Related Research Articles
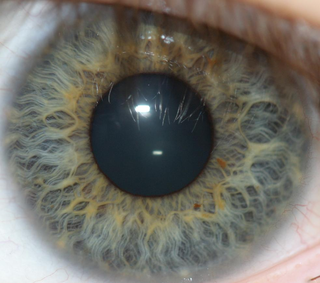
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.

A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image.

An electronic identification ("eID") is a digital solution for proof of identity of citizens or organizations. They can be used to view to access benefits or services provided by government authorities, banks or other companies, for mobile payments, etc. Apart from online authentication and login, many electronic identity services also give users the option to sign electronic documents with a digital signature.
Daon is an international biometrics and identity assurance software company founded in 1999 by Irish entrepreneur Dermot Desmond. The name, Daon, was chosen because it stems from the Celtic word for human being, duine daonna. Daon is headquartered just outside of Washington, DC in Fairfax, VA. Daon also has operations in Dublin, located in the International Financial Services Center (IFSC). It has additional offices in Belgrade, Serbia and Canberra, Australia.
Biometrics refers to the automated recognition of individuals based on their biological and behavioral characteristics, not to be confused with statistical biometrics; which is used to analyse data in the biological sciences. Biometrics for the purposes of identification may involve DNA matching, facial recognition, fingerprints, retina and iris scanning, voice analysis, handwriting, gait, and even body odor.
IDEMIA is a multinational technology company headquartered in Courbevoie, France. It provides identity-related security services, and sells facial recognition and other biometric identification products and software to private companies and governments.
Identity-based security is a type of security that focuses on access to digital information or services based on the authenticated identity of an entity. It ensures that the users and services of these digital resources are entitled to what they receive. The most common form of identity-based security involves the login of an account with a username and password. However, recent technology has evolved into fingerprinting or facial recognition.

A biometric device is a security identification and authentication device. Such devices use automated methods of verifying or recognising the identity of a living person based on a physiological or behavioral characteristic. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial images, iris and voice recognition.
ID.me is an American online identity network company that allows people to provide proof of their legal identity online. ID.me digital credentials can be used to access government services, healthcare logins, or discounts from retailers. The company is based in McLean, Virginia.
DeepFace is a deep learning facial recognition system created by a research group at Facebook. It identifies human faces in digital images. The program employs a nine-layer neural network with over 120 million connection weights and was trained on four million images uploaded by Facebook users. The Facebook Research team has stated that the DeepFace method reaches an accuracy of 97.35% ± 0.25% on Labeled Faces in the Wild (LFW) data set where human beings have 97.53%. This means that DeepFace is sometimes more successful than human beings. As a result of growing societal concerns Meta announced that it plans to shut down Facebook facial recognition system, deleting the face scan data of more than one billion users. This change will represent one of the largest shifts in facial recognition usage in the technology's history. Facebook planned to delete by December 2021 more than one billion facial recognition templates, which are digital scans of facial features. However, it did not plan to eliminate DeepFace which is the software that powers the facial recognition system. The company has also not ruled out incorporating facial recognition technology into future products, according to Meta spokesperson.
Clear Secure, Inc. is an American technology company that operates biometric travel document verification systems at some major airports and stadiums.
FindFace is a face recognition technology developed by the Russian company NtechLab that specializes in neural network tools. The company provides a line of services for the state and various business sectors based on FindFace algorithm. Previously, the technology was used as a web service that helped to find people on the VK social network using their photos.
Onfido is a technology company that helps businesses verify people's identities using a photo-based identity document, a selfie and artificial intelligence algorithms.
Acuant is an identity verification, document authentication and fraud prevention technology services provider headquartered in Los Angeles, with engineering and development centers in New Hampshire and Israel.
Digital identity is used in Australia by residents to validate who they are over digital media, such as over the Internet.
Mbogo, Ethan (2014-09-03). "USAA and Mitek Settle Lawsuit". GlobeNewswire News Room. Retrieved 2023-11-29.
The NHS App allows patients using the National Health Service in England to book appointments with their GP, order repeat prescriptions and access their GP record. Available since late 2018, the app was developed by NHS Digital and NHS England. The health ministers Jeremy Hunt and Matt Hancock both stressed their support for the project. Hancock presented it as the key a radical overhaul of NHS technology. Hunt claimed it would mark 'the death-knell of the 8am scramble for GP appointments that infuriates so many patients'.
Veriff is a global identity verification service company founded and headquartered in Tallinn, Estonia. The company offers services for online businesses to mitigate fraud attempts and assisting regulatory compliance. Offering protection from identity fraud and identity theft, Veriff verifies a customer's identity automatically, using an AI that analyzes a multitude of technological and behavioural indicators, including facial recognition. The service is provided to companies as an API, which has been compared to Stripe.
Proof of personhood (PoP) is a means of resisting malicious attacks on peer to peer networks, particularly, attacks that utilize multiple fake identities, otherwise known as a Sybil attack. Decentralized online platforms are particularly vulnerable to such attacks by their very nature, as notionally democratic and responsive to large voting blocks. In PoP, each unique human participant obtains one equal unit of voting power, and any associated rewards.

Neurotechnology is an algorithm and software development company founded in Vilnius, Lithuania in 1990.
References
- ↑ Digital Onboarding Toolkit | Remote Identity Verification. Innovatrics.com. [cit. 2021-08-26]. . (english)
- ↑ eKYC - Online Customer Onboarding and Identity Verification. Innovatrics.com. [cit. 2021-08-26]. . (english)
- ↑ Latest NIST FRVT Results: Innovatrics Face Recognition Algorithm Among Global Top 10. Innovatrics.com . [cit. 2020-04-15]. . (english)
- ↑ Innovatrics algorithms power VeriFace onboarding service launch. Biometricupdate.com . [cit. 2022-05-09]. . (english)