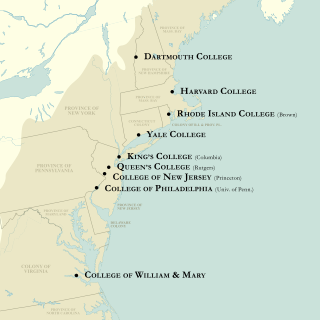
The colonial colleges are nine institutions of higher education chartered in the Thirteen Colonies before the founding of the United States of America during the American Revolution. These nine have long been considered together, notably since the survey of their origins in the 1907 The Cambridge History of English and American Literature.
The Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education (PASSHE) is a state agency of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania that oversees 10 state-owned universities. Collectively, it is the largest provider of higher education in the commonwealth. All of the schools are primarily NCAA Division II members and affiliated with the Pennsylvania State Athletic Conference (PSAC).
The Commonwealth System of Higher Education is a statutory designation by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania that confers "state-related" status on four universities in Pennsylvania: Lincoln University, the Pennsylvania State University, Temple University, and the University of Pittsburgh. The designation establishes the schools as an "instrumentality of the commonwealth" and provides each university with annual, non-preferred financial appropriations in exchange offering tuition discounts to students who are residents of Pennsylvania and a minority state-representation on each school's board of trustees.

Mansfield University of Pennsylvania is a campus of Commonwealth University of Pennsylvania and it is located it in Mansfield, Pennsylvania. Part of the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education (PASSHE), the campus's total enrollment is 1,637 students.
The following is a timeline of women's colleges in the United States. These are institutions of higher education in the United States whose student population comprises exclusively, or almost exclusively, women. They are often liberal arts colleges. There are approximately 35 active women's colleges in the U.S. as of 2021.

The California State Normal School was a teaching college founded on May 2, 1862, which later evolved into San José State University in San Jose. Its southern branch campus evolved into the University of California, Los Angeles in Los Angeles.

The educational system in California consists of public, NPS, and private schools in the U.S. state of California, including the public University of California, California State University, and California Community Colleges systems, private colleges and universities, and elementary, middle, and high schools.

The Middle States Commission on Higher Education is a voluntary, peer-based, non-profit membership organization that performs peer evaluation and accreditation of public and private universities and colleges in the United States and foreign higher education institutions. Until federal regulations changed on July 1, 2020, it was considered one of the seven regional accreditation organizations dating back 130 years. MSCHE, which is now an institutional accreditor, is recognized by the United States Department of Education and the Council for Higher Education Accreditation.

New England Female Medical College (NEFMC), originally Boston Female Medical College, was founded in 1848 by Samuel Gregory and was the first school to train women in the field of medicine. It merged with Boston University to become the Boston University School of Medicine in 1874.
There are numerous elementary, secondary, and higher institutions of learning in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, which is home to 500 public school districts, thousands of private schools, many publicly funded colleges and universities, and over 100 private institutions of higher education.
Hooghly Mohsin College, established in 1836, is one of the oldest colleges in Chinsurah, in the Hooghly district, West Bengal, India. It offers undergraduate and postgraduate courses in Arts, Commerce and Sciences. It is affiliated to University of Burdwan.

Bloomsburg University of Pennsylvania is a campus of Commonwealth University of Pennsylvania and it is located in Bloomsburg, Pennsylvania. It is part of the Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education (PASSHE). The campus is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education with some degree programs accredited by specialized accreditors.

A female seminary is a private educational institution for women, popular especially in the United States in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when opportunities in educational institutions for women were scarce. The movement was a significant part of a remarkable transformation in American education in the period 1820–1850. Supporting academic education for women, the seminaries were part of a large and growing trend toward women's 'equality'. Some trace its roots to 1815, and characterize it as at the confluence of various liberation movements. Some of the seminaries gradually developed as four-year colleges.
The history of higher education in the United States begins in 1636 and continues to the present time. American higher education is known throughout the world for its dramatic expansion. It was also heavily influenced by British models in the colonial era, and German models in the 19th century. The American model includes private schools, mostly founded by religious denominations, as well as universities run by state governments, and a few military academies that are run by the national government.

Pennsylvania Western University (PennWest) is a public university in Pennsylvania, United States. It has three campuses in the Pennsylvanian boroughs of California, Clarion, and Edinboro.
References
- ↑ Cope, Gilbert; Ashmead, Henry Graham (1904). Historic Homes and Institutions, and Genealogical and Personal Memoirs of Chester and Delaware Counties, Pennsylvania. New York: Lewis Publishing Company. pp. 107–110.
- Sack, Saul (1963). History of higher education in Pennsylvania. Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. pp. 168–171. hdl:2027/mdp.39015014825221.