
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Xen Project is a type-1 hypervisor, providing services that allow multiple computer operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently. It was developed by the University of Cambridge and is now being developed by the Linux Foundation with support from Intel.
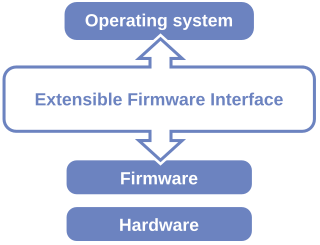
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.
Nucleus RTOS is a real-time operating system (RTOS) offered by the Embedded Software Division of Mentor Graphics, a Siemens Business, supporting 32 and 64 bit embedded platforms. The Nucleus RTOS is designed for real-time embedded systems for use in medical, industrial, consumer, aerospace, and IoT applications. Nucleus RTOS was first released in 1993. The latest version of Nucleus RTOS is v3.x which includes features such as power management, process model, 64 bit support, safety certification, and support for heterogeneous multicore SOCs.

Wind River Systems, also known as Wind River, is an Alameda, California-based wholly owned subsidiary of TPG Capital. The company develops embedded system software consisting of run-time software, industry-specific software suites, simulation technology, development tools and middleware, which is software and operating systems for information appliances and devices for intelligent connected systems.

The Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality supplied by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
A hypervisor is a computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platform and manages the execution of the guest operating systems. Multiple instances of a variety of operating systems may share the virtualized hardware resources: for example, Linux, Windows, and macOS instances can all run on a single physical x86 machine. This contrasts with operating-system-level virtualization, where all instances must share a single kernel, though the guest operating systems can differ in user space, such as different Linux distributions with the same kernel.
Parallels Workstation is the first commercial software product released by Parallels, Inc., a developer of desktop and server virtualization software. The Workstation software consists of a virtual machine suite for Intel x86-compatible computers which allows the simultaneous creation and execution of multiple x86 virtual computers. The product is distributed as a download package. Parallels Workstation has been discontinued for Windows and Linux as of 2013.
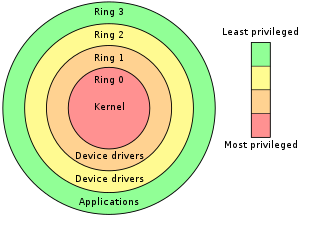
In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are mechanisms to protect data and functionality from faults and malicious behavior. This approach is diametrically opposite to that of capability-based security.
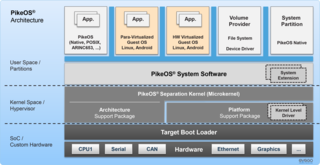
PikeOS is a commercial, hard real-time operating system (RTOS) that offers a separation kernel based hypervisor with multiple partition types for many other operating systems and applications. It enables users to build certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things according to the high quality, safety and security standards of different industries.
Microsoft Hyper-V, codenamed Viridian, formerly known as Windows Server Virtualization, is a native hypervisor; it can create virtual machines on x86-64 systems running Windows. Starting with Windows 8, Hyper-V superseded Windows Virtual PC as the hardware virtualization component of the client editions of Windows NT. A server computer running Hyper-V can be configured to expose individual virtual machines to one or more networks. Hyper-V was first released with Windows Server 2008, and has been available without additional charge since Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8. A standalone Windows Hyper-V Server is free, but with command line interface only.
Lynx Software Technologies, Inc. is a San Jose, California software company founded in 1988. Lynx Software Technologies specializes in secure virtualization and open and reliable real-time operating system (RTOS). Originally known as Lynx Real-Time Systems, the company changed its name to LynuxWorks in 2000 after acquiring, and merging with, ISDCorp a nine-year-old embedded systems company with a strong Linux background. In May 2014, the company changed its name to Lynx Software Technologies as a representation of the company’s forward direction as the LynxOS RTOS family of products and the LynxSecure hypervisor continued to gain increased traction both with current customers and markets, and with the new Internet connected embedded world.

ELinOS is a commercial development environment for embedded Linux. It consists of a Linux distribution for the target embedded system and development tools for a development host computer. The development host computer usually is a standard desktop computer running Linux or Windows. The Linux system and the application software for the target device are both created on the development host.

XtratuM is a bare-metal hypervisor specially designed for embedded real-time systems available for the instruction sets x86, LEON2 and LEON3, ARM Cortex-R4F processors.
An embedded hypervisor is a hypervisor that supports the requirements of embedded systems.
Open Kernel Labs is a privately owned company that develops microkernel-based hypervisors and operating systems for embedded systems. The company was founded in 2006 by Steve Subar and Gernot Heiser as a spinout from NICTA. It is headquartered in Chicago, while research and development was located in Sydney, Australia. The company was acquired by General Dynamics in September 2012.
Mobile virtualization is hardware virtualization on a mobile phone or connected wireless device. It enables multiple operating systems or virtual machines to run simultaneously on a mobile phone or connected wireless device. It uses a hypervisor to create secure separation between the underlying hardware and the software that runs on top of it; this can be considered a form of an embedded hypervisor, or a close analogue. Virtualization technology has been used widely for many years in other fields such as data servers and personal computers.
Second Level Address Translation (SLAT), also known as nested paging, is a hardware-assisted virtualization technology which makes it possible to avoid the overhead associated with software-managed shadow page tables.
RISC-V is an open-source hardware instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles.
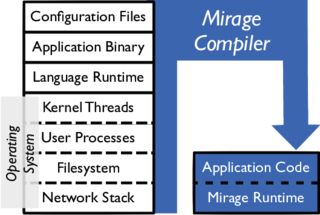
A unikernel is a specialised, single address space machine image constructed by using library operating systems. A developer selects, from a modular stack, the minimal set of libraries which correspond to the OS constructs required for their application to run. These libraries are then compiled with the application and configuration code to build sealed, fixed-purpose images (unikernels) which run directly on a hypervisor or hardware without an intervening OS such as Linux or Windows.










