
An ion thruster or ion drive is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. It creates thrust by accelerating cations by utilizing electricity. The term refers strictly to gridded electrostatic ion thrusters, and is often incorrectly loosely applied to all electric propulsion systems including electromagnetic plasma thrusters.

A magnetoplasmadynamic (MPD) thruster (MPDT) is a form of electrically powered spacecraft propulsion which uses the Lorentz force to generate thrust. It is sometimes referred to as Lorentz Force Accelerator (LFA) or MPD arcjet.
The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) is a research organization at the University of Colorado Boulder. LASP is a research institute with over one hundred research scientists ranging in fields from solar influences, to Earth's and other planetary atmospherics processes, space weather, space plasma and dusty plasma physics. LASP has advanced technical capabilities specializing in designing, building, and operating spacecraft and spacecraft instruments.

The mesosphere is the layer of the Earth's atmosphere that is directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as the altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define its limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere, and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere with temperatures below −143 °C. The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season, but the lower boundary is usually located at heights from 50 to 65 kilometres above the Earth's surface and the upper boundary (mesopause) is usually around 85 to 100 kilometres.
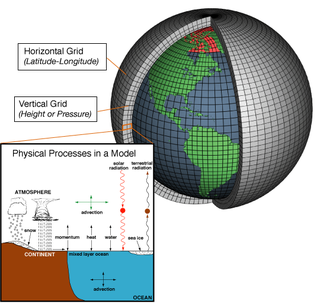
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources. These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components.

Robert Hutchings Goddard was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket. Goddard successfully launched his model on March 16, 1926, ushering in an era of space flight and innovation. He and his team launched 34 rockets between 1926 and 1941, achieving altitudes as high as 2.6 km (1.6 mi) and speeds as fast as 885 km/h (550 mph).

A sounding rocket, sometimes called a research rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to carry instruments from 30 to 90 miles above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about 25 mi (40 km) and the minimum for satellites is approximately 75 mi (121 km). Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 620 and 930 miles, such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion, lifting 600–1,000-pound (270–450 kg) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 60 and 125 miles.

The R-1 rocket was a Tactical ballistic missile manufactured in the Soviet Union based on the German V-2 rocket. Even though it was a copy, it was manufactured using Soviet industrial plants and gave the Soviets valuable experience which later enabled the USSR to construct its own much more capable rockets.

The Aerojet General X-8 was an unguided, spin-stabilized sounding rocket designed to launch a 150 lb (68 kg) payload to 200,000 feet (61.0 km). The X-8 was a version of the prolific Aerobee rocket family.

The Van Allen Probes, formerly known as the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, are two robotic spacecraft being used to study the Van Allen radiation belts that surround Earth. NASA is conducting the Van Allen Probes mission as part of the Living With a Star program. Understanding the radiation belt environment and its variability has important practical applications in the areas of spacecraft operations, spacecraft system design, mission planning and astronaut safety. The probes were launched on 30 August 2012.

This is a list of known spaceflights launched before 1951.

The Hermes project was started in response to Germany's rocket attacks in Europe. Project Hermes was to determine the missile needs of army field forces. "Accordingly the Ordnance Department entered into a research and development contract with the General Electric Company on 20 November 1944. "This contract authorized the General Electric Company to seek the development of long-range missiles that could be used against both ground targets and high-altitude aircraft. The contractor agreed to perform investigations, research, experiments, design, development, and engineering work in connection with the development of long-range missiles for use against ground targets and high-altitude aircraft." General Electric was also to investigate ramjets, solid rocket motors, liquid propellant rocket engines, and hybrid propellants. "The contract also required the General Electric Company to develop remote control equipment, ground equipment, fire control devices, and homing devices."
William Gould Dow was an American scientist, educator and inventor. He was a pioneer in a variety of fields, including electrical engineering, space research, computer engineering, and nuclear engineering. He helped develop life-saving radar jamming technology during World War II, and was a long-time professor at the University of Michigan.

The Advanced Research and Global Observation Satellite (ARGOS), not to be confused with the Argos System which employs mostly NOAA satellites, was launched on 23 Feb 1999 carrying nine payloads for research and development missions by nine separate researchers. The mission terminated on 31 July 2003.

German V-2 rockets captured by the United States Army at the end of World War II were used as sounding rockets to carry scientific instruments into the earth's upper atmosphere at White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) for a program of atmospheric and solar investigation through the late 1940s. Rocket trajectory was intended to carry the rocket about 100 miles (160 km) high and 30 miles (48 km) horizontally from WSMR Launch Complex 33. Impact velocity of returning rockets was reduced by inducing structural failure of the rocket airframe upon atmospheric re-entry. More durable recordings and instruments might be recovered from the rockets after ground impact, but telemetry was developed to transmit and record instrument readings during flight.

Robert Eugene Bourdeau was an American physicist known for major contributions to the study of the ionosphere, plasma physics and radio science using space vehicles including satellites and rockets. Among his many achievements was the launch on November 3, 1960 of Explorer 8 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. This occurred during his 16-year career at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). He was both Project Manager and Project Scientist for Explorer 8 which added significant knowledge to the understanding of these fields.




















