
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a transmission network. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid.

A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems.

The Bonneville Power Administration (BPA) is an American federal agency operating in the Pacific Northwest. BPA was created by an act of Congress in 1937 to market electric power from the Bonneville Dam located on the Columbia River and to construct facilities necessary to transmit that power. Congress has since designated Bonneville to be the marketing agent for power from all of the federally owned hydroelectric projects in the Pacific Northwest. Bonneville is one of four regional Federal power marketing agencies within the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).

The Pacific DC Intertie is an electric power transmission line that transmits electricity from the Pacific Northwest to the Los Angeles area using high voltage direct current (HVDC). The line capacity is 3.1 gigawatts, which is enough to serve two to three million Los Angeles households and represents almost half of the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) electrical system's peak capacity.

Path 27, also called the Intermountain or the Southern Transmission System (STS), is a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electrical transmission line running from the coal-fired Intermountain Power Plant near Delta, Utah, to the Adelanto Converter Station at Adelanto, California, in the Southwestern United States. It was installed by Asea, a company based in Sweden, and commercialized in July 1986. The system is designed to carry power generated at the power plant in Utah to areas throughout Southern California. It is owned and operated by the Intermountain Power Agency, a cooperative consisting of six Los Angeles-area cities, the largest member being the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP), and 29 smaller Utah municipalities.

The Western Interconnection is a wide area synchronous grid and one of the two major alternating current (AC) power grids in the North American power transmission grid. The other major wide area synchronous grid is the Eastern Interconnection. The minor interconnections are the Québec Interconnection, the Texas Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnections.

Path 15 is an 84-mile (135 km) portion of the north–south power transmission corridor in California, U.S. It forms a part of the Pacific AC Intertie and the California-Oregon Transmission Project. Path 15 is part of The Western Electricity Coordinating Council's links of electrical intertie paths in the western United States.

California Oregon Intertie (COI), identified as Path 66 by Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC), is a corridor of three roughly parallel 500 kV alternating current power lines connecting the electric grids of Oregon and California. Their combined power transmission capacity is 4800 MW.

Path 26 is a set of three Southern California Edison (SCE) 500 kV power lines, located primarily in Los Angeles County, and extending into Kern and Ventura counties, all in California. Path 26 is part of the Western Electricity Coordinating Council's links of electrical intertie paths in the western United States. The Path 26 lines are located in: the San Joaquin Valley of the southern Central Valley; the Tehachapi Mountains and other central Transverse Ranges; and the Antelope Valley section of the Mojave Desert.
The Sylmar Converter Station is the southern converter station of the Pacific DC Intertie, an electric power transmission line which transmits electricity from the Celilo Converter Station outside The Dalles, Oregon to Sylmar, a neighborhood in the northeastern San Fernando Valley region of Los Angeles, California. The station converts the 500 kV direct current coming from the northern converter station Celilo to alternating current at 60 Hz and 230 kV synchronized with the Los Angeles power grid. The station capacity is 3,100 megawatts. It is jointly owned by two electric utility providers, Southern California Edison and Los Angeles Department of Water and Power.

The Celilo Converter Station, built in 1970 and owned and operated by the Bonneville Power Administration, is the northern terminus of the Pacific DC Intertie, near The Dalles, Oregon, in the United States.
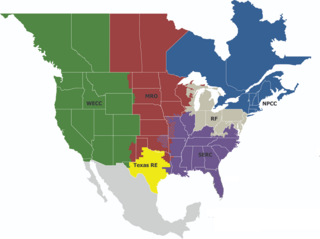
The Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) promotes Bulk Electric System (BES) reliability for the entire Western Interconnection system. WECC is the Regional Entity responsible for compliance monitoring and enforcement. In addition, WECC provides an environment for the development of Reliability Standards and the coordination of the operating and planning activities of its members as set forth in the WECC Bylaws.
Path 61 or the Lugo - Victorville 500 kV Line is a relatively short AC 500 kV power line that runs from Southern California Edison's (SCE) Lugo substation southwest of Hesperia to Los Angeles Department of Water and Power's (LADW&P) Victorville substation north of Victorville, California. Path 61 is part of the Western Electricity Coordinating Council's links of electrical intertie paths in the western United States.This line is an important connection between two out of the four parts that make up the massive Path 46 transmission system in southeast California since the line allows power flow to be rerouted on Path 46 when necessary. Half of the length of the 500 kV power line is owned by SCE to the south and LADW&P to the north. The entire line is located in the Mojave Desert and the High Desert regions of California.
Path 46, also called West of Colorado River, Arizona-California West-of-the-River Path (WOR), is a set of fourteen high voltage alternating-current transmission lines that are located in southeast California and Nevada up to the Colorado River.
A super grid or supergrid is a wide-area transmission network, generally trans-continental or multinational, that is intended to make possible the trade of high volumes of electricity across great distances. It is sometimes also referred to as a "mega grid". Super grids typically are proposed to use high-voltage direct current (HVDC) to transmit electricity long distances. The latest generation of HVDC power lines can transmit energy with losses of only 1.6% per 1,000 km.
The Mead substation is a major electric power interconnection point in the western United States. The station is located in the El Dorado Valley of Nevada just outside of Boulder City, at the end of Buchanan Boulevard south of its grade separation with Interstate 11. The facility is owned and operated by the Western Area Power Administration.

The 2011 Southwest blackout, also known as the Great Blackout of 2011, was a widespread power outage that affected the San Diego–Tijuana area, southern Orange County, Imperial Valley, Mexicali Valley, Coachella Valley, and parts of Arizona. It occurred on Thursday, September 8, 2011, beginning at about 3:38pm PDT, and was the largest power failure in California history.

The electrical power grid that powers Northern America is not a single grid, but is instead divided into multiple wide area synchronous grids. The Eastern Interconnection and the Western Interconnection are the largest. Three other regions include the Texas Interconnection, the Quebec Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnection. Each region delivers power at a nominal 60 Hz frequency. The regions are not usually directly connected or synchronized to each other, but there exist some HVDC interconnectors. The Eastern and Western grids are connected via seven links that allow 1.32 GW to flow between them. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that increasing these interconnections would save energy costs.
The TransWest Express Transmission Line Project (TWE) is a planned bipolar HVDC transmission line between Rawlins, Wyoming and Marketplace substation near Las Vegas.
A balancing authority (BA) is an entity in the US electric system that is responsible for grid balancing: resource planning and unit commitment ahead of time, maintenance of the load-interchange-generation balance within a balancing authority area and support for real-time load-frequency control. The balancing authorities are connected by metered high-voltage tie lines and grouped into interconnections:















