
Domitian was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed.

Vespasian was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire brought political stability and a vast building program.
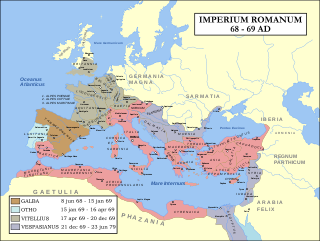
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Titus Caesar Vespasianus was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death, becoming the first Roman emperor to succeed his biological father.

Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46.

Domitia Longina was a Roman empress and wife to the Roman emperor Domitian. She was the youngest daughter of the general and consul Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo. Domitia divorced her first husband, Lucius Aelius Lamia Plautius Aelianus in order to marry Domitian in AD 71. The marriage produced only one son, whose early death is believed to have been the cause of a temporary rift between Domitia and her husband in 83. She became the empress upon Domitian's accession in 81, and remained so until his assassination in 96. She is believed to have died sometime between AD 126 and 130.

The Flavian dynasty ruled the Roman Empire between AD 69 and 96, encompassing the reigns of Vespasian (69–79), and his two sons Titus (79–81) and Domitian (81–96). The Flavians rose to power during the civil war of 69, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. After Galba and Otho died in quick succession, Vitellius became emperor in mid 69. His claim to the throne was quickly challenged by legions stationed in the eastern provinces, who declared their commander Vespasian emperor in his place. The Second Battle of Bedriacum tilted the balance decisively in favour of the Flavian forces, who entered Rome on 20 December. The following day, the Roman Senate officially declared Vespasian emperor of the Roman Empire, thus commencing the Flavian dynasty. Although the dynasty proved to be short-lived, several significant historic, economic and military events took place during their reign.

The gens Flavia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Its members are first mentioned during the last three centuries of the Republic. The first of the Flavii to achieve prominence was Marcus Flavius, tribune of the plebs in 327 and 323 BC; however, no Flavius attained the consulship until Gaius Flavius Fimbria in 104 BC. The gens became illustrious during the first century AD, when the family of the Flavii Sabini claimed the imperial dignity.

Julia Flavia or Flavia Julia, nicknamed Julia Titi, was the daughter of Roman Emperor Titus and his first wife Arrecina Tertulla.
Titus Flavius Petro was the paternal grandfather of the Roman emperor Vespasian.
Titus Flavius Titi filius Titi nepos Clemens was a Roman politician and cousin of the emperor Domitian, with whom he served as consul from January to April in AD 95. Shortly after leaving the consulship, Clemens was executed, allegedly for atheism, although the exact circumstances remain unclear. Over time, he came to be regarded as an early Christian martyr.

Flavia Domitilla Major was the wife of the Roman Emperor Vespasian and mother of the emperors Titus and Domitian. She died before her husband became emperor in 69 AD. After her death she is thought to have been deified by the name Diva Domitilla.
Flavia Domitilla was a Roman noblewoman of the 1st century AD. She was a granddaughter of Emperor Vespasian and a niece of Emperors Titus and Domitian. She married her second cousin, the consul Titus Flavius Clemens, a grand-nephew of Vespasian through his father Titus Flavius Sabinus.

Titus Flavius T. f. Sabinus was a Roman eques and the father of the emperor Vespasian.
Titus Flavius T. f. T. n. Sabinus was a Roman politician and soldier. A native of Reate, he was the elder son of Titus Flavius Sabinus and Vespasia Polla, and brother of the Emperor Vespasian.
Titus Flavius Sabinus was a Roman senator who was active in the first century AD. He was twice consul suffectus, first in the nundinium of April through June of 69 with his brother Gnaeus Arulenus Caelius Sabinus, and again in May and June of 72 as the colleague of Gaius Licinius Mucianus.
Titus Flavius T. f. T. n. Sabinus was a Roman senator, who was active during the second half of the first century AD. He was the son of Titus Flavius Sabinus, consul suffectus in AD 69. In that year the younger Sabinus was besieged with his grandfather in the Capitol, but escaped when it was burnt down. He married Julia Flavia, the daughter of his cousin, the future emperor Titus.
Cornelius Fuscus was a Roman general who fought campaigns under the Emperors of the Flavian dynasty. He first distinguished himself as one of Vespasian's most ardent supporters during the civil war of 69 AD, known as the Year of the Four Emperors. Vespasian's son Domitian employed Fuscus as prefect of the Praetorian Guard, a post he held from 81 until his death.

Arrecina Tertulla was a Roman woman who lived in the 1st century. She was the first wife of Titus and mother of his daughter Julia Flavia.
The gens Poppaea was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens first appear under the early Empire, when two brothers served as consuls in AD 9. The Roman empress Poppaea Sabina was a descendant of this family, but few others achieved any prominence in the Roman state. A number of Poppaei are known from inscriptions. The name is sometimes confused with that of Pompeia.












