
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains are a mountain range consisting of parallel smaller chains extending c. 1,200 km (750 mi) along the length of peninsular Italy. In the northwest they join with the Ligurian Alps at Altare. In the southwest they end at Reggio di Calabria, the coastal city at the tip of the peninsula. Since 2000 the Environment Ministry of Italy, following the recommendations of the Apennines Park of Europe Project, has been defining the Apennines System to include the mountains of north Sicily, for a total distance of 1,500 kilometres (930 mi). The system forms an arc enclosing the east side of the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian seas.
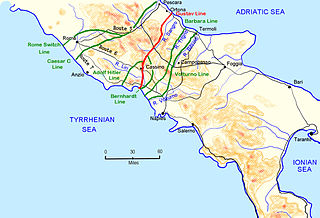
The Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section of Italy, focused around the town of Monte Cassino, through which ran the important Highway 6 which led uninterrupted to Rome. The primary Gustav Line ran across Italy from just north of where the Garigliano River flows into the Tyrrhenian Sea in the west, through the Apennine Mountains to the mouth of the Sangro River on the Adriatic coast in the east. The two subsidiary lines, the Bernhardt Line and the Hitler Line, ran much shorter distances from the Tyrrehnian Sea to just northeast of Cassino where they would merge into the Gustav Line. Relative to the Gustav Line, the Hitler Line stood to the northwest and the Bernhardt Line to the southeast of the primary defenses.
The Garfagnana is a historical and geographical region of central Italy, today part of the province of Lucca, in Tuscany. It is the upper valley or basin of the river Serchio, and thus lies between the main ridge of the Northern Apennines to the north-east and the Alpi Apuane to the west. The principal towns are Castelnuovo di Garfagnana and Barga.

The Liri is one of the principal rivers of central Italy, flowing into the Tyrrhenian Sea a little below Minturno under the name Garigliano.

The province of Caserta is a province in the Campania region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Caserta, situated about 36 kilometres (22 mi) by road north of Naples. The province has an area of 2,651.35 square kilometres (1,023.69 sq mi), and had a total population of 924,414 in 2016. The Palace of Caserta is located near to the city, a former royal residence which was constructed for the Bourbon kings of Naples. It was the largest palace and one of the largest buildings erected in Europe during the 18th century. In 1997, the palace was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The province of Frosinone is a province in the Lazio region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Frosinone. It has an area of 3,247 square kilometres (1,254 sq mi) and a total population of 493,605 (2016). The province contains 91 comuni, listed in the comuni of the province of Frosinone.

The Via Valeria was an ancient Roman road of Italy, the continuation north-eastwards of the Via Tiburtina from Tibur. It probably owed its origin to Marcus Valerius Messalla, censor in 154 BC.

Latium adiectum or Latium Novum was a region of Roman Italy between Monte Circeo and the river Garigliano, south of and immediately adjacent to Old Latium, hence its name of attached Latium.

Veroli is a town and comune in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, central Italy, in the Latin Valley.

Roccasecca is a town and comune in the Province of Frosinone, in the Lazio region of central Italy. It is the birthplace of Thomas Aquinas.

Canistro is a comune (municipality) and town in the province of L'Aquila in the Abruzzo region of central Italy.

Civitella Roveto is a comune and town in the province of L'Aquila in the Abruzzo region of central Italy.

San Vincenzo Valle Roveto is a comune and town in the province of L'Aquila in the Abruzzo region of Italy.

The Fucine Lake was a large endorheic karst lake between 650 and 680 m above sea level and surrounded by the Monte Sirente-Monte Velino mountain ranges to the north-northeast, Mount Salviano to the west, Vallelonga to the south, and the Valle del Giovenco to the east-southeast. Located in western Abruzzo in central Italy, the town of Avezzano lies to the northwest, Ortucchio to the southeast, and Trasacco to the southwest of the historic lake. Once the third largest lake in Italy after Lake Garda and Lake Maggiore, it was finally drained in 1878.

The Monti Ernici are a mountain range in central Italy, part of the sub-Apennines of Lazio. They are bounded by the valley of the river Aniene to the north-east, that of the Liri to the east, and, from south to west, by the valleys of the Cosa and Sacco. They are the natural border between two central Italian regions, Lazio and Abruzzo.

The Sacco is a river of central Italy, a right tributary of the Liri. It flows between the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital and the province of Frosinone in Lazio.

Valle Latina is an Italian geographical and historical region that extends from the south of Rome to Cassino, corresponding to the eastern area of ancient Roman Latium.

Monte Terminillo is a massif in the Monti Reatini, part of the Abruzzi Apennine range in central Italy. It is located some 20 km from Rieti and 100 km from Rome and has a highest altitude of 2,217 metres (7,274 ft).

The Valle del Liri is a valley and a geographical region of southern Lazio and part of the larger Latin Valley, located in the province of Frosinone, crossed by the Liri river. The main urban center of the area is Sora.


















