Related Research Articles
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and an end in obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science.

Fan-Rong King Chung Graham, known professionally as Fan Chung, is an American mathematician who works mainly in the areas of spectral graph theory, extremal graph theory and random graphs, in particular in generalizing the Erdős–Rényi model for graphs with general degree distribution.

Béla Bollobás FRS is a Hungarian-born British mathematician who has worked in various areas of mathematics, including functional analysis, combinatorics, graph theory, and percolation. He was strongly influenced by Paul Erdős since the age of 14.

Raj Chandra Bose (or Basu) (19 June 1901 – 31 October 1987) was an Indian American mathematician and statistician best known for his work in design theory, finite geometry and the theory of error-correcting codes in which the class of BCH codes is partly named after him. He also invented the notions of partial geometry, association scheme, and strongly regular graph and started a systematic study of difference sets to construct symmetric block designs. He was notable for his work along with S. S. Shrikhande and E. T. Parker in their disproof of the famous conjecture made by Leonhard Euler dated 1782 that for no n do there exist two mutually orthogonal Latin squares of order 4n + 2.
Combinatorial design theory is the part of combinatorial mathematics that deals with the existence, construction and properties of systems of finite sets whose arrangements satisfy generalized concepts of balance and/or symmetry. These concepts are not made precise so that a wide range of objects can be thought of as being under the same umbrella. At times this might involve the numerical sizes of set intersections as in block designs, while at other times it could involve the spatial arrangement of entries in an array as in sudoku grids.

In graph theory, a rook's graph is an undirected graph that represents all legal moves of the rook chess piece on a chessboard. Each vertex of a rook's graph represents a square on a chessboard, and there is an edge between any two squares sharing a row (rank) or column (file), the squares that a rook can move between. These graphs can be constructed for chessboards of any rectangular shape. Although rook's graphs have only minor significance in chess lore, they are more important in the abstract mathematics of graphs through their alternative constructions: rook's graphs are the Cartesian product of two complete graphs, and are the line graphs of complete bipartite graphs. The square rook's graphs constitute the two-dimensional Hamming graphs.

In graph theory, a graceful labeling of a graph with m edges is a labeling of its vertices with some subset of the integers from 0 to m inclusive, such that no two vertices share a label, and each edge is uniquely identified by the absolute difference between its endpoints, such that this magnitude lies between 1 and m inclusive. A graph which admits a graceful labeling is called a graceful graph.
Sharadchandra Shankar Shrikhande was an Indian mathematician with notable achievements in combinatorial mathematics. He was notable for his breakthrough work along with R. C. Bose and E. T. Parker in their disproof of the famous conjecture made by Leonhard Euler dated 1782 that there do not exist two mutually orthogonal latin squares of order 4n + 2 for any n. Shrikhande's specialties were combinatorics and statistical designs. The Shrikhande graph is used in statistical design.

In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Shrikhande graph is a graph discovered by S. S. Shrikhande in 1959. It is a strongly regular graph with 16 vertices and 48 edges, with each vertex having degree 6. Every pair of nodes has exactly two other neighbors in common, whether or not the pair of nodes is connected.
Algebraic combinatorics is an area of mathematics that employs methods of abstract algebra, notably group theory and representation theory, in various combinatorial contexts and, conversely, applies combinatorial techniques to problems in algebra.
In graph theory, particularly in the theory of hypergraphs, the line graph of a hypergraphH, denoted L(H), is the graph whose vertex set is the set of the hyperedges of H, with two vertices adjacent in L(H) when their corresponding hyperedges have a nonempty intersection in H. In other words, L(H) is the intersection graph of a family of finite sets. It is a generalization of the line graph of a graph.
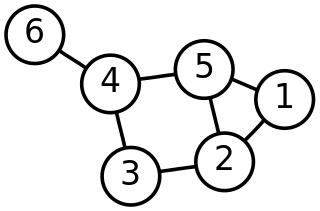
In graph theory, a discipline within mathematics, the frequency partition of a graph is a partition of its vertices grouped by their degree. For example, the degree sequence of the left-hand graph below is and its frequency partition is 6 = 3 + 2 + 1. This indicates that it has 3 vertices with some degree, 2 vertices with some other degree, and 1 vertex with a third degree. The degree sequence of the bipartite graph in the middle below is and its frequency partition is 9 = 5 + 3 + 1. The degree sequence of the right-hand graph below is and its frequency partition is 7 = 6 + 1.
In graph theory, a bivariegated graph is a graph whose vertex set can be partitioned into two equal parts such that each vertex is adjacent to exactly one vertex from the other set not containing it. In a bivarigated graph G with 2n vertices, there exists a set of n independent edges such that no odd number of them lie on a cycle of G.
Navin Madhavprasad Singhi is an Indian mathematician and a Professor Emeritus at Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, specializing in combinatorics and graph theory. He is the recipient of the prestigious Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology. Singhi is known for his research in block designs, projective planes, Intersection graphs of hypergraphs, and coding theory. He was a visiting professor at IIT Mumbai, University of Mumbai, Indian Statistical Institute and other various universities in the United States and Europe.

In graph theory, Graph equations are equations in which the unknowns are graphs. One of the central questions of graph theory concerns the notion of isomorphism. We ask: When are two graphs the same? The graphs in question may be expressed differently in terms of graph equations.
In the mathematical field of graph theory, an integral graph is a graph whose adjacency matrix's spectrum consists entirely of integers. In other words, a graph is an integral graph if all of the roots of the characteristic polynomial of its adjacency matrix are integers.
Daniela Kühn is a German mathematician and the Mason Professor in Mathematics at the University of Birmingham in Birmingham, England. She is known for her research in combinatorics, and particularly in extremal combinatorics and graph theory.
Carolyn Ray Boone Mahoney is an American mathematician who served as president of Lincoln University of Missouri. Her research interests include combinatorics, graph theory, and matroids.
Judith Querida Longyear was an American mathematician and professor whose research interests included graph theory and combinatorics. Longyear was the second woman to ever earn a mathematics Ph.D. from Pennsylvania State University, where she studied under the supervision of Sarvadaman Chowla and wrote a thesis entitled Tactical Configurations. Longyear taught mathematics at several universities including California Institute of Technology, Dartmouth College and Wayne State University. She worked on nested block designs and Hadamard matrices.
Kristina L. Vušković is a Serbian mathematician and theoretical computer scientist working in graph theory. She is Professor in Algorithms and Combinatorics in the School of Computing at the University of Leeds, and a professor of computer science at Union University (Serbia).
References
- ↑ Vasanti N. Bhat-Nayak at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ Rao, Nithyanand (12 November 2017), "Celebrating Sharadchandra Shrikhande, the Mathematician Who Disproved Euler", The Wire
- ↑ "American Mathematical Society" . Retrieved 16 February 2024.