
Siberia is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over 13.1 million square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region.
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geographical terms and is coextensive with the Asian part of Russia, and consists of three Russian regions east of the Ural Mountains: Ural, Siberia, and the Russian Far East. North Asia is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to its north; by Eastern Europe to its west; by Central and East Asia to its south; and by the Pacific Ocean and North America to its east. It covers an area of 13,100,000 square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), or 8.8% of Earth's total land area; and is the largest subregion of Asia by area, but is also the least populated, with a population of around 33 million, accounting for merely 0.74% of Asia's population.

An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above. Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a weather phenomenon over the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level (SLP) between the Icelandic Low and the Azores High. Through fluctuations in the strength of the Icelandic Low and the Azores High, it controls the strength and direction of westerly winds and location of storm tracks across the North Atlantic.

A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.

A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation.

The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend towards the poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere.

A tropical wave, in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves from east to west across the tropics, causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. Tropical waves form in the easterly flow along the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge or belt of high air pressure which lies north and south of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Tropical waves are generally carried westward by the prevailing easterly winds along the tropics and subtropics near the equator. They can lead to the formation of tropical cyclones in the north Atlantic and northeastern Pacific basins. A tropical wave study is aided by Hovmöller diagrams, a graph of meteorological data.
The Siberian High is a massive collection of cold dry air that accumulates in the northeastern part of Eurasia from September until April. It is usually centered on Lake Baikal. It reaches its greatest size and strength in the winter when the air temperature near the center of the high-pressure area is often lower than −40 °C (−40 °F). The atmospheric pressure is often above 1,040 millibars (31 inHg). The Siberian High is the strongest semi-permanent high in the northern hemisphere and is responsible for both the lowest temperature in the Northern Hemisphere, of −67.8 °C (−90.0 °F) on 15 January 1885 at Verkhoyansk, and the highest pressure, 1083.8 mbar at Agata, Krasnoyarsk Krai on 31 December 1968, ever recorded. The Siberian High is responsible both for severe winter cold and attendant dry conditions with little snow and few or no glaciers across Siberia, Mongolia, and China. During the summer, the Siberian High is largely replaced by the Asiatic low.
The North American High is an impermanent high-pressure area or anticyclone created by a formative process that occurs when cool or cold dry air settles over North America. During summer, it is replaced with an Arctic Low, or a North American Low should it move over continental land.
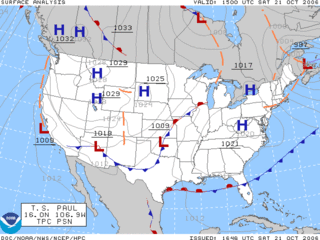
A pressure system is a peak or lull in the sea level pressure distribution. The surface pressure at sea level varies minimally, with the lowest value measured 87 kilopascals (26 inHg) and the highest recorded 108.57 kilopascals (32.06 inHg). High- and low-pressure systems evolve due to interactions of temperature differentials in the atmosphere, temperature differences between the atmosphere and water within oceans and lakes, the influence of upper-level disturbances, as well as the amount of solar heating or radiationized cooling an area receives. Pressure systems cause weather to be experienced locally. Low-pressure systems are associated with clouds and precipitation that minimize temperature changes throughout the day, whereas high-pressure systems normally associate with dry weather and mostly clear skies with larger diurnal temperature changes due to greater radiation at night and greater sunshine during the day. Pressure systems are analyzed by those in the field of meteorology within surface weather maps.

A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure without a closed isobaric contour that would define it as a low pressure area. Since low pressure implies a low height on a pressure surface, troughs and ridges refer to features in an identical sense as those on a topographic map.

A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ridge line. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough.

Blocks in meteorology are large-scale patterns in the atmospheric pressure field that are nearly stationary, effectively "blocking" or redirecting migratory cyclones. They are also known as blocking highs or blocking anticyclones. These blocks can remain in place for several days or even weeks, causing the areas affected by them to have the same kind of weather for an extended period of time. In the Northern Hemisphere, extended blocking occurs most frequently in the spring over the eastern Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Whilst these events are linked to the occurrence of extreme weather events such as heat waves, particularly the onset and decay of these events is still not well captured in numerical weather forecasts and remains an open area of research.

The geography of South America contains many diverse regions and climates. Geographically, South America is generally considered a continent forming the southern portion of the landmass of the Americas, south and east of the Colombia–Panama border by most authorities, or south and east of the Panama Canal by some. South and North America are sometimes considered a single continent or supercontinent, while constituent regions are infrequently considered subcontinents.
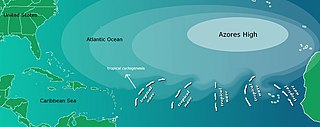
The Azores High also known as North Atlantic (Subtropical) High/Anticyclone or the Bermuda-Azores High, is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure typically found south of the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse latitudes. It forms one pole of the North Atlantic oscillation, the other being the Icelandic Low. The system influences the weather and climatic patterns of vast areas of North Africa and Southern Europe, and to a lesser extent, eastern North America. The aridity of the Sahara Desert and the summer drought of the Mediterranean Basin is due to the large-scale subsidence and sinking motion of air in the system. In its summer position, the high is centered near Bermuda, and creates a southwest flow of warm tropical air toward the East Coast of the United States. In summer, the Azores-Bermuda High is strongest. The central pressure hovers around 1024 mbar (hPa).

The climate of Hungary, is characterized by its position. Hungary is in the eastern part of Central Europe, roughly equidistant from the Equator and the North Pole, more than 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) from either and about 1,000 kilometres from the Atlantic Ocean.
Centers of action are extensive and almost stationary low or high pressure areas which control the movement of atmospheric disturbances over a large area. This does not mean that the position of the center is constant over a specific area but that the monthly atmospheric pressure corresponds to a high or a low pressure.

The West Siberian taiga ecoregion covers the West Siberian Plain in Russia, from the Ural mountains in the west to the Yenisei River in the east, and roughly from 56° N to 66° N latitude. It is a vast, flat lowland region of boreal forests (taiga), and wetlands, covering an area about 1,800 km west–east, by 1,000 km north–south.

Anticyclone Hartmut was a storm that began on 22 February 2018, and brought a cold wave to Great Britain and Ireland. Anticyclone Hartmut also brought widespread unusually low temperatures and heavy snowfall to large areas. The cold wave combined with Storm Emma, part of the 2017–18 European windstorm season, which made landfall in southwest England and the south of Ireland on 2 March.















