
The Tiger II was a German heavy tank of the Second World War. The final official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen Tiger Ausf. B, often shortened to Tiger B. The ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 182.. It was also known informally as the Königstiger. Contemporaneous Allied soldiers usually called it the King Tiger or Royal Tiger.

The Panzer II is the common name used for a family of German tanks used in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen II.

The Panzerkampfwagen IV, commonly known as the Panzer IV, is a German medium tank developed in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 161.

Panzerkampfwagen VIII Maus was a German World War II super-heavy tank completed in late 1944. It is the heaviest fully enclosed armored fighting vehicle ever built. Five were ordered, but only two hulls and one turret were completed, the turret being attached before the testing grounds were captured by advancing Soviet military forces. This vehicle was also built to compete with the Soviet heavy Kliment Voroshilov tank.

Elefant was a heavy tank destroyer used by German Panzerjäger during World War II. Ninety-one units were built in 1943 under the name Ferdinand using VK 45.01 (P) tank hulls which had been produced for the Tiger I tank before the competing Henschel design had been selected.

Nazi Germany developed numerous tank designs used in World War II. In addition to domestic designs, Germany also used various captured and foreign-built tanks.

The Entwicklung series, more commonly known as the E-Series, was a late-World War II attempt by Nazi Germany to produce a standardised series of tank designs. There were to be standard designs in five different weight classes from which several specialised variants were to be developed. This intended to reverse the favor of extremely complex tank designs that had resulted in poor production rates and mechanical unreliability.

The Bergepanzerwagen V, often referred to as the "Bergepanther", was an armoured recovery vehicle used by the German Army in WWII. It was a variant of the Panzerkampfwagen V Panther.

The Tiger I was a German heavy tank of World War II that operated beginning in 1942 in Africa and in the Soviet Union, usually in independent heavy tank battalions. It gave the German Army its first armoured fighting vehicle that mounted the 8.8 cm KwK 36 gun. 1,347 were built between August 1942 and August 1944. After August 1944, production of the Tiger I was phased out in favour of the Tiger II.
The VK 45.01 (P), also informally known as Tiger (P) or Porsche Tiger, was a gasoline-electric drive heavy tank prototype designed by Porsche in Germany. Losing to its Henschel competitor on trials, it was not selected for mass production and the Henschel design was produced as the Tiger I. Most of the already produced chassis were rebuilt as Elefant tank destroyers.
Grosstraktor was the codename given to six prototype medium tanks built by Rheinmetall-Borsig, Krupp, and Daimler-Benz, for the Weimar Republic, in violation of the Treaty of Versailles. Constructed in secret, they were tested by Reichswehr units at the Kama tank school in the Soviet Union. They were used for training and retired as monuments after the Nazi party came to power.
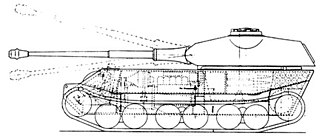
The VK 45.02 (P) was the official designation for an unsuccessful heavy tank project designed by Ferdinand Porsche in Nazi Germany during World War II to compete with Henschel's design.

The VK 20 series were the proposed replacements of the Panzer IV and Panzer III tanks with entries by MAN, Krupp and Daimler Benz. It was initially projected to weigh 20 tonnes, but grew to 24 tonnes. By November 1941, the designs almost reached completion but against the professional judgement of Wa Pruef 6, political interference in December 1941 led to all of the designs being dropped. The root of this adverse decision came from encounters with increasing numbers of T-34 and KV-1 tanks. Reichsminister Fritz Todt declared that a new tank, 30 tons in weight should be designed and produced. Oberst Fichtner argued that time would be lost developing this new 30 ton tank, the number produced would be reduced and engineer bridges could not support such a tank. This new tank chosen from the VK 30 series would become the Panther, replacing the VK 20 series. This decision would place the rushed MAN Panther into production as Germany's new standard medium tank, which was plagued with issues never fully addressed especially those caused by MAN's final drive. It would also arrive too late, with Germany's position in a steep decline, having lost the initiative.
The Versuchskonstruktion 30 were two series of tank designs by Germany in World War II, originally intended as heavy 'breakthrough' tanks, but later switching completely to designate medium tanks to succeed the Panzer III, IV, and the planned VK 20 series tanks. These were requested in response to the Soviet T-34 and KV-1 tanks, with far heavier armour and armament than the mobile armoured vehicles fielded by the Wehrmacht at the time. Many German companies submitted projects, including Maschinenfabrik Augsburg-Nürnberg (MAN), Daimler-Benz (DB), Henschel, and Porsche. The winning entry tanks would go on to become the famous Tiger I and Panther tanks, capable opponents to the T-34, but it was ultimately too late and at too small of a scale to affect the course of the war.

The Schmalturm was a tank turret designed for use on the Panther Ausf. F medium tank. There was a Krupp proposal to fit it onto the Panzer IV medium tank as well. It featured a narrow front to maximize protection while minimizing weight. It was both lighter and easier to manufacture than the standard Panther turret. The turret had a stereoscopic rangefinder with lenses on either side of the turret, located in spherical bulges. No Schmalturms entered series production.

The VK 30.01 (D) and VK 30.02 (D), also known as VK.3001 (DB) were two tank designs made by Daimler Benz submitted for the VK 30 project for a 30 tonne tank to be used by the German army.

The VK 30.01 (H) is a German prototype heavy tank developed by Henschel in Germany during World War II. It was rejected for production likely due to being outdated by the time it was meant to be produced. The chassis from this project went on to form the chassis for the Sturer Emil self-propelled anti-tank gun project.

The Panzerkampfwagen II Ausf. L "Luchs" is a German light tank from the Second World War, developed between 1940 and 1942 by Daimler-Benz and MAN. The Luchs was the only Panzer II design with the Schachtellaufwerk overlapping/interleaved road wheels and "slack track" configuration to enter series production, with 100 being built from September 1943 to January 1944 in addition to the conversion of the four Ausf. M tanks. Originally given the experimental designation VK 13.03, it was adopted under the alternate name Panzerspähwagen II and given the popular name Luchs. The Luchs was larger than the Panzer II Ausf. G in most dimensions. With a six speed transmission, it could reach a speed of 60 km/h (37 mph) with a range of 260 km (160 mi). The FuG 12 and FuG Spr radios were installed, while 330 rounds of 20 mm and 2,250 rounds of 7.92 mm ammunition were carried.
















