
The Argentine Navy is the navy of Argentina. It is one of the three branches of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic, together with the Army and the Air Force.

Puerto Williams is the city, port and naval base on Navarino Island in Chile. It faces the Beagle Channel. It is the capital of the Chilean Antarctic Province, one of four provinces in the Magellan and Chilean Antarctica Region, and administers the communes of Chilean Antarctic Territory and Cabo de Hornos. It has a population of 2,874, including both naval personnel and civilians. Puerto Williams claims the title of world's southernmost city. The settlement was founded in 1953, and was first named Puerto Luisa. The town was later named after John Williams Wilson, a British man who founded Fuerte Bulnes, the first settlement in the Strait of Magellan. It has served primarily as a naval base for Chile. The Chilean Navy runs the Guardiamarina Zañartu Airport and hospital, as well as nearby meteorological stations. Since the late 20th century, the number of navy personnel has decreased in Puerto Williams and the civilian population has increased. In that period, tourism and support of scientific research have contributed to an increase in economic activity.

Base Orcadas is an Argentine scientific station in Antarctica, and the oldest of the stations in Antarctica still in operation. It is located on Laurie Island, one of the South Orkney Islands, at 4 meters (13 ft) above sea level and 170 meters (558 ft) from the coastline. Established by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition in 1903 and transferred to the Argentine government in 1904, the base has been permanently populated since, being one of six Argentine permanent bases in Argentina's claim to Antarctica, and the first permanently inhabited base in Antarctica.
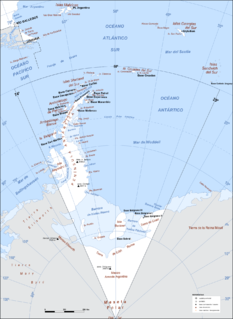
Argentine Antarctica is a sector of Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps the British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. Argentina's Antarctic claim is based on its continued presence in the region since 1904, and the area's proximity to the South American continent. Argentina's claim to this area is subject to the Antarctic Treaty. Administratively, Argentine Antarctica is a department of the province of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica, and South Atlantic Islands. The provincial authorities are based in Ushuaia. Despite the claim to this Antarctic area, Argentine authority extends no further than the nation's bases. The Argentine exploration of the continent started early in the 20th century. José María Sobral was the first Argentine to set foot on Antarctica, in 1902, where he spent two seasons with the Swedish Antarctic Expedition of Otto Nordenskiöld. Shortly afterward, in 1904, the Orcadas permanent base was already fully operational. Years later other bases would be created, some permanent and others seasonal. The first Argentine expedition to reach the South Pole was the 1965 Operación 90.

ARA Bahía Buen Suceso (B-6) was a Bahía Aguirre-class 5,000-ton fleet transport that served in the Argentine Navy from 1950 to 1982. She took part in the Falklands War as a logistics ship tasked with resupplying the Argentine garrisons scattered around the Falkland Islands. Captured by British forces on 15 June after running aground at Fox Bay, she sank in deep waters while being used as target practice by the Royal Navy on 21 October 1982.

Brown Station is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Admiral William Brown, the father of the Argentine Navy. It is located on Sanavirón Peninsula along Paradise Harbor, Danco Coast, in Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula.

ARA Patagonia (B-1) is a multi-product replenishment oiler of the Durance class in service in the Argentine Navy. She was the lead ship of her class serving in the French Navy as Durance from 1977 to 1999. In French service, the ship served with the Force d'action navale. In Argentine service the vessel is used in multi-national naval exercises and supplies the Antarctic missions operating from Ushuaia. In 2017, Patagonia was used to search for the missing submarine ARA San Juan.

Port Belgrano Naval Base is the largest naval base of the Argentine Navy, situated next to Punta Alta, near Bahía Blanca, about 560 km (348 mi) south of Buenos Aires. It is named after the brigantine General Belgrano which sounded the area in late 1824.

Naval Base Ventura County (NBVC) is a United States Navy base in Port Hueneme, California. NBVC is a diverse installation comprising three main facilities—Point Mugu, Port Hueneme and San Nicolas Island—and serving as an all-in-one mobilization site, deep water port, railhead, and airfield. Adjacent to Oxnard, the base was formed in 2000 through the merger of Naval Air Station Point Mugu and Naval Construction Battalion Center Port Hueneme. NBVC supports more than 100 tenant commands with a base population of more than 19,000 personnel, making it the largest employer in Ventura County.

The Nigerian Navy (NN) is a branch of the Nigerian Armed Forces. It is among the largest navies on the African continent, consisting of several thousand personnel, including those of the Coast Guard.

USS Luiseno (ATF-156) was an Abnaki-class fleet ocean tug built for the United States Navy during World War II. Named after the Luiseño peoples, she was the only U.S. Naval vessel to bear the name.

The Drummond class are three corvettes designed and built in France based on the A69 D'Estienne d'Orves-class avisos. The ships were commissioned in the Argentine Navy between 1978 and 1982.

The Instituto Antártico Argentino is the Argentine federal agency in charge of orientating, controlling, addressing and performing scientific and technical research and studies in the Antarctic.
ARA Comodoro Somellera (A-10) was a Sotoyomo-class rescue tug that served in the Argentine Navy from 1972 to 1998 classified as an aviso. She previously served in the US Navy as USS Catawba (ATA-210) from 1945 to 1972. After being damaged beyond repair in 1998, she was sunk on purpose as a weapons target in November 2017.

Ellsworth Scientific Station was a permanent, all year-round originally American, then Argentine Antarctic scientific research station named after American polar explorer Lincoln Ellsworth. It was located on Gould Bay, on the Filchner Ice Shelf.

ARA Suboficial Castillo (A-6) is an Abnaki-class tug/patrol boat of the Argentine Navy. She previously served in the US Navy as USS Takelma (ATF-113) from 1944 to 1992.

ARA Alférez Sobral (A-9) is an 800-ton ocean-going tug that was in service with the Argentine Navy from 1972 until 2019, where she was classified as an aviso. She had previously served in the US Navy as the fleet tug USS Salish (ATA-187). In Argentine service an aviso is a small naval vessel used for a number of auxiliary tasks, including tugging, laying buoys, and replenishing other ships, lighthouses and naval bases.

Melchior Base is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station. It is located on Gamma Island, Melchior Islands, Dallmann Bay, in Palmer Archipelago on Bellingshausen Sea, Antarctic Peninsula.

NOAAS Researcher, was an American oceanographic research vessel in commission in the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) from 1970 to 1996. She had been delivered to the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1970 as USC&GS Researcher, but did not enter commission until after her transfer to NOAA later that year. In 1988, Researcher was renamed NOAAS Malcolm Baldrige.

The Mar del Plata Naval Base is a Naval port facility of the Argentine Navy, situated in Mar del Plata in the province of Buenos Aires and home to the Argentine Submarine Fleet.




















