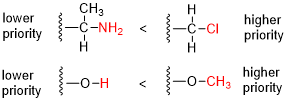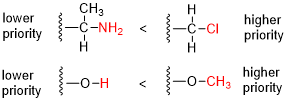
In organic chemistry, the Cahn–Ingold–Prelog (CIP) sequence rules are a standard process to completely and unequivocally name a stereoisomer of a molecule. The purpose of the CIP system is to assign an R or S descriptor to each stereocenter and an E or Z descriptor to each double bond so that the configuration of the entire molecule can be specified uniquely by including the descriptors in its systematic name. A molecule may contain any number of stereocenters and any number of double bonds, and each usually gives rise to two possible isomers. A molecule with an integer n describing the number of stereocenters will usually have 2n stereoisomers, and 2n−1 diastereomers each having an associated pair of enantiomers. The CIP sequence rules contribute to the precise naming of every stereoisomer of every organic molecule with all atoms of ligancy of fewer than 4.

The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Greta Heydenrych.

In organic chemistry, acetyl is a functional group with the chemical formula −COCH3 and the structure −C(=O)−CH3. It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac. In IUPAC nomenclature, acetyl is called ethanoyl, although this term is rarely heard.
Mesitylene or 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene is a derivative of benzene with three methyl substituents positioned symmetrically around the ring. The other two isomeric trimethylbenzenes are 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene) and 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene (hemimellitene). All three compounds have the formula C6H3(CH3)3, which is commonly abbreviated C6H3Me3. Mesitylene is a colorless liquid with sweet aromatic odor. It is a component of coal tar, which is its traditional source. It is a precursor to diverse fine chemicals. The mesityl group (Mes) is a substituent with the formula C6H2Me3 and is found in various other compounds.

Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year.
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products. Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.

Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer was a German chemist who synthesised indigo and developed a nomenclature for cyclic compounds. He was ennobled in the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1885 and was the 1905 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
Barbituric acid or malonylurea or 6-hydroxyuracil is an organic compound based on a pyrimidine heterocyclic skeleton. It is an odorless powder soluble in water. Barbituric acid is the parent compound of barbiturate drugs, although barbituric acid itself is not pharmacologically active. The compound was first synthesised by Adolf von Baeyer.
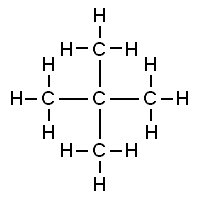
Neopentane, also called 2,2-dimethylpropane, is a double-branched-chain alkane with five carbon atoms. Neopentane is a flammable gas at room temperature and pressure which can condense into a highly volatile liquid on a cold day, in an ice bath, or when compressed to a higher pressure.
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
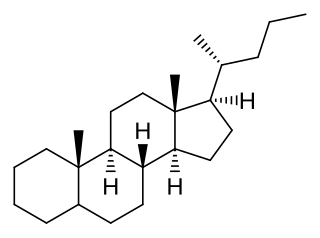
Cholane is a triterpene which can exist as either of two stereoisomers, 5α-cholane and 5β-cholane. Its name is derived from Greek: χολή (chole) meaning 'bile' in reference to its original discovery from the bile of the American bullfrog. The compound itself has no known uses. However, various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals, typically in the form of sterols, steroids and bile acids.
The suffix -oate is the IUPAC nomenclature used in organic chemistry to form names of compounds formed from carboxylic acids. They are of two types:
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among the possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choosing between multiple possibilities in situations where it is important to decide on a unique name. It is intended for use in legal and regulatory situations.
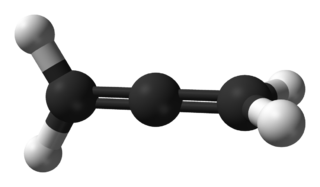
Propadiene or allene is the organic compound with the formula H2C=C=CH2. It is the simplest allene, i.e. a compound with two adjacent carbon double bonds. As a constituent of MAPP gas, it has been used as a fuel for specialized welding.

Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, commonly referred to by chemists as the Blue Book, is a collection of recommendations on organic chemical nomenclature published at irregular intervals by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). A full edition was published in 1979, an abridged and updated version of which was published in 1993 as A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Both of these are now out-of-print in their paper versions, but are available free of charge in electronic versions. After the release of a draft version for public comment in 2004 and the publication of several revised sections in the journal Pure and Applied Chemistry, a fully revised edition was published in print in 2013 and its online version is also available.
In chemistry, a ring is an ambiguous term referring either to a simple cycle of atoms and bonds in a molecule or to a connected set of atoms and bonds in which every atom and bond is a member of a cycle. A ring system that is a simple cycle is called a monocycle or simple ring, and one that is not a simple cycle is called a polycycle or polycyclic ring system. A simple ring contains the same number of sigma bonds as atoms, and a polycyclic ring system contains more sigma bonds than atoms.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided initially into seven IUPC Colour Books: Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and Red. There is also an eighth book, the "Silver Book".
In chemical nomenclature, a descriptor is a notational prefix placed before the systematic substance name, which describes the configuration or the stereochemistry of the molecule. Some listed descriptors are only of historical interest and should not be used in publications anymore as they do not correspond with the modern recommendations of the IUPAC. Stereodescriptors are often used in combination with locants to clearly identify a chemical structure unambiguously.
![Numbered skeletal formula of bicyclo[4.4.0]decane or Decalin. The grey numbers represent numbering according to the von Baeyer nomenclature. Decahydronaphthalene.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c8/Decahydronaphthalene.svg/220px-Decahydronaphthalene.svg.png)