Related Research Articles

Henschel & Son was a German company, located in Kassel, best known during the 20th century as a maker of transportation equipment, including locomotives, trucks, buses and trolleybuses, and armoured fighting vehicles and weapons.

The Panzer II is the common name used for a family of German tanks used in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen II.

Panzerkampfwagen VIII Maus was a German World War II super-heavy tank completed in late 1944. It is the heaviest fully enclosed armored fighting vehicle ever built. Five were ordered, but only two hulls and one turret were completed, the turret being attached before the testing grounds were captured by advancing Soviet military forces. This vehicle was also built to compete with the Soviet heavy Kliment Voroshilov tank.

Nazi Germany developed numerous tank designs used in World War II. In addition to domestic designs, Germany also used various captured and foreign-built tanks.

The Daimler-Benz DB 603 was a German aircraft engine used during World War II. It was a liquid-cooled 12-cylinder inverted V12 enlargement of the 33.9 Liter DB 601, which was in itself a development of the DB 600. Production of the DB 603 commenced in May 1942, and with a 44.5 liter displacement figure, was the largest displacement inverted V12 aviation engine to be produced and used in front line aircraft of the Third Reich during World War II.

This article deals with the tanks serving in the German Army throughout history, such as the World War I tanks of the Imperial German Army, the interwar and World War II tanks of the Nazi German Wehrmacht, the Cold War tanks of the West German and East German Armies, all the way to the present day tanks of the Bundeswehr.

The Tiger I was a German heavy tank of World War II that operated beginning in 1942 in Africa and in the Soviet Union, usually in independent heavy tank battalions. It gave the German Army its first armoured fighting vehicle that mounted the 8.8 cm KwK 36 gun. 1,347 were built between August 1942 and August 1944. After August 1944, production of the Tiger I was phased out in favour of the Tiger II.

The VK 30.01 (P) was the official designation for a heavy tank prototype proposed in Germany. Only two prototype chassis were built. The tank never entered serial production, but was further developed into the VK 45.01 Tiger (P). Porsche called it the Typ (Type) 100.

Prior to the invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II, the German armed forces were not aware of two newly developed Soviet tanks, the T-34 and the KV. As a result, they were surprised when they met them in combat for the first time in June 1941. The Germans' standard anti-tank weapons were found to be ineffective against these new Soviet vehicles. This experience prompted a notable leap in tank development in Nazi Germany, mainly in an effort to counter these new threats.
The VK 45.01 (P), also informally known as Tiger (P) or Porsche Tiger, was a gasoline-electric drive heavy tank prototype designed by Porsche in Germany. Losing to its Henschel competitor on trials, it was not selected for mass production and the Henschel design was produced as the Tiger I. Most of the already produced chassis were rebuilt as Elefant tank destroyers.
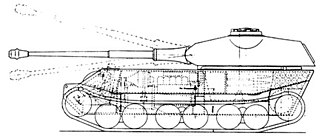
The VK 45.02 (P) was the official designation for an unsuccessful heavy tank project designed by Ferdinand Porsche in Nazi Germany during World War II to compete with Henschel's design.

The VK 20 series were the proposed replacements of the Panzer IV and Panzer III tanks with entries by MAN, Krupp and Daimler Benz. It was initially projected to weigh 20 tonnes, but grew to 24 tonnes. By November 1941, the designs almost reached completion but against the professional judgement of Wa Pruef 6, political interference in December 1941 led to all of the designs being dropped. The root of this adverse decision came from encounters with increasing numbers of T-34 and KV-1 tanks. Reichsminister Fritz Todt declared that a new tank, 30 tons in weight should be designed and produced. Oberst Fichtner argued that time would be lost developing this new 30 ton tank, the number produced would be reduced and engineer bridges could not support such a tank. This new tank chosen from the VK 30 series would become the Panther, replacing the VK 20 series. This decision would place the rushed MAN Panther into production as Germany's new standard medium tank, which was plagued with issues never fully addressed especially those caused by MAN's final drive. It would also arrive too late, with Germany's position in a steep decline, having lost the initiative.

The VK 36.01 (H) was an experimental German heavy tank, developed during World War II. The VK 36.01 H was further development of the VK 30.01 (H) experimental medium tank, and subsequently lead to the development of the VK 45.01 (H).

The VK 30.01 (D) and VK 30.02 (D), also known as VK.3001 (DB) were two tank designs made by Daimler Benz submitted for the VK 30 project for a 30 tonne tank to be used by the German army.

The VK 30.01 (H) is a German prototype heavy tank developed by Henschel in Germany during World War II. It was rejected for production likely due to being outdated by the time it was meant to be produced. The chassis from this project went on to form the chassis for the Sturer Emil self-propelled anti-tank gun project.
References
- ↑ Ellis & Chamberlain p.4
- ↑ Jentz, Thomas; Doyle, Hilary (1993). Tiger I Heavy Tank 1942-45. Osprey Publishing Ltd. pp 16–18. ISBN 1855323370.