External links
- Virtual Link Aggregation Control Protocol (VLACP) Retrieved 29 July 2011
- ERS-8600 All Documentation -Retrieved 29 July 2011
- VSP 7000 Command Line Interface Commands Reference, Command: vlacp Retrieved 1 May 2020
Virtual LACP (VLACP) is an Avaya extension of the Link Aggregation Control Protocol to provide a Layer 2 handshaking protocol which can detect end-to-end failure between two physical Ethernet interfaces. It allows the switch to detect unidirectional or bi-directional link failures irrespective of intermediary devices and enables link recovery in less than one second.
With VLACP, far-end failures can be detected, which allows a Link aggregation trunk to fail over properly when end-to-end connectivity is not guaranteed for certain links through the internet in an aggregation group. When a remote link failure is detected, the change is propagated to the partner port.

Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a telecommunications standard defined by the American National Standards Institute and International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector for digital transmission of multiple types of traffic. ATM was developed to meet the needs of the Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network as defined in the late 1980s, and designed to integrate telecommunication networks. It can handle both traditional high-throughput data traffic and real-time, low-latency content such as telephony (voice) and video. ATM provides functionality that uses features of circuit switching and packet switching networks by using asynchronous time-division multiplexing. ATM was seen in the 1990s as a competitor to Ethernet and networks carrying IP traffic as, unlike Ethernet, it was faster and designed with quality-of-service in mind, but it fell out of favor once Ethernet reached speeds of 1 gigabits per second.

In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and other computer programs to access hardware functions without needing to know precise details about the hardware being used.

In computer networking, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer communication protocol between two routers directly without any host or any other networking in between. It can provide loop detection, authentication, transmission encryption, and data compression.

Frame Relay is a standardized wide area network (WAN) technology that specifies the physical and data link layers of digital telecommunications channels using a packet switching methodology. Originally designed for transport across Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) infrastructure, it may be used today in the context of many other network interfaces.

In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine from the human end, while the machine simultaneously feeds back information that aids the operators' decision-making process. Examples of this broad concept of user interfaces include the interactive aspects of computer operating systems, hand tools, heavy machinery operator controls and process controls. The design considerations applicable when creating user interfaces are related to, or involve such disciplines as, ergonomics and psychology.
Virtual private network (VPN) is a network architecture for virtually extending a private network across one or multiple other networks which are either untrusted or need to be isolated.
SOCKS is an Internet protocol that exchanges network packets between a client and server through a proxy server. SOCKS5 optionally provides authentication so only authorized users may access a server. Practically, a SOCKS server proxies TCP connections to an arbitrary IP address, and provides a means for UDP packets to be forwarded. A SOCKS server accepts incoming client connection on TCP port 1080, as defined in RFC 1928.

Null modem is a communication method to directly connect two DTEs using an RS-232 serial cable. The name stems from the historical use of RS-232 cables to connect two teleprinter devices or two modems in order to communicate with one another; null modem communication refers to using a crossed-over RS-232 cable to connect the teleprinters directly to one another without the modems. It is also used to serially connect a computer to a printer, since both are DTE, and is known as a Printer Cable.
Diameter is an authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) protocol for computer networks. It evolved from the earlier RADIUS protocol. It belongs to the application layer protocols in the Internet protocol suite.
In computer networks, a tunneling protocol is a communication protocol which allows for the movement of data from one network to another. It can, for example, allow private network communications to be sent across a public network, or for one network protocol to be carried over an incompatible network, through a process called encapsulation.

The RapidIO architecture is a high-performance packet-switched electrical connection technology. It supports messaging, read/write and cache coherency semantics. Based on industry-standard electrical specifications such as those for Ethernet, RapidIO can be used as a chip-to-chip, board-to-board, and chassis-to-chassis interconnect.
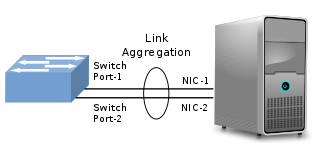
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods. Link aggregation increases total throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and provides redundancy where all but one of the physical links may fail without losing connectivity. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports.

A metropolitan-area Ethernet, Ethernet MAN, carrier Ethernet or metro Ethernet network is a metropolitan area network (MAN) that is based on Ethernet standards. It is commonly used to connect subscribers to a larger service network or for internet access. Businesses can also use metropolitan-area Ethernet to connect their own offices to each other.
In computer networking, a reliable protocol is a communication protocol that notifies the sender whether or not the delivery of data to intended recipients was successful. Reliability is a synonym for assurance, which is the term used by the ITU and ATM Forum.
Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) is a Cisco Systems proprietary networking protocol, which is used for the automated, link aggregation of Ethernet switch ports, known as an EtherChannel. PAgP is proprietary to Cisco Systems. A similar protocol known as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) — released by the IEEE — is an industry standard and is not tied to a specific vendor.

Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers.
Simple Loop Prevention Protocol (SLPP) in computer networking is a data link layer protocol developed by Nortel to protect against Layer 2 network loops. SLPP uses a small hello packet to detect network loops. The SLPP protocol checks packets from the originating switch and the peer switch in a SMLT configuration. Sending hello packets on a per VLAN basis allows SLPP to detect VLAN based network loops for un-tagged as well as tagged IEEE 802.1Q VLAN link configurations. If a loop is detected, the associated port is shut down.
Carrier Ethernet is a marketing term for extensions to Ethernet for communications service providers that utilize Ethernet technology in their networks.
IEEE 802.1aq is an amendment to the IEEE 802.1Q networking standard which adds support for Shortest Path Bridging (SPB). This technology is intended to simplify the creation and configuration of Ethernet networks while enabling multipath routing.
Virtual Link Trunking (VLT) is a name that has been used for at least two proprietary network protocols. A link aggregation protocol developed by Force10 and an early VLAN tagging capability from 3Com.