Asia is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population, having more people than all other continents combined.

The Balkans, corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.

Europe is a continent comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish straits.

Imperialism is the practice, theory or attitude of maintaining or extending power over foreign nations, particularly through expansionism, employing not only hard power, but also soft power. Imperialism focuses on establishing or maintaining hegemony and a more or less formal empire.

The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai, is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north.
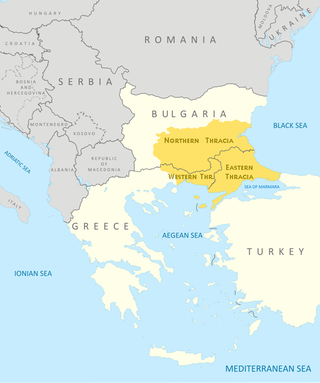
Thrace is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria, northeastern Greece, and the European part of Turkey, roughly the Roman Province of Thrace. Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia.

Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The region stretches from the Ural Mountains in the east to the borders of Poland and Romania. Most definitions include the countries of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine while less restrictive definitions also include Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Moldova, Poland, Romania, and Slovakia.
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics, human impact characteristics, and the interaction of humanity and the environment. Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. More confined or well bounded portions are called locations or places.

Travel is the movement of people between distant geographical locations. Travel can be done by foot, bicycle, automobile, train, boat, bus, airplane, ship or other means, with or without luggage, and can be one way or round trip. Travel can also include relatively short stays between successive movements, as in the case of tourism.
Geopolitics is the study of the effects of Earth's geography on politics and international relations. While geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of states: de facto independent states with limited international recognition and relations between sub-national geopolitical entities, such as the federated states that make up a federation, confederation, or a quasi-federal system.

National Geographic is an American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine months after the establishment of the society, but is now a popular magazine. In 1905, it began including pictures, a style for which it became well-known. Its first color photos appeared in the 1910s. During the Cold War, the magazine committed itself to present a balanced view of the physical and human geography of countries beyond the Iron Curtain. Later, the magazine became outspoken on environmental issues.

An academic discipline or field of study is a branch of knowledge, taught and researched as part of higher education. A scholar's discipline is commonly defined by the university faculties and learned societies to which they belong and the academic journals in which they publish research.

The Handbook of Texas is a comprehensive encyclopedia of geography, history, and historical persons of Texas, United States, published by the Texas State Historical Association (TSHA).
National Geographic is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by the National Geographic Global Networks unit of Disney Entertainment and National Geographic Partners, a joint venture between The Walt Disney Company (73%) and the National Geographic Society (27%), with the operational management handled by Disney Entertainment.
In warfare, a theater or theatre is an area in which important military events occur or are in progress. A theater can include the entirety of the airspace, land and sea area that is or that may potentially become involved in war operations.

Military geography is a sub-field of geography that is used by the military, as well as academics and politicians, to understand the geopolitical sphere through the military lens. To accomplish these ends, military geographers consider topics from geopolitics to physical locations’ influences on military operations and the cultural and economic impacts of a military presence. On a tactical level, a military geographer might put together the terrain and the drainage system below the surface, so a unit is not at a disadvantage if the enemy uses the drainage system to ambush it, especially in urban warfare. On a strategic level, an emerging field of strategic and military geography seeks to understand the changing human and biophysical environments that alter the security and military domains. Climate change, for example, is adding and multiplying the complexity of military strategy, planning and training. Emerging responsibilities for the military to be involved in: protection of civilian populations, women and ethnic groups; provision of humanitarian aid and disaster response (HADR); new technology and domains of training and operations, such as in cybergeography, make military geography a dynamic frontier.
If a general desired to be a successful actor in the great drama of war, his first duty is to study carefully the theater of operations so that he may see clearly the relative advantages and disadvantages it presents for himself and his enemies.
Sultan Mansur Shah ibni Almarhum Sultan Muzaffar Shah was the sixth Sultan of Malacca from 1459 to 1477. He ascended the throne after the death of his father, Muzaffar Shah.

A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single landmass or a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe. Due to this, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging North America and South America into America, Asia and Europe into Eurasia, and Africa, Asia, and Europe into Afro-Eurasia.

Ghurab or gurab is a type of merchant and warship from the Nusantara archipelago. The ship was a result of Mediterranean influences in the region, particularly introduced by the Arabs, Persians, and Ottomans. For their war fleet, the Malays prefer to use shallow draught, oared longships similar to the galley, such as lancaran, penjajap, and kelulus. This is very different from the Javanese who prefer long-range, deep-draught round ships such as jong and malangbang. The reason for this difference is that the Malays operated their ships in riverine water, sheltered straits zone, and archipelagic environment, while the Javanese are often active in the open and high sea. After contact with Iberian people, both the Javanese and Malay fleets began to use the ghurab and ghali more frequently.