Related Research Articles

Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Aquaculture is also a practice used for restoring and rehabilitating marine and freshwater ecosystems. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, is aquaculture in seawater habitats and lagoons, as opposed to freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food.

Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root brak. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment.

Fish farming or pisciculture involves commercial breeding of fish, most often for food, in fish tanks or artificial enclosures such as fish ponds. It is a particular type of aquaculture, which is the controlled cultivation and harvesting of aquatic animals such as fish, crustaceans, molluscs and so on, in natural or pseudo-natural environments. A facility that releases juvenile fish into the wild for recreational fishing or to supplement a species' natural numbers is generally referred to as a fish hatchery. Worldwide, the most important fish species produced in fish farming are carp, catfish, salmon and tilapia.

The European eel is a species of eel. They are critically endangered due to overfishing by fisheries on coasts for human consumption and parasites.
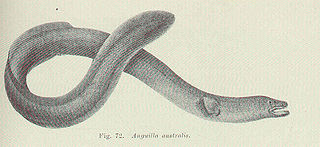
The short-finned eel, also known as the shortfin eel, is one of the 15 species of eel in the family Anguillidae. It is native to the lakes, dams and coastal rivers of south-eastern Australia, New Zealand, and much of the South Pacific, including New Caledonia, Norfolk Island, Lord Howe Island, Tahiti, and Fiji.

A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention, also known as "The Convention on Wetlands", an international environmental treaty signed on 2 February 1971 in Ramsar, Iran, under the auspices of UNESCO. It came into force on 21 December 1975, when it was ratified by a sufficient number of nations. It provides for national action and international cooperation regarding the conservation of wetlands, and wise sustainable use of their resources. Ramsar identifies wetlands of international importance, especially those providing waterfowl habitat.
Oyster farming is an aquaculture practice in which oysters are bred and raised mainly for their pearls, shells and inner organ tissue, which is eaten. Oyster farming was practiced by the ancient Romans as early as the 1st century BC on the Italian peninsula and later in Britain for export to Rome. The French oyster industry has relied on aquacultured oysters since the late 18th century.

The European seabass, also known as the European bass, sea bass, common bass, white bass, capemouth, white salmon, sea perch, white mullet, sea dace or Loup de Mer, is a primarily ocean-going fish native to the waters off Europe's western and southern and Africa's northern coasts, though it can also be found in shallow coastal waters and river mouths during the summer months and late autumn. It is one of only six species in its family, Moronidae, collectively called the temperate basses.

The Lessepsian migration is the migration of marine species along the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other marine animals and plants were exposed to an artificial passage between the two naturally separate bodies of water, and cross-contamination was made possible between formerly isolated ecosystems. The phenomenon is still occurring today. It is named after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat in charge of the canal's construction.

Integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) provides the byproducts, including waste, from one aquatic species as inputs for another. Farmers combine fed aquaculture with inorganic extractive and organic extractive aquaculture to create balanced systems for environment remediation (biomitigation), economic stability and social acceptability.

The Missolonghi-Aitoliko lagoons complex is located in the north part of the Gulf of Patras in the central west coast of Greece. It is one of the most important Mediterranean lagoons. It is a shallow area of 150 km2, extended between the Acheloos and Evinos rivers. It is protected by the Ramsar Convention and it is also included in the Natura 2000 network.

The European anchovy is a forage fish somewhat related to the herring. It is a type of anchovy; anchovies are placed in the family Engraulidae. It lives off the coasts of Europe and Africa, including in the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and the Sea of Azov. It is fished by humans throughout much of its range.
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, and Slovenia.
Sea sponge aquaculture is the process of farming sea sponges under controlled conditions. It has been conducted in the world's oceans for centuries using a number of aquaculture techniques. There are many factors such as light, salinity, pH, dissolved oxygen and the accumulation of waste products that influence the growth rate of sponges. The benefits of sea sponge aquaculture are realised as a result of its ease of establishment, minimum infrastructure requirements and the potential to be used as a source of income for populations living in developing countries. Sea sponges are produced on a commercial scale to be used as bath sponges or to extract biologically active compounds which are found in certain sponge species. Techniques such as the rope and mesh bag method are used to culture sponges independently or within an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system setting. One of the only true sustainable sea sponges cultivated in the world occur in the region of Micronesia, with a number of growing and production methods used to ensure and maintain the continued sustainability of these farmed species.

Paracentrotus lividus is a species of sea urchin in the family Parechinidae commonly known as the purple sea urchin. It is the type species of the genus and occurs in the Mediterranean Sea and eastern Atlantic Ocean.

Octopus aquaculture describes the captive-raising of octopuses and commercial sale of their meat. A complex and labor-intensive form of farming, octopus aquaculture is being driven by strong market demand in the Mediterranean and in South American and Asian countries. Annual global demand for octopus more than doubled from 1980 to 2019, from roughly 180,000 to about 370,000 tons. The supply of octopus has been constrained by overfishing in many key fisheries and proponents of farming suggest human-induced culturing could help restock natural populations. Opponents of the nascent industry argue that cephalopod intelligence and emotional capacity, as well as the solitary and carnivorous character of octopuses, make them particularly ill-suited to intensive, captive breeding. Commercial sale may stimulate market demand, hastening rather than offsetting the decline in wild stocks. An announcement that a Spanish firm would begin octopus aquaculture as early as 2022 prompted ethical and scientific controversy.
Saltwater aquaponics is a combination of plant cultivation and fish rearing, systems with similarities to standard aquaponics, except that it uses saltwater instead of the more commonly used freshwater. In some instances, this may be diluted saltwater. The concept is being researched as a sustainable way to eliminate the stresses that are put on local environments by conventional fish farming practices who expel wastewater into the coastal zones, all while creating complementary crops.
Amyloodinium ocellatum is a cosmopolitan ectoparasite dinoflagellate of numerous aquatic organisms living in brackish and seawater environments. The dinoflagellate is endemic in temperate and tropical areas, and is capable of successfully adapting to a variety of different environments and to a great number of hosts, having been identified in four phyla of aquatic organisms: Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca and Platyhelminthes. Moreover, it is the only dinoflagellate capable of infecting teleosts and elasmobranchs.
Tuna penning is a practice used in marine aquaculture, in which smaller tuna are caught off shore and moved back to large, in-water enclosures. The pens are typically located in the relatively shallow waters of sheltered areas, such as bays or coves. Tuna penning is primarily used for Atlantic Bluefin Tuna (ABT), a highly profitable stock for the global fish market. The tuna caught for penning are typically caught between May and July by purse-seine vessels, and then transported back to pens, where they are fattened until October–January before being frozen and shipped out. While in the pens, the tuna are fed primarily fresh fish, such as sardines, squid, and mackerel. In the past decade, tuna penning has become a large sector within the fish aquaculture industry, and takes place primarily in the Mediterranean. In 2010, ABT constituted 8% of global fish exports, the majority of which was shipped to Japan. Tuna penning is regulated by the International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT), and each farm is required to register both the number of tuna it has and the total capacity of the farm.
References
- ↑ Bunting, Stuart W. (2013-01-25). Principles of Sustainable Aquaculture: Promoting Social, Economic and Environmental Resilience. Routledge. pp. 98–102. ISBN 978-1-136-46250-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Ravagnan, G. "Technics Used for Intensive Rearing and Alimentation of Fish and Shellfish" (PDF). Mediterranean Regional Aquaculture Project– via Food and Agricultural Organization.
- ↑ Lumare, Febo. "Italian Valliculture and Its Future Development" (PDF). Institute for the Biological Exploitation of Lagoons National Research Council: 85–88.
- 1 2 3 Emiroglu, Dilek. "Fish Production and Marketing in the Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons" (PDF). New Medit.