Related Research Articles

Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens–Johnson/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), it forms a spectrum of disease, with SJS being less severe. Erythema multiforme (EM) is generally considered a separate condition. Early symptoms of SJS include fever and flu-like symptoms. A few days later, the skin begins to blister and peel, forming painful raw areas. Mucous membranes, such as the mouth, are also typically involved. Complications include dehydration, sepsis, pneumonia and multiple organ failure.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, but is named for its appearance. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

Sweet syndrome (SS), or acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, is a skin disease characterized by the sudden onset of fever, an elevated white blood cell count, and tender, red, well-demarcated papules and plaques that show dense infiltrates by neutrophil granulocytes on histologic examination.

Necrolytic migratory erythema is a red, blistering rash that spreads across the skin. It particularly affects the skin around the mouth and distal extremities; but may also be found on the lower abdomen, buttocks, perineum, and groin. It is strongly associated with glucagonoma, a glucagon-producing tumor of the pancreas, but is also seen in a number of other conditions including liver disease and intestinal malabsorption.

Papillon–Lefèvre syndrome (PLS), also known as palmoplantar keratoderma with periodontitis, is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in cathepsin C.

In medicine, a drug eruption is an adverse drug reaction of the skin. Most drug-induced cutaneous reactions are mild and disappear when the offending drug is withdrawn. These are called "simple" drug eruptions. However, more serious drug eruptions may be associated with organ injury such as liver or kidney damage and are categorized as "complex". Drugs can also cause hair and nail changes, affect the mucous membranes, or cause itching without outward skin changes.

Allopurinol hypersensitivity syndrome typically occurs in persons with preexisting kidney failure. Weeks to months after allopurinol is begun, the patient develops a morbilliform eruption or, less commonly, develops one of the far more serious and potentially lethal severe cutaneous adverse reactions viz., the DRESS syndrome, Stevens Johnson syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis.

Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare skin reaction that in 90% of cases is related to medication.
Fixed drug reactions are common and so named because they recur at the same site with each exposure to a particular medication. Medications inducing fixed drug eruptions are usually those taken intermittently.
IgA pemphigus is a subtype of pemphigus with two distinct forms:
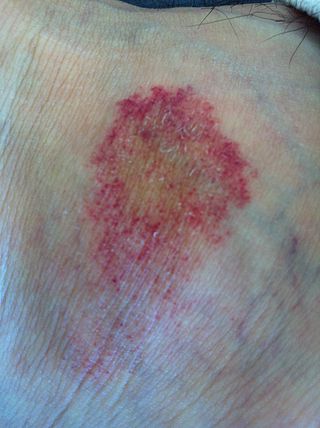
Pigmented purpuric dermatosis refers to one of the three major classes of skin conditions characterized by purpuric skin eruptions.
Gougerot–Blum syndrome is a variant of pigmented purpuric dermatitis, a skin condition characterized by minute, rust-colored to violaceous, lichenoid papules that tend to fuse into plaques of various hues. Relative to other variants, it is characterized clinically by a male predominance, pruritus, with a predilection for the legs, and histologically, it features a densely cellular lichenoid infiltrate.

A sebaceous adenoma, a type of adenoma, a cutaneous condition characterized by a slow-growing tumor usually presenting as a pink, flesh-coloured, or yellow papule or nodule.
Haber syndrome is a cutaneous disorder of hyperpigmentation characterized by reticulated pigmentation of the person's skin. A rare genodermatosis, its key features include "rosacea-like facial eruption[,] reticulated hyperpigmentation of major flexures, comedones on the back and neck, and pitted facial scars."
Laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome is a rare epithelial disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. It is characterized by abnormalities in the larynx, nails, and skin ("cutaneous"). The disorder is only found in Punjabi Muslims and only a few cases have been reported.
Photoleukomelanodermatitis of Kobori is a cutaneous condition, a dyschromic drug eruption that occurs after ingestion of afloqualone, thiazides or tetracyclines, followed by exposure to sunlight.

Necrolytic acral erythema is a cutaneous condition that is a manifestation of hepatitis C viral infection or zinc deficiency.
Neonatal toxic shock-like exanthematous disease is a cutaneous condition characterized by a generalized diffuse macular erythema or morbilliform eruption with confluence.
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis of infancy is a cutaneous condition characterized by recurrent pruritic crops of follicular vesiculopustular lesions.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.