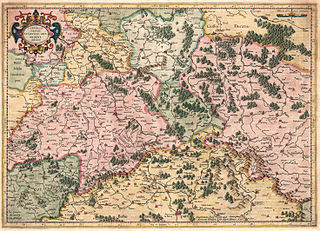
Upper Saxony (German : Obersachsen) was the name given to the majority of the German lands held by the House of Wettin, in what is now called Central Germany (Mitteldeutschland).

Upper Saxony (German : Obersachsen) was the name given to the majority of the German lands held by the House of Wettin, in what is now called Central Germany (Mitteldeutschland).
The name derives from the period when, after the fall of Duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the medieval Duchy of Saxony dissolved and the Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg lands passed to the House of Ascania and later to the Wettins in the Margraviate of Meissen. These dynasties subdued the areas east of the Saale river inhabited by Polabian Slavs, and took the tribal name Sachsen (Saxons) upstream the Elbe with them.
It was particularly to distinguish the lands from 'Lower Saxony', a concept which arose later in popular usage (though never enforced) as a term for the original Saxon lands in north and west Germany (where Low German dialects had spread), in what is now the state of Lower Saxony, as well as the adjacent Westphalian region, Holstein and the western part of today's Saxony-Anhalt north of the Harz range (Eastphalia).
According to the Golden Bull of 1356, the Saxe–Wittenberg lands up the Elbe formed an Electorate, which in 1423 merged with Meissen under the Wettin dynasty and headed the Upper Saxon Circle. The Wettins acquired the Lusatia region by the 1635 Peace of Prague and finally were elevated to Kings of Saxony in 1806. Thus the citizens of the present-day German state of Saxony today are simply known as Saxons. This is true of the media, though the East Central German dialects of Upper Saxon (Meißenisch and Osterländisch) are placed in the Thuringian-Upper Saxon continuum.
The House of Ascania was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.

Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of 18,413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants.

The history of Saxony-Anhalt began with Old Saxony, which was conquered by Charlemagne in 804 and transformed into the Duchy of Saxony within the Carolingian Empire. Saxony went on to become one of the so-called stem duchies of the German Kingdom and subsequently the Holy Roman Empire which formed out of the eastern partition of the Carolingian Empire. The duchy grew to become a powerful state within the empire, ruling over much of what is now northern Germany, but following conflicts with the emperor it was partitioned into numerous minor states, including the Principality of Anhalt, around the end of the 12th century and early 13th century. The territories of the Duchy of Saxony, the Principality of Anhalt, and their successors are now part of the modern German state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Duchy of Saxony was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 AD and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected German king in 919.

The House of Wettin was a dynasty which included Saxon kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany.

Eastphalia is a historical region in northern Germany, encompassing the eastern Gaue (shires) of the historic stem duchy of Saxony, roughly confined by the River Leine in the west and the Elbe and Saale in the east. The territory corresponds with modern southeastern Lower Saxony, western Saxony-Anhalt, and northern Thuringia. Together with Westphalia, central Angria, and Nordalbingia, it was one of the four main Saxon administrative regions.

Lower Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the south, Lower Lusatia is a settlement area of the West Slavic Sorbs whose endangered Lower Sorbian language is related to Upper Sorbian and Polish.

The Margravate or Margraviate of Meissen was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast Marca Geronis in 965. Under the rule of the Wettin dynasty, the margravate finally merged with the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg into the Saxon Electorate by 1423.

The Ernestine duchies, also known as the Saxon duchies, were a group of small states whose number varied, which were largely located in the present-day German state of Thuringia and governed by dukes of the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin.
The history of Saxony began with a small tribe living on the North Sea between the Elbe and Eider River in what is now Holstein. The name of this tribe, the Saxons, was first mentioned by the Greek author Ptolemy. The name Saxons is derived from the Seax, a knife used by the tribe as a weapon.

Landsberg is a town in the Saalekreis in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany

The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony, was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356 to 1806 initially centred on Wittenberg that came to include areas around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. It was a major Holy Roman state, being an electorate and the original protecting power of Protestant principalities until that role was later taken by its neighbor, Brandenburg-Prussia.

The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. The Ascanian dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity until their duchy was finally elevated to the Electorate of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356.

The Treaty of Leipzig or Partition of Leipzig was signed on 11 November 1485 between Elector Ernest of Saxony and his younger brother Albert III, the sons of Elector Frederick II of Saxony from the House of Wettin. The agreement perpetuated the division of the Wettin lands into a Saxon and a Thuringian part, which in the long run obstructed the further development of a Central German hegemonic power in favour of Brandenburg-Prussia.

The Saxon Eastern March was a march of the Holy Roman Empire from the 10th until the 12th century. The term "eastern march" stems from the Latin term marchia Orientalis and originally could refer to either a march created on the eastern frontier of the East Frankish duchy of Saxony or another on the eastern border of the Duchy of Bavaria: the Bavarian marchia Orientalis, corresponding to later Austria.
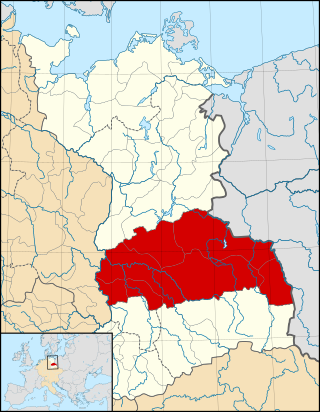
The March or Margraviate of Lusatia was an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast Marca Geronis. Ruled by several Saxon margravial dynasties, among them the House of Wettin, the lordship was contested by the Polish kings as well as by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg. The remaining territory was finally incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown in 1367.

Bernhard, a member of the House of Ascania, was Count of Anhalt and Ballenstedt, and Lord of Bernburg through his paternal inheritance. From 1180 he was also Duke of Saxony.

The Division of Altenburg was the plan for the division of the Meissen lands agreed upon by the two hostile Wettin brothers Elector Frederick II of Saxony and William III on 16 July 1445 at Altenburg. The brothers had attempted to reconcile, but eventually the division led the Saxon Fratricidal War, which began in 1446 and lasted for five years, until the Peace of Naumburg was negotiated in 1451. Following the peace, the subsequent Treaty of Eger in 1459, and the deaths of Frederick II and William III, the two sons of Frederick II eventually gained control of the land of both their father and William III.