Related Research Articles
The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) is a United Nations-run carbon offset scheme allowing countries to fund greenhouse gas emissions-reducing projects in other countries and claim the saved emissions as part of their own efforts to meet international emissions targets. It is one of the three Flexible Mechanisms defined in the Kyoto Protocol. The CDM, defined in Article 12 of the Protocol, was intended to assist non-Annex I countries achieve sustainable development and reduce their carbon footprints, and to assist Annex I countries achieve compliance with greenhouse gas emissions reduction commitments.

Carbon offsetting is a carbon trading mechanism that enables entities to compensate for offset greenhouse gas emissions by investing in projects that reduce, avoid, or remove emissions elsewhere. When an entity invests in a carbon offsetting program, it receives carbon credit or offset credit, which account for the net climate benefits that one entity brings to another. After certification by a government or independent certification body, credits can be traded between entities. One carbon credit represents a reduction, avoidance or removal of one metric tonne of carbon dioxide or its carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e).

The European Union Emissions Trading System is a carbon emission trading scheme that began in 2005 and is intended to lower greenhouse gas emissions in the EU. Cap and trade schemes limit emissions of specified pollutants over an area and allow companies to trade emissions rights within that area. The ETS covers around 45% of the EU's greenhouse gas emissions.
Flexible mechanisms, also sometimes known as Flexibility Mechanisms or Kyoto Mechanisms, refers to emissions trading, the Clean Development Mechanism and Joint Implementation. These are mechanisms defined under the Kyoto Protocol intended to lower the overall costs of achieving its emissions targets. These mechanisms enable Parties to achieve emission reductions or to remove carbon from the atmosphere cost-effectively in other countries. While the cost of limiting emissions varies considerably from region to region, the benefit for the atmosphere is in principle the same, wherever the action is taken.

The Carbonfund.org Foundation was formerly a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit organization based in East Aurora, New York. It still provides carbon offsetting and greenhouse gas reduction options to individuals, businesses, and organizations. Carbonfund.org Foundation purchases and retires certified carbon offsets on behalf of its donors. Donors are given a choice of project type to which they may donate, including renewable energy, reforestation, and energy efficiency projects. Carbonfund.org Foundation sources carbon credits verified by the Verra carbon standard and Gold Standard. The organization has helped develop four Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD+) projects in Brazil under the VERRA and Climate, Community and Biodiversity standards.
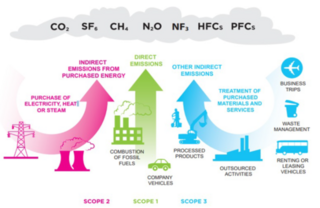
Carbon accounting is a framework of methods to measure and track how much greenhouse gas (GHG) an organization emits. It can also be used to track projects or actions to reduce emissions in sectors such as forestry or renewable energy. Corporations, cities and other groups use these techniques to help limit climate change. Organizations will often set an emissions baseline, create targets for reducing emissions, and track progress towards them. The accounting methods enable them to do this in a more consistent and transparent manner.
The Gold Standard (GS), or Gold Standard for the Global Goals, is a standard and logo certification mark program, for non-governmental emission reductions projects in the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM), the Voluntary Carbon Market and other climate and development interventions. It is published and administered by the Gold Standard Foundation, a non-profit foundation headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. It was designed with an intent to ensure that carbon credits are real, verifiable, and that projects make measurable contributions to sustainable development. The objective of the GS is to add branding, with a quality label, to carbon credits generated by projects which can then be bought and traded by countries that have a binding legal commitment according to the Kyoto Protocol, businesses, or other organizations for carbon offsetting purposes.

Certified emission reductions (CERs) originally designed a type of emissions unit issued by the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) Executive Board for emission reductions achieved by CDM projects and verified by a DOE under the rules of the Kyoto Protocol.

ClimateCare is a profit for purpose environmental and social impact company known for its role providing carbon offset services, with a particular focus on using carbon and other results based finance to support its 'Climate+Care Projects'. It also provides businesses and governments with sustainable development programmes, environmental and social impact measurement and project development.
ecosecurities is a company specialized in carbon markets and greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation projects worldwide. ecosecurities specializes in sourcing, developing and financing projects on renewable energy, energy efficiency, forestry and waste management with a positive environmental impact.

myclimate was spun off from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich in 2002 as a nonprofit climate protection organisation based in Switzerland to enable climate protection with economic mechanisms such as price-tagging carbon dioxide and integrating the externality into the market. They promote climate protection on three levels: avoidance techniques such as capacity building and teaching, reduction and carbon offsetting. myclimate advocates for the development of a carbon market while setting new standards in carbon emissions and in designing a sustainable society.
Personal carbon credits are carbon credits created and owned by individuals who reduce their green house gas (GHG) emissions by a real and verifiable amount. Individuals cause GHG emissions from a variety of direct and indirect activities including transportation use, electrical use and home heating and cooling. Verifiable reductions in GHG emissions are aggregated into 1 metric ton increments and they become personal Carbon Credits. There are many firms that are creating applications to efficiently measure and track these emissions, while providing options to purchase and offset personal emissions.
Emissions reduction currency systems (ERCS) are schemes that provide a positive economic and or social reward for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, either through distribution or redistribution of national currency or through the publishing of coupons, reward points, local currency, or complementary currency.
The Climate, Community & Biodiversity Alliance (CCBA) is a partnership consisting of Conservation International, CARE, The Nature Conservancy, Rainforest Alliance, and the Wildlife Conservation Society that is primarily active in the field of land management activities.
Pedro Moura Costa is an entrepreneur involved in environmental finance with a focus on the international efforts for greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions. Of particular relevance, he was the founder and President of EcoSecurities Group Plc., one of the leading project developers for the international carbon markets, and has written widely about the policy and science of climate change mitigation, including contributions to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports.
The Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), formerly the Voluntary Carbon Standard, is a standard for certifying carbon credits to offset emissions. VCS is administered by Verra, a 501(c)(3) organization. Verra is a certifier of voluntary carbon offsets. As of 2020 there were over 1,500 certified VCS projects covering energy, transport, waste, forestry, and other sectors. In 2021 Verra issued 300 MtCO2e worth of offset credits for 110 projects. There are also specific methodologies for REDD+ projects. Verra is a program of choice for most of the forest credits in the voluntary market, and almost all REDD+ projects.
Environmental certification is a form of environmental regulation and development where a company can voluntarily choose to comply with predefined processes or objectives set forth by the certification service. Most certification services have a logo which can be applied to products certified under their standards. This is seen as a form of corporate social responsibility allowing companies to address their obligation to minimise the harmful impacts to the environment by voluntarily following a set of externally set and measured objectives.
The Woodland Carbon Code is the UK standard for afforestation projects for climate change mitigation. It provides independent validation and verification and assurance about the levels of carbon sequestration from woodland creation projects and their contribution to climate change mitigation.

CO2balance UK Ltd is a British profit-for-purpose carbon management consultancy and project developer founded in 2003. It is known for developing carbon finance projects in developing countries that reduce carbon emissions and support the Sustainable Development Goals. CO2balance also provides businesses and individuals with carbon footprint calculation and reduction services, bestowing the label of ‘CarbonZero’ on those organisations that completely offset the footprint of their operations.
Global Carbon Council (GCC), formerly known as Global Carbon Trust (GCT), is MENA region's first voluntary carbon offsetting program. It facilitates global stakeholders in implementing climate actions through provision of voluntary carbon offsetting program.
References
- ↑ Hamilton, Katherine; Sjardin, Milo; Peters-Stanley and, Molly; Marcello, Thomas (2010-06-14). Building Bridges: State of the Voluntary Carbon Markets 2010 (PDF). Ecosystem Marketplace & Bloomberg New Energy Finance. Retrieved 2010-10-18.
Credits sourced specifically for the OTC market are often generically referred to as Verified (or Voluntary) Emission Reductions (VERs) (p 9)
- ↑ "Verified Emission Reductions". First Climate. 2010. Retrieved 2010-10-18.
A VER project has its GHG emission reductions certified under a voluntary certification process. VERs (Verified Emission Reductions) can be traded on the so-called voluntary carbon market
- ↑ "VER - Verified Emission Reduction". Glossary. Ireland: EcoSecurities Group plc. Retrieved 2010-10-19.
- ↑ "Developing voluntary market projects to produce Verified Emission Reductions (VERs) - VER Projects". EcoSecurities Group plc. Retrieved 2010-10-19.
- ↑ "Sources of VERs, Types of VER, Land use change, Carbon Capture storage, biofuels, Forestry, Afforestation". CDM Update. Retrieved 2010-10-19.