
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Founded in 1386 on instruction of Pope Urban VI, Heidelberg is Germany's oldest university and one of the world's oldest surviving universities. It was the third university established in the Holy Roman Empire.

Coveney is a Professor of Physical Chemistry, Honorary Professor of Computer Science, and the Director of the Centre for Computational Science (CCS) at University College London (UCL). He is also a Professor of Applied High Performance Computing at University of Amsterdam (UvA), Professor Adjunct in the Medical School at Yale University and Member of Academia Europaea.

The European Research Council (ERC) is a public body for funding of scientific and technological research conducted within the European Union (EU). Established by the European Commission in 2007, the ERC is composed of an independent Scientific Council, its governing body consisting of distinguished researchers, and an Executive Agency, in charge of the implementation. It forms part of the framework programme of the union dedicated to research and innovation, Horizon 2020, preceded by the Seventh Research Framework Programme (FP7). The ERC budget is over €13 billion from 2014 – 2020 and comes from the Horizon 2020 programme, a part of the European Union's budget. Under Horizon 2020 it is estimated that around 7,000 ERC grantees will be funded and 42,000 team members supported, including 11,000 doctoral students and almost 16,000 post-doctoral researchers.

The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon.

The Energy Sciences Network (ESnet) is a high-speed computer network serving United States Department of Energy (DOE) scientists and their collaborators worldwide. It is managed by staff at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Virtual currency, or virtual money, is a digital currency that is largely unregulated and issued and usually controlled by its developers and used and accepted electronically among the members of a specific virtual community. In 2014, the European Banking Authority defined virtual currency as "a digital representation of value that is neither issued by a central bank or a public authority, nor necessarily attached to a fiat currency, but is accepted by natural or legal persons as a means of payment and can be transferred, stored or traded electronically." A digital currency issued by a central bank is referred to as a central bank digital currency.

The Excellence Initiative of the German Council of Science and Humanities and the German Research Foundation aims to promote cutting-edge research and to create outstanding conditions for young scholars at universities, to deepen cooperation between disciplines and institutions, to strengthen international cooperation of research, and to enhance the international appeal of excellent German universities. It is the result of lengthy negotiations between the federal government and the German states.
The European Institute for Biomedical Imaging Research (EIBIR) was established in 2006 as a non-profit, limited liability company on the initiative of the European Society of Radiology with funding of the European Commission within the Sixth Framework Programme.

The Distributed European Infrastructure for Supercomputing Applications (DEISA) was a European Union supercomputer project. A consortium of eleven national supercomputing centres from seven European countries promoted pan-European research on European high-performance computing systems. By extending the European collaborative environment in the area of supercomputing, DEISA followed suggestions of the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures.
The Free Knowledge Institute (FKI) is a non-profit organisation founded in 2006 in the Netherlands. Inspired by the free software movement, the FKI fosters the free exchange of knowledge in all areas of society by promoting freedom of use, modification, copying, and distribution of knowledge pertaining to education, technology, culture, and science.
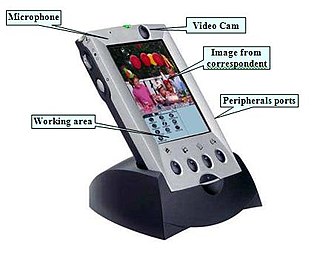
The first integration between mobile phone and Palm occurred in 1999, as a result of an Italian–lead project submitted to the action line V1.1 CPA1 "Integrated application platforms and services" 5th Framework Program of the European Community . The project, called MTM , was a multimedia platform, including both phone and PDA features; it also integrated the first miniature camera and a unidirectional microphone for video conferencing and commands interpretation through voice recognition. The creator and coordinator of the project, Alessandro Pappa, worked in a team with other European partners:

Several centers for supercomputing exist across Europe, and distributed access to them is coordinated by European initiatives to facilitate high-performance computing. One such initiative, the HPC Europa project, fits within the Distributed European Infrastructure for Supercomputing Applications (DEISA), which was formed in 2002 as a consortium of eleven supercomputing centers from seven European countries. Operating within the CORDIS framework, HPC Europa aims to provide access to supercomputers across Europe.
The HPC-Europa programmes are European Union (EU) funded research initiatives in the field of high-performance computing (HPC). The programmes concentrate on the development of a European Research Area, and in particular, improving the ability of European researchers to access the European supercomputing infrastructure provided by the programmes' partners. The programme is currently in its third iteration, known as "HPC-Europa3" or "HPCE3", and fully titled the "Transnational Access Programme for a Pan-European Network of HPC Research Infrastructures and Laboratories for scientific computing".
The Cluster of Excellence "Asia and Europe in a Global Context" is a research facility funded in the framework of the German Universities Excellence Initiative of the federal state governments of Germany since October 2007. It is a trans- and interdisciplinary network of researchers affiliated with Heidelberg University. Key research areas of the Cluster are the processes of exchange between cultures of Asia and Europe, ranging from migration and trade to the formation of concepts and institutions.

The European Union Centers of Excellence in the United States is a network of eight university programs dedicated to the promotion of the study of the European Union as well as the strengthening of ties between the people of the EU and the United States. The centres operate through teaching programs, as well as academic research and community outreach. Their development has allowed for the growth and improvement of EU studies in US higher education and made them a source of information for a far-reaching US audience.

SDEWES Centre, is a non-governmental scientific organization based at the University of Zagreb, Croatia.
The SPOTLIGHT project is a research project led by VU University Medical Center Amsterdam and part-funded by the European Union 7th Framework Programme concerning health. Initial EU funding is for the period 2013–2016, covering part of the budget of €3.7m. The project is listed on the European Commission CORDIS site.
Eurodesk is an international non-profit association created in 1990. It is a European network of European and national information centers for young people and those involved with them. It offers youth information and international learning opportunities and is an organisation supported by the Erasmus+ programme (2014–2020). In 2004, Eurodesk – with the help of its financier European Commission - launched the European Youth Portal. From 2007 to 2013, Eurodesk was part of the Youth in Action programme. Through the participation of the Erasmus+ programme in the year 2014, Eurodesk is already present in 5 countries. In the year 2015 Eurodesk celebrated its 25th anniversary.

The Smart Cities EMC Network for Training (SCENT) is a project funded by the European Union's Horizon 2020 research program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 812391. It is a Ph.D training network program in the field of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) especially in the smart cities application. Three universities and twelve industries collaborate in SCENT project. Supported by the IEEE EMC Society Technical Committee 7: beside Ph.D training program, SCENT project also perform scientific training programs and social outreach programs.











