Colombia is a unitary republic made up of thirty-two departments and a Capital District. Each department has a governor (gobernador) and an Assembly, elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy.

The Second Republic of Venezuela is the name used to refer to the reestablished Venezuelan Republic declared by Simón Bolívar on 7 August 1813. This declaration followed the defeat of Domingo Monteverde by Bolívar during the Admirable Campaign in the west and Santiago Mariño in his campaign in the east. The republic came to an end in the following year, after a series of defeats at the hands of José Tomás Boves.

The Anthem of the Carabobo State, Venezuela is one of a number of anthems for Venezuelan states composed in the early 20th century. It has lyrics composed in rhyme by Santiago González Guiñán; the music was added by Sebastián Díaz Peña. The anthem was first played on July 5, 1908 at the Bolìvar Square of Valencia.

Maynas is one of the eight provinces in the Loreto Region in northeastern Peru. Its capital, Iquitos, is also Loreto's regional capital and the largest city in the Peruvian Amazon Rainforest.

The Republic of New Granada was a 1831–1858 centralist unitary republic consisting primarily of present-day Colombia and Panama with smaller portions of today's Costa Rica, Ecuador, Venezuela, Peru and Brazil. On 9 May 1834, the national flag was adopted and was used until 26 November 1861, with the Gran Colombian colours in Veles' arrangement. The merchant ensign had the eight-pointed star in white.

Gran Colombia, or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Panama, and Venezuela, along with parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil and Guyana. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiographically to distinguish it from the current Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state.

The Real Audiencia of Quito was an administrative unit in the Spanish Empire which had political, military, and religious jurisdiction over territories that today include Ecuador, parts of northern Peru, parts of southern Colombia and parts of northern Brazil. It was created by Royal Decree on 29 August 1563 by Philip II of Spain in the city of Guadalajara. It ended in 1822 with the incorporation of the area into the Republic of Gran Colombia.

The Isthmus Department, or Department of Panama, was one of the departments of the Republic of Gran Colombia and later of the Republic of Colombia. It was created in 1824 and named after the Isthmus of Panama. It covered the territory of what is now the country of Panama and some coastal territories farther northward along the Caribbean shoreline of present-day Costa Rica and Nicaragua.
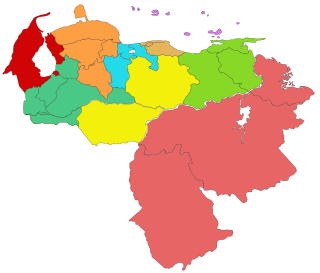
The Zulian Region is one of the 10 administrative regions into which Venezuela is divided for its development plans. This region is coterminous with Zulia State and is administrated by CORPOZULIA. The people from this region seek autonomy from the central government.
The Republic of Gran Colombia was a former independent country in northern South America, a post-Spanish colonial country that existed from 1819 to 1831. Its initial subdivisions, created in 1820, were revised and expanded in 1824.

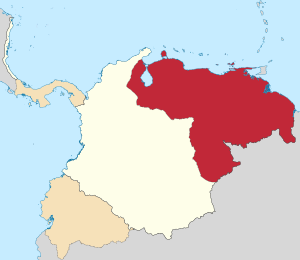
Zulia Department from 1824 to 1830 was one of the departments of Gran Colombia. It was split from the Venezuela Department.

The Venezuela Province was a province of the Spanish Empire, of Gran Colombia (1824-1830) and later of Venezuela, apart from an interlude when it was contracted as a concession by the King of Spain to the German Welser banking family, as Klein-Venedig.

New Andalusia Province or Province of Cumaná (1537–1864) was a province of the Spanish Empire, and later of Gran Colombia and Venezuela. It included the territory of present-day Venezuelan states Sucre, Anzoátegui and Monagas. Its most important cities were the Capital City Cumaná and New Barcelona.

Barcelona Province (1811–1864) was one of the provinces of Venezuela which signed the 1811 Venezuelan Declaration of Independence from the Spanish Empire. It became one of the provinces of Gran Colombia after Venezuela's independence from Gran Colombia in 1830. During the times of Gran Colombia, it was part of the Orinoco Department.
The Provinces of Venezuela were administrative divisions used from Venezuela's independence from Gran Colombia in 1830 to 1864, when the States of Venezuela were created. There were initially 11 provinces, with 4 created later, until in 1856 the Law of Territorial Division divided Venezuela into 21 provinces.

Venezuela Department was one of the departments of Gran Colombia from 1824 to 1830.

Margarita Province was one of the provinces of the Spanish Empire, then one of the provinces of Gran Colombia, and later one of the Provinces of Venezuela. In Gran Colombia it belonged to the Orinoco Department which was created in 1824. With the creation of the States of Venezuela in 1864 it became Nueva Esparta.

Carabobo Province (1824–1864) was one of the provinces of Gran Colombia, and later one of the provinces of Venezuela, after Venezuelan independence in 1830. It was split from Caracas Province. In Gran Colombia it belonged to the Venezuela Department which was created in 1824.

Mérida Province was one of the provinces of Gran Colombia, until the independence of Venezuela in 1830, when it became one of the Provinces of Venezuela. In Gran Colombia it belonged to the Zulia Department which was created in 1824.

The 1827 Guayaquil uprising, also known as the Guayaquil Department rebellion, was a set of actions carried out by the Guayaquil authorities —during its period as a department of Gran Colombia— in rejection of the centralist policies of the Republic of Colombia and others that harmed the interests of various municipalities. This is one of the first rebellions with a separatist tint that took place in the country of Gran Colombia prior to the start of its dissolution process in 1829.