
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) is an international financial institution that offers investment, advisory, and asset-management services to encourage private-sector development in less developed countries. The IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States.
The Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC) was an independent agency of the United States federal government that served as a lender of last resort to US banks and businesses. Established in 1932 by the Hoover administration to restore public confidence in the economy and banking to their pre-Depression levels, the RFC provided financial support to state and local governments, recapitalized banks to prevent bank failures and stimulate lending, and made loans to railroads, mortgage associations, and other large businesses.

The Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) was the United States Government's Development finance institution until it merged with the Development Credit Authority (DCA) of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) to form the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC). OPIC mobilized private capital to help solve critical development challenges and in doing so, advanced the foreign policy of the United States and national security objectives.

The Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA), or Ginnie Mae, is a government-owned corporation of the United States Federal Government within the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). It was founded in 1968 and works to expand affordable housing by guaranteeing housing loans (mortgages) thereby lowering financing costs such as interest rates for those loans. It does that through guaranteeing to investors the on-time payment of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) even if homeowners default on the underlying mortgages and the homes are foreclosed upon.

The Business Development Bank of Canada is a Crown corporation and national development bank wholly owned by the Government of Canada, mandated to help create and develop Canadian businesses through financing, growth and transition capital, venture capital and advisory services, with a focus on small and medium-sized enterprises.
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance a need, program, or project. While this is usually in the form of money, it can also take the form of effort or time from an organization or company. Generally, this word is used when a firm uses its internal reserves to satisfy its necessity for cash, while the term financing is used when the firm acquires capital from external sources.
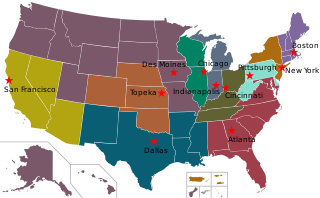
The Federal Home Loan Banks are 11 U.S. government-sponsored banks that provide liquidity to financial institutions to support housing finance and community investment.
A government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) is a type of financial services corporation created by the United States Congress. Their intended function is to enhance the flow of credit to targeted sectors of the economy, to make those segments of the capital market more efficient and transparent, and to reduce the risk to investors and other suppliers of capital. The desired effect of the GSEs is to enhance the availability and reduce the cost of credit to the targeted borrowing sectors primarily by reducing the risk of capital losses to investors: agriculture, home finance and education. Well known GSEs are the Federal National Mortgage Association, known as Fannie Mae, and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, or Freddie Mac.
The Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) is a wholly owned United States government corporation that was created in 1933 to "stabilize, support, and protect farm income and prices". The CCC is authorized to buy, sell, lend, make payments, and engage in other activities for the purpose of increasing production, stabilizing prices, assuring adequate supplies, and facilitating the efficient marketing of agricultural commodities.
The IDBI Bank Limited is a Scheduled Commercial Bank under the ownership of Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) and Government of India. It was established by Government of India as a wholly owned subsidiary of Reserve Bank of India in 1964 as Industrial Development Bank of India, a Development Finance Institution, which provided financial services to industrial sector. In 2005, the institution was merged with its subsidiary commercial division, IDBI Bank, and was categorised as "Other Development Finance Institution" category. Later in March 2019, Government of India asked LIC to infuse capital in the bank due to high NPA and capital adequacy issues and also asked LIC to manage the bank to meet the regulatory norms. Consequent upon LIC acquiring 51% of the total paid-up equity share capital, the bank was categorised as a 'Private Sector Bank' for regulatory purposes by Reserve Bank of India with effect from 21 January 2019. IDBI was put under Prompt Corrective Action of the Reserve Bank of India and on 10 March 2021 IDBI came out of the same. At present direct and indirect shareholding of Government of India in IDBI Bank is approximately 95%, which Government of India (GoI) vide its communication F.No. 8/2/2019-BO-II dated 17 December 2019, has clarified and directed all Central/State Government departments to consider IDBI Bank for allocation of Government Business. Many national institutes find their roots in IDBI like SIDBI, EXIM, National Stock Exchange of India, SEBI, National Securities Depository Limited. Presently, IDBI Bank is one of the largest Commercial Banks in India.

The Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA), is a United States federal law enacted in the wake of the savings and loan crisis of the 1980s.
Industrial Development Bank of Pakistan is a Pakistani state-owned development bank located in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. It is among the oldest financing institutions in Pakistan.
Federal financing for small businesses in Canada is facilitated via a number of programs and agencies. Financing is available in the form of grants, loans, loan guarantees, income support and subsidized hiring and/or training programs. The government also provides funding for no-cost or subsidized services to small businesses, including workshops, business plan consulting, education, and federally sponsored trade missions. Financing, and federally funded or subsidized services are available both to established businesses looking to grow or expand into new markets and to entrepreneurs seeking to launch a new business.
China's banking sector had CN¥417 trillion in assets at the end of 2023. The "Big Four" state-owned commercial banks are the Bank of China, the China Construction Bank, the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and the Agricultural Bank of China, all of which are among the largest banks in the world as of 2018. Other notable big and also the largest banks in the world are China Merchants Bank and Ping An Bank.
The history of banking in China includes the business of dealing with money and credit transactions in China.
Crown corporations are government organizations in Canada with a mixture of commercial and public-policy objectives. They are directly and wholly owned by the Crown.
Pennsylvania Department of Community and Economic Development is a cabinet-level state agency in Pennsylvania. The mission of the department is to enhance investment opportunities for businesses and to improve the quality of life for residents. The department works to attract outside corporations, spur expansion of existing local employers, and foster start-ups by providing tax incentives and technical assistance. Additionally, the agency provides grant funding to community groups and local governments for projects such as revitalizing "Main Street" infrastructure, enhancing low income housing availability, or improving access to technology.

A public bank is a bank, a financial institution, in which a state, municipality, or public actors are the owners. It is an enterprise under government control. Prominent among current public banking models are the Bank of North Dakota, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe in Germany, and many nations' postal bank systems.

The Clean Energy Finance Corporation (CEFC) is an Australian Government-owned green bank that invests in clean energy, to help achieve Australia's national goal of net zero emissions by 2050. The CEFC invests billions of dollars on behalf of the Australian Government in economy-wide decarbonisation opportunities. It aims to help transform the Australian energy grid, as well as supporting sustainable housing initiatives, and climate tech innovators. It was established by and operates under the Clean Energy Finance Corporation Act 2012, along with other subsidiary legislation. As of March 2024 Steven Skala is CEFC chair and Ian Learmonth is CEFC Chief Executive Officer.

Carlos "Sonny" García Domínguez III is a distinguished Filipino businessman who was appointed as Philippine Cabinet Secretary thrice: as Minister of Natural Resources (1986-1987), Secretary of Agriculture (1987-1989), and as Secretary of Finance (2016-2022).








