Related Research Articles

Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.
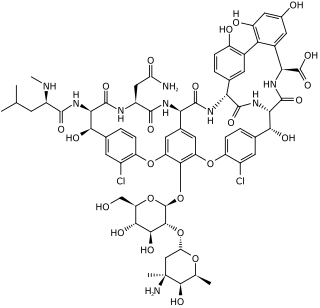
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is used intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose. Vancomycin is also taken orally as a treatment for severe Clostridium difficile colitis. When taken orally it is poorly absorbed.

Teicoplanin is an semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic with a spectrum of activity similar to vancomycin. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis. It is used in the prophylaxis and treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis.

Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) are strains of Staphylococcus aureus that have acquired resistance to the glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin. Bacteria can acquire resistant genes either by random mutation or through the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another. Resistance genes interfere with the normal antibiotic function and allow bacteria to grow in the presence of the antibiotic. Resistance in VRSA is conferred by the plasmid-mediated vanA gene and operon. Although VRSA infections are uncommon, VRSA is often resistant to other types of antibiotics and a potential threat to public health because treatment options are limited. VRSA is resistant to many of the standard drugs used to treat S. aureus infections. Furthermore, resistance can be transferred from one bacterium to another.
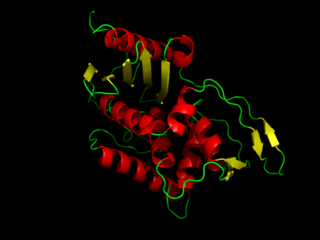
DD-transpeptidase is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the R-L-αα-D-alanyl moiety of R-L-αα-D-alanyl-D-alanine carbonyl donors to the γ-OH of their active-site serine and from this to a final acceptor. It is involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, namely, the transpeptidation that crosslinks the peptide side chains of peptidoglycan strands.

Glycopeptide antibiotics are a class of drugs of microbial origin that are composed of glycosylated cyclic or polycyclic nonribosomal peptides. Significant glycopeptide antibiotics include the anti-infective antibiotics vancomycin, teicoplanin, telavancin, ramoplanin and decaplanin, corbomycin, complestatin and the antitumor antibiotic bleomycin. Vancomycin is used if infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is suspected.

Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS. Infections can be localized or systemic, and are often associated with the insertion of medical devices. The highly antibiotic-resistant phenotype and ability to form biofilms make S. haemolyticus a difficult pathogen to treat. Its most closely related species is Staphylococcus borealis.

Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, or vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), are bacterial strains of the genus Enterococcus that are resistant to the antibiotic vancomycin.

Enterococcus faecalis – formerly classified as part of the group D Streptococcus system – is a Gram-positive, commensal bacterium inhabiting the gastrointestinal tracts of humans. Like other species in the genus Enterococcus, E. faecalis is found in healthy humans and can be used as a probiotic. The probiotic strains such as Symbioflor1 and EF-2001 are characterized by the lack of specific genes related to drug resistance and pathogenesis. As an opportunistic pathogen, E. faecalis can cause life-threatening infections, especially in the nosocomial (hospital) environment, where the naturally high levels of antibiotic resistance found in E. faecalis contribute to its pathogenicity. E. faecalis has been frequently found in reinfected, root canal-treated teeth in prevalence values ranging from 30% to 90% of the cases. Re-infected root canal-treated teeth are about nine times more likely to harbor E. faecalis than cases of primary infections.
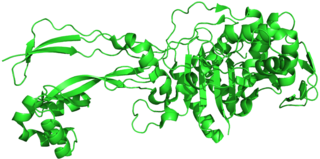
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) are a group of proteins that are characterized by their affinity for and binding of penicillin. They are a normal constituent of many bacteria; the name just reflects the way by which the protein was discovered. All β-lactam antibiotics bind to PBPs, which are essential for bacterial cell wall synthesis. PBPs are members of a subgroup of enzymes called transpeptidases. Specifically, PBPs are DD-transpeptidases.
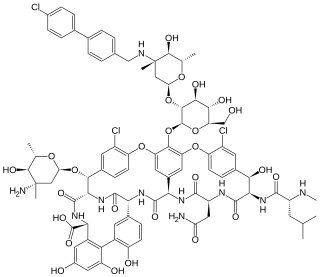
Oritavancin, sold under the brand name Orbactiv among others, is a semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic medication for the treatment of serious Gram-positive bacterial infections. Its chemical structure as a lipoglycopeptide is similar to vancomycin.

Lysins, also known as endolysins or murein hydrolases, are hydrolytic enzymes produced by bacteriophages in order to cleave the host's cell wall during the final stage of the lytic cycle. Lysins are highly evolved enzymes that are able to target one of the five bonds in peptidoglycan (murein), the main component of bacterial cell walls, which allows the release of progeny virions from the lysed cell. Cell-wall-containing Archaea are also lysed by specialized pseudomurein-cleaving lysins, while most archaeal viruses employ alternative mechanisms. Similarly, not all bacteriophages synthesize lysins: some small single-stranded DNA and RNA phages produce membrane proteins that activate the host's autolytic mechanisms such as autolysins.

Dalbavancin, sold under the brand names Dalvance in the US and Xydalba in the EU among others, is a second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic medication. It belongs to the same class as vancomycin, the most widely used and one of the treatments available to people infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Enterococcus gallinarum is a species of Enterococcus. E. gallinarum demonstrates an inherent, low-level resistance to vancomycin. Resistance is due to a chromosomal gene, vanC, which encodes for a terminal D-alanine-D-serine instead of the usual D-alanine-D-alanine in cell wall peptidoglycan precursor proteins. That is a separate mechanism than the vancomycin resistance seen in VRE isolates of E. faecium and E. faecalis which is mediated by vanA or vanB. This species is known to cause clusters of infection, although it considered very rare. It is the only other known enterococcal species besides E. faecium and E. faecalis known to cause outbreaks and spread in hospitals.

Enzybiotics are an experimental antibacterial therapy. The term is derived from a combination of the words “enzyme” and “antibiotics.” Enzymes have been extensively utilized for their antibacterial and antimicrobial properties. Proteolytic enzymes called endolysins have demonstrated particular effectiveness in combating a range of bacteria and are the basis for enzybiotic research. Endolysins are derived from bacteriophages and are highly efficient at lysing bacterial cells. Enzybiotics are being researched largely to address the issue of antibiotic resistance, which has allowed for the proliferation of drug-resistant pathogens posing great risk to animal and human health across the globe.
D-Ala-D-Ala dipeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-alanine—(R)-lactate ligase (EC 6.1.2.1, VanA, VanB, VanD) is an enzyme with systematic name D-alanine:(R)-lactate ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-Alanine—D-serine ligase is an enzyme with systematic name D-alanine:D-serine ligase (ADP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.

Lipid II is a precursor molecule in the synthesis of the cell wall of bacteria. It is a peptidoglycan, which is amphipathic and named for its bactoprenol hydrocarbon chain, which acts as a lipid anchor, embedding itself in the bacterial cell membrane. Lipid II must translocate across the cell membrane to deliver and incorporate its disaccharide-pentapeptide "building block" into the peptidoglycan mesh. Lipid II is the target of several antibiotics.
References
- ↑ Evers S, Courvalin P (March 1996). "Regulation of VanB-type vancomycin resistance gene expression by the VanS(B)-VanR (B) two-component regulatory system in Enterococcus faecalis V583". J. Bacteriol. 178 (5): 1302–9. doi:10.1128/jb.178.5.1302-1309.1996. PMC 177803 . PMID 8631706.
- ↑ Arthur M, Molinas C, Courvalin P (October 1992). "Sequence of the vanY gene required for production of a vancomycin-inducible D,D-carboxypeptidase in Enterococcus faecium BM4147". Gene. 120 (1): 111–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90017-j. PMID 1398115.