In computer programming, a reference is a value that enables a program to indirectly access a particular data, such as a variable's value or a record, in the computer's memory or in some other storage device. The reference is said to refer to the datum, and accessing the datum is called dereferencing the reference. A reference is distinct from the datum itself.
The syntax of the C programming language is the set of rules governing writing of software in the C language. It is designed to allow for programs that are extremely terse, have a close relationship with the resulting object code, and yet provide relatively high-level data abstraction. C was the first widely successful high-level language for portable operating-system development.
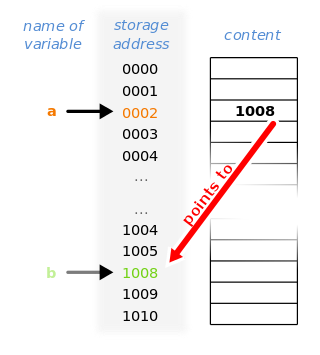
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer references a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as dereferencing the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture.
This article compares two programming languages: C# with Java. While the focus of this article is mainly the languages and their features, such a comparison will necessarily also consider some features of platforms and libraries. For a more detailed comparison of the platforms, see Comparison of the Java and .NET platforms.
In class-based, object-oriented programming, a constructor is a special type of subroutine called to create an object. It prepares the new object for use, often accepting arguments that the constructor uses to set required member variables.
A struct in the C programming language is a composite data type declaration that defines a physically grouped list of variables under one name in a block of memory, allowing the different variables to be accessed via a single pointer or by the struct declared name which returns the same address. The struct data type can contain other data types so is used for mixed-data-type records such as a hard-drive directory entry, or other mixed-type records.
The syntax of Java refers to the set of rules defining how a Java program is written and interpreted.
In computing, an uninitialized variable is a variable that is declared but is not set to a definite known value before it is used. It will have some value, but not a predictable one. As such, it is a programming error and a common source of bugs in software.
In some programming languages, const is a type qualifier that indicates that the data is read-only. While this can be used to declare constants, const in the C family of languages differs from similar constructs in other languages in being part of the type, and thus has complicated behavior when combined with pointers, references, composite data types, and type-checking. In other languages, the data is not in a single memory location, but copied at compile time on each use. Languages which utilize it include C, C++, D, JavaScript, Julia, and Rust.
C++/CLI is a variant of the C++ programming language, modified for Common Language Infrastructure. It has been part of Visual Studio 2005 and later, and provides interoperability with other .NET languages such as C#. Microsoft created C++/CLI to supersede Managed Extensions for C++. In December 2005, Ecma International published C++/CLI specifications as the ECMA-372 standard.
In a programming language, an evaluation strategy is a set of rules for evaluating expressions. The term is often used to refer to the more specific notion of a parameter-passing strategy that defines the kind of value that is passed to the function for each parameter and whether to evaluate the parameters of a function call, and if so in what order. The notion of reduction strategy is distinct, although some authors conflate the two terms and the definition of each term is not widely agreed upon.
C# and Visual Basic .NET are the two primary languages used to program on the .NET Framework.
Nullable types are a feature of some programming languages which allow a value to be set to the special value NULL instead of the usual possible values of the data type. In statically typed languages, a nullable type is an option type, while in dynamically typed languages, equivalent behavior is provided by having a single null value.
This is an overview of Fortran 95 language features. Included are the additional features of TR-15581:Enhanced Data Type Facilities, which have been universally implemented. Old features that have been superseded by new ones are not described – few of those historic features are used in modern programs although most have been retained in the language to maintain backward compatibility. The current standard is Fortran 2018; many of its new features are still being implemented in compilers. The additional features of Fortran 2003, Fortran 2008 and Fortran 2018 are described by Metcalf, Reid and Cohen.
The null coalescing operator is a binary operator that is part of the syntax for a basic conditional expression in several programming languages, including C#, PowerShell as of version 7.0.0, Perl as of version 5.10, Swift, and PHP 7.0.0. While its behavior differs between implementations, the null coalescing operator generally returns the result of its left-most operand if it exists and is not null, and otherwise returns the right-most operand. This behavior allows a default value to be defined for cases where a more specific value is not available.
Protel stands for "Procedure Oriented Type Enforcing Language". It is a programming language created by Nortel Networks and used on telecommunications switching systems such as the DMS-100. Protel-2 is the object-oriented version of Protel.
This article describes the syntax of the C# programming language. The features described are compatible with .NET Framework and Mono.
This comparison of programming languages compares how object-oriented programming languages such as C++, Java, Smalltalk, Object Pascal, Perl, Python, and others manipulate data structures.
In computer programming, a constant is a value that should not be altered by the program during normal execution, i.e., the value is constant. When associated with an identifier, a constant is said to be "named," although the terms "constant" and "named constant" are often used interchangeably. This is contrasted with a variable, which is an identifier with a value that can be changed during normal execution, i.e., the value is variable.
The Is functions are a set of functions in Microsoft's Visual Basic 6, Visual Basic for Applications, VBScript, and Visual Basic .NET. Several of them are also provided in Transact-SQL by the .NET Framework Data Provider for Microsoft SQL Server.

