| Urech hydantoin synthesis | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Friedrich Urech |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
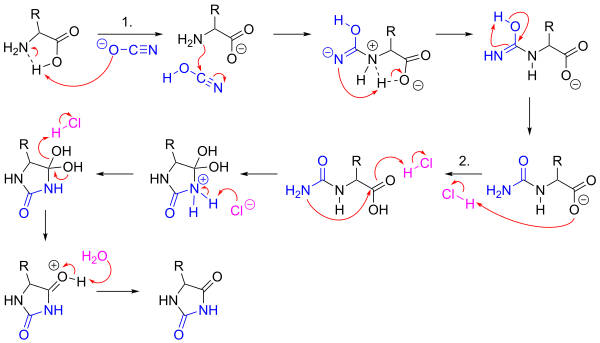
The Urech hydantoin synthesis is the chemical reaction of amino acids with potassium cyanate and hydrochloric acid to give hydantoins. [1] [2]
Contents

| Urech hydantoin synthesis | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Friedrich Urech |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
The Urech hydantoin synthesis is the chemical reaction of amino acids with potassium cyanate and hydrochloric acid to give hydantoins. [1] [2]