Related Research Articles

A randomized controlled trial is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments.
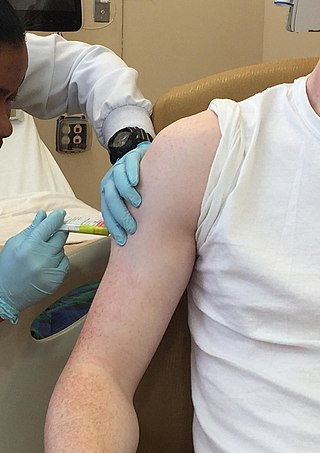
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.
Selection bias is the bias introduced by the selection of individuals, groups, or data for analysis in such a way that proper randomization is not achieved, thereby failing to ensure that the sample obtained is representative of the population intended to be analyzed. It is sometimes referred to as the selection effect. The phrase "selection bias" most often refers to the distortion of a statistical analysis, resulting from the method of collecting samples. If the selection bias is not taken into account, then some conclusions of the study may be false.

A scientific control is an experiment or observation designed to minimize the effects of variables other than the independent variable. This increases the reliability of the results, often through a comparison between control measurements and the other measurements. Scientific controls are a part of the scientific method.
In the design of experiments, hypotheses are applied to experimental units in a treatment group. In comparative experiments, members of a control group receive a standard treatment, a placebo, or no treatment at all. There may be more than one treatment group, more than one control group, or both.

The number needed to treat (NNT) or number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) is an epidemiological measure used in communicating the effectiveness of a health-care intervention, typically a treatment with medication. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional bad outcome. It is defined as the inverse of the absolute risk reduction, and computed as , where is the incidence in the treated (exposed) group, and is the incidence in the control (unexposed) group. This calculation implicitly assumes monotonicity, that is, no individual can be harmed by treatment. The modern approach, based on counterfactual conditionals, relaxes this assumption and yields bounds on NNT.

In statistics, a confounder is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Confounding is a causal concept, and as such, cannot be described in terms of correlations or associations. The existence of confounders is an important quantitative explanation why correlation does not imply causation.
In medicine an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis of the results of a randomized controlled trial is based on the initial treatment assignment and not on the treatment eventually received. ITT analysis is intended to avoid various misleading artifacts that can arise in intervention research such as non-random attrition of participants from the study or crossover. ITT is also simpler than other forms of study design and analysis, because it does not require observation of compliance status for units assigned to different treatments or incorporation of compliance into the analysis. Although ITT analysis is widely employed in published clinical trials, it can be incorrectly described and there are some issues with its application. Furthermore, there is no consensus on how to carry out an ITT analysis in the presence of missing outcome data.
Zelen's design is an experimental design for randomized clinical trials proposed by Harvard School of Public Health statistician Marvin Zelen (1927-2014). In this design, patients are randomized to either the treatment or control group before giving informed consent. Because the group to which a given patient is assigned is known, consent can be sought conditionally.

A quasi-experiment is an empirical interventional study used to estimate the causal impact of an intervention on target population without random assignment. Quasi-experimental research shares similarities with the traditional experimental design or randomized controlled trial, but it specifically lacks the element of random assignment to treatment or control. Instead, quasi-experimental designs typically allow the researcher to control the assignment to the treatment condition, but using some criterion other than random assignment.
Impact evaluation assesses the changes that can be attributed to a particular intervention, such as a project, program or policy, both the intended ones, as well as ideally the unintended ones. In contrast to outcome monitoring, which examines whether targets have been achieved, impact evaluation is structured to answer the question: how would outcomes such as participants' well-being have changed if the intervention had not been undertaken? This involves counterfactual analysis, that is, "a comparison between what actually happened and what would have happened in the absence of the intervention." Impact evaluations seek to answer cause-and-effect questions. In other words, they look for the changes in outcome that are directly attributable to a program.
Repeated measures design is a research design that involves multiple measures of the same variable taken on the same or matched subjects either under different conditions or over two or more time periods. For instance, repeated measurements are collected in a longitudinal study in which change over time is assessed.
In the statistical analysis of observational data, propensity score matching (PSM) is a statistical matching technique that attempts to estimate the effect of a treatment, policy, or other intervention by accounting for the covariates that predict receiving the treatment. PSM attempts to reduce the bias due to confounding variables that could be found in an estimate of the treatment effect obtained from simply comparing outcomes among units that received the treatment versus those that did not. Paul R. Rosenbaum and Donald Rubin introduced the technique in 1983.
A glossary of terms used in clinical research.

Placebo-controlled studies are a way of testing a medical therapy in which, in addition to a group of subjects that receives the treatment to be evaluated, a separate control group receives a sham "placebo" treatment which is specifically designed to have no real effect. Placebos are most commonly used in blinded trials, where subjects do not know whether they are receiving real or placebo treatment. Often, there is also a further "natural history" group that does not receive any treatment at all.

In the design of experiments, a between-group design is an experiment that has two or more groups of subjects each being tested by a different testing factor simultaneously. This design is usually used in place of, or in some cases in conjunction with, the within-subject design, which applies the same variations of conditions to each subject to observe the reactions. The simplest between-group design occurs with two groups; one is generally regarded as the treatment group, which receives the ‘special’ treatment, and the control group, which receives no variable treatment and is used as a reference The between-group design is widely used in psychological, economic, and sociological experiments, as well as in several other fields in the natural or social sciences.
Circles of Support and Accountability (CoSA) are groups of volunteers with professional supervision to support sex offenders as they reintegrate into society after their release from incarceration. Evaluations of CoSA indicate that participation in a CoSA can result in statistically significant reductions in repeat sexual offenses in 70% of cases, relative to what would be predicted by risk assessment or matched comparison subjects. CoSA projects exist throughout Canada, the United Kingdom, and some regions of the United States.
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays.
Self-control therapy is a behavioral treatment method based on a self-control model of depression, that was modeled after Frederick Kanfer's behavioral (1971) model of self-control.
In medicine, a stepped-wedge trial is a type of randomised controlled trial (RCT). An RCT is a scientific experiment that is designed to reduce bias when testing a new medical treatment, a social intervention, or another testable hypothesis.
References
- ↑ Elliott SA, Brown JS. (2002). What are we doing to waiting list controls? Behav Res Ther. 2002 Sep; 40(9): 1047–52.