Exercise intolerance is a condition of inability or decreased ability to perform physical exercise at the normally expected level or duration for people of that age, size, sex, and muscle mass. It also includes experiences of unusually severe post-exercise pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting or other negative effects. Exercise intolerance is not a disease or syndrome in and of itself, but can result from various disorders.
Treatment of ME/CFS is variable and uncertain, and the condition is primarily managed rather than cured.

Clinical descriptions of ME/CFS vary. Different groups have produced sets of diagnostic criteria that share many similarities. The biggest differences between criteria are whether post-exertional malaise (PEM) is required, and the number of symptoms needed. The pathology of ME/CFS is unknown, and it can be a difficult condition to diagnose because there is no standard test, many symptoms are non-specific, and because doctors and patients may be unfamiliar with post-exertional malaise. Subgroup analysis suggests that, depending on the applied definition, CFS may represent a variety of conditions rather than a single disease entity.
Graded exercise therapy (GET) is a programme of physical activity that starts very slowly and gradually increases over time, intended as a treatment for chronic fatigue syndrome. Most public health bodies, including the CDC and NICE, consider it ineffective, and its safety is disputed. However, GET still enjoys support among a minority of clinicians and organizations.

Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a debilitating long-term medical condition. People with ME/CFS experience lengthy flare-ups of the illness following relatively minor physical or mental activity. This is known as post-exertional malaise (PEM) and is the hallmark symptom of the illness. Other core symptoms are a greatly reduced ability to do tasks that were previously routine, severe fatigue, and sleep disturbances. The baseline fatigue in ME/CFS does not improve much with rest. Orthostatic intolerance, memory and concentration problems, and chronic pain are common. About a quarter of people with ME/CFS are severely affected and unable to leave their bed or home.

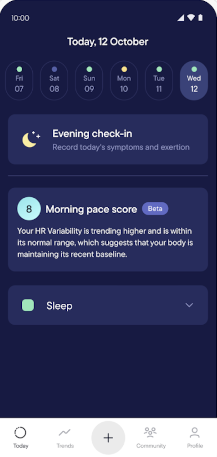
An activity tracker involves the practice of measuring and collecting data on an individual's physical and psychological activity to keep track and maintain documentation regarding their health and wellness. Used for many groups even animals as seen in collar-mounted activity trackers for dogs. A lot of the data is collected through wearable technology such as wristbands which sync with mobile apps through Apple and Samsung. As daily technologies such as phones and computers have been innovated, it paved the way for such wearable tracking technologies to be advanced. There are a variety of stakeholders involved in the usage of activity tracking through wearable technology and mobile health apps, knowing how much they track ranging from fitness, mood, sleep, water intake, medicine usage, sexual activity, menstruation, and potential diseases raises the concern on privacy given a lot of data is collected and analyzed. Through many studies that have been reviewed, data on the various demographics and goals these technologies are used provide more insight into their purposes.

Health is a health informatics mobile app, announced by Apple Inc. on June 2, 2014, at its Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC). The app is available on iPhone and iPod Touch devices running iOS 8 or later, and on iPads running iPadOS 17 or later. The application holds health data such as blood pressure measurement and glucose levels, but also holds physical tracking data such as step counts. It can pull data from fitness trackers, smartwatches, smart scales, and other devices.
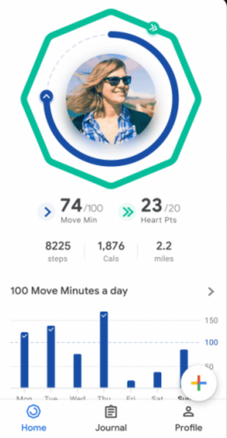
Google Fit is a health-tracking platform developed by Google for the Android operating system, Wear OS, and iOS. It is a single set of APIs that blends data from multiple apps and devices. Google Fit uses sensors in a user's activity tracker or mobile device to record physical fitness activities, which are measured against the user's fitness goals to provide a comprehensive view of their fitness.
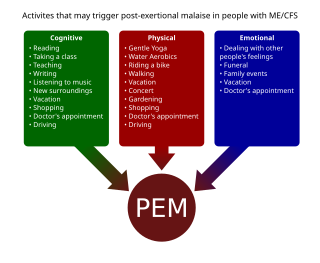
Post-exertional malaise (PEM), sometimes referred to as post-exertional symptom exacerbation (PESE), is a worsening of symptoms that occurs after minimal exertion. It is the hallmark symptom of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and common in long COVID. PEM is often severe enough to be disabling, and is triggered by ordinary activities that healthy people tolerate. Typically, it begins 12–48 hours after the activity that triggers it, and lasts for days, but this is highly variable and may persist much longer. Management of PEM is symptom-based, and patients are recommended to pace their activities to avoid triggering PEM.
Flo is a health app that provides menstruation tracking, cycle prediction, and information regarding preparation for conception, pregnancy, early motherhood, and menopause.
Empatica Inc. is an MIT Media Lab spinoff company born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, operating in Healthcare, providing AI-enabled tools to advance forecasting, monitoring, research, and treatment. Empatica produces medical-grade wearables, software and algorithms for the collection and interpretation of physiological data. Empatica's wearables, Embrace2 and E4, track physiological signals such as Heart Rate Variability, electrodermal activity, acceleration and movement, skin temperature, and autonomic arousal. Embrace2 has been cleared by the FDA as a seizure alerting solution for epilepsy patients with generalized tonic-clonic seizures. The E4 is used by researchers for real-time physiological data capture. The company is headquartered in Boston, MA with offices in Milan, Italy, and Seoul, South Korea.

COVID-19 apps include mobile-software applications for digital contact-tracing - i.e. the process of identifying persons ("contacts") who may have been in contact with an infected individual - deployed during the COVID-19 pandemic.

The (Google/Apple) Exposure Notification (GAEN) system, originally known as the Privacy-Preserving Contact Tracing Project, is a framework and protocol specification developed by Apple Inc. and Google to facilitate digital contact tracing during the COVID-19 pandemic. When used by health authorities, it augments more traditional contact tracing techniques by automatically logging close approaches among notification system users using Android or iOS smartphones. Exposure Notification is a decentralized reporting protocol built on a combination of Bluetooth Low Energy technology and privacy-preserving cryptography. It is an opt-in feature within COVID-19 apps developed and published by authorized health authorities. Unveiled on April 10, 2020, it was made available on iOS on May 20, 2020 as part of the iOS 13.5 update and on December 14, 2020 as part of the iOS 12.5 update for older iPhones. On Android, it was added to devices via a Google Play Services update, supporting all versions since Android Marshmallow.

NHS COVID-19 was a voluntary contact tracing app for monitoring the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic in England and Wales. It had been available since 24 September 2020 for Android and iOS smartphones, and can be used by anyone aged 16 or over.

The Zoe Health Study, formerly the COVID Symptom Study, is a health research project of British company Zoe Limited which uses a mobile app that runs on Android and iOS.
Pacing is an activity management technique for managing a long-term health condition or disability, aiming to maximize what a person can do while reducing, or at least controlling, any symptoms that restrict activity. Pacing is commonly used to help manage conditions that cause chronic pain or chronic fatigue.
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial period of COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after the initial COVID-19 infection, but other agencies define it as starting at four weeks after the initial infection.
WHOOP is an American wearable technology company headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. Its principal product is a fitness tracker that measures strain, recovery, and sleep. The device is best known for its use by athletes. The device is often used to keep track of overall health and even detection of illness.
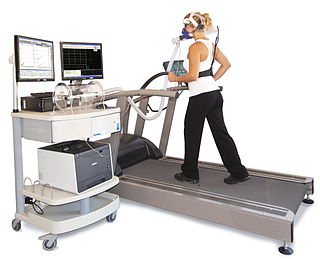
A 2-day CPET is a cardiopulmonary exercise test given on two successive days to measure the effect of post-exertional malaise (PEM) on a patient's ability to exercise. PEM is a cardinal symptom of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome and is common in long COVID as well.
Post-acute infection syndromes (PAISs) or post-active phase of infection syndromes are a group of medical conditions characterized by chronic illness triggered by an infection. They are sometimes referred to as infection-associated chronic illnesses as well. While it is commonly assumed that people either recover or die from infections, illness is a possible outcome as well. Examples include long COVID, chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), and post-Ebola virus syndrome. Common symptoms include post-exertional malaise (PEM), severe fatigue, neurocognitive symptoms, flu-like symptoms, and pain. The pathology of most of these conditions is not understood and management is generally symptomatic.