This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Wara art is the Japanese art of making large sculptures from rice straw.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Wara art is the Japanese art of making large sculptures from rice straw.
Traditionally, rice straw was used for making tatami mats and other objects. At the beginning of the 21st century, these objects were increasingly replaced by manmade materials, leaving rice farmers with a problem, namely what to do with the rice straw. In 2007, the farming community in Niigata prefecture, Japan, a major rice growing prefecture, asked Professor Shingo Miyajima of the Department of Science and Design at the Musashino University to find a creative solution for the problem. He suggested using the straw to create sculptures of animals supported by a wooden frame. This straw art is called in Japan, wara art, “wara” meaning rice straw.
Since 2007, there have been annual festivals of wara art in Niigata prefecture, Nishikan-ku ward. Some of the Wara art statues have been as high as 9 metres tall, but they are usually around 4 metres in height.

Wara art sculptures of endangered Australian animals, designed by Professor Miyajima, have also been created in York, Western Australia as part of the annual York Festival. There are seven statues in York. They were constructed by Australian fibre artists and Japanese wara artists brought to Australia as part of Japanese/ Australian art exchanges, assisted by many volunteers. As there is no rice straw in Western Australia, the York sculptures are made from wheat straw sourced from a York farm that still harvests in stooks. [1]

Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sculptural processes originally used carving and modelling, in stone, metal, ceramics, wood and other materials but, since Modernism, there has been an almost complete freedom of materials and process. A wide variety of materials may be worked by removal such as carving, assembled by welding or modelling, or moulded or cast.

A handicraft, sometimes more expressed as artisanal handicraft or handmade, is any of a wide variety of types of work where useful and decorative objects are made completely by one’s hand or by using only simple, non-tech related tools like scissors, carving implements, or hooks. It is a traditional main sector of craft making and applies to a wide range of creative and design activities that are related to making things with one's hands and skill, including work with textiles, moldable and rigid materials, paper, plant fibers, etc. One of the world's oldest handicraft is Dhokra; this is a sort of metal casting that has been used in India for over 4,000 years and is still used. In Iranian Baluchistan, women still make red ware hand made pottery with dotted ornaments much similar to the 5000 year old pottery tradition of Kalpurgan, an archaeological site near the village. Usually, the term is applied to traditional techniques of creating items that are both practical and aesthetic. Handicraft industries are those that produce things with hands to meet the needs of the people in their locality without using machines.

A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals or non-representational forms are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size; a sculpture that represents persons or animals in full figure but that is small enough to lift and carry is a statuette or figurine, whilst one more than twice life-size is a colossal statue.

Niigata Prefecture is a prefecture in the Chūbu region of Honshu of Japan. Niigata Prefecture has a population of 2,227,496 and is the fifth-largest prefecture of Japan by geographic area at 12,584.18 km2 (4,858.78 sq mi). Niigata Prefecture borders Toyama Prefecture and Nagano Prefecture to the southwest, Gunma Prefecture to the south, Fukushima Prefecture to the east, and Yamagata Prefecture to the northeast.
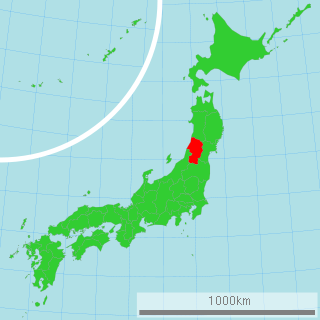
Yamagata Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Yamagata Prefecture has a population of 1,079,950 and has a geographic area of 9,325 km². Yamagata Prefecture borders Akita Prefecture to the north, Miyagi Prefecture to the east, Fukushima Prefecture to the south, and Niigata Prefecture to the southwest.

Tōkamachi is a city located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 July 2019, the city had an estimated population of 28,728 in 19,823 households, and a population density of 86.3 persons per km². The total area of the city was 590.39 square kilometres (227.95 sq mi), although some borders of the city are not well defined. Tōkamachi derives its name from the fact that a market was held every tenth day of the month. Similarly, the nearby former town of Muikamachi had its own local market held on days ending in six each month.

African art describes the modern and historical paintings, sculptures, installations, and other visual culture from native or indigenous Africans and the African continent. The definition may also include the art of the African diasporas, such as African American, Caribbean or art in South American societies inspired by African traditions. Despite this diversity, there are unifying artistic themes present, when considering the totality of the visual culture from the continent of Africa.

Wearable art, also known as Artwear or "art to wear", refers to individually designed pieces of (usually) handmade clothing or jewellery created as fine or expressive art. While the making of any article of clothing or other wearable object typically involves aesthetic considerations, the term wearable art implies that the work is intended to be accepted as a serious and unique artistic creation or statement. Pieces may be sold and/or exhibited. The modern idea of wearable art seems to have surfaced more than once in various forms. Marbeth Schon's book on modernist jewellery refers to a "wearable art movement" spanning roughly the years 1930 to 1960. A 2003 The New York Times review of a book on knitting refers to "the 60s Art to Wear movement".

Uonuma is a city located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 July 2019, the city had an estimated population of 35,027 in 13,289 households, and a population density of 37 persons per km2. Its total area is 946.76 square kilometres (365.55 sq mi). The city is famous for its koshihikari rice, which commands a premium in the Japanese market.

The Shinano River, known as the Chikuma River in its upper reaches, is the longest and widest river in Japan and the third largest by basin area. It is located in northeastern Honshu, rising in the Japanese Alps and flowing generally northeast through Nagano and Niigata Prefectures before emptying into the Sea of Japan.

A Chiwara is a ritual object representing an antelope, used by the Bambara ethnic group in Mali. The Chiwara initiation society uses Chiwara masks, as well as dances and rituals associated primarily with agriculture, to teach young Bamana men social values as well as agricultural techniques.

The sculpture of Japan started from the clay figure. Japanese sculpture received the influence of the Silk Road culture in the 5th century, and received influence from Chinese sculpture afterwards. The influence of the Western world was received since the Meiji era. The sculptures were made at local shops, used for sculpting and painting. Most sculptures were found at areas in front of houses and along walls of important buildings.

Shimenawa are lengths of laid rice straw or hemp rope used for ritual purification in the Shinto religion.
Wara may refer to:
Novelty architecture, also called programmatic or mimetic architecture, is a type of architecture in which buildings and other structures are given unusual shapes for purposes such as advertising or to copy other famous buildings without any intention of being authentic. Their size and novelty means that they often serve as landmarks. They are distinct from architectural follies, in that novelty architecture is essentially usable buildings in eccentric form whereas follies are non-usable, ornamental buildings often in eccentric form.

Nagaoka is a city located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. It is the second largest city in the prefecture, after the capital city of Niigata. As of 1 December 2020, the city had an estimated population of 266,539 in 108,901 households and a population density of 300 inhabitants per square kilometre (780/sq mi). The total area of the city was 891.06 square kilometres (344.04 sq

Jōetsu is a city located in Niigata Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 December 2020, the city had an estimated population of 189,430, in 76,461 households with a population density of 190 persons per km². The total area of the city was 973.81 square kilometres (375.99 sq mi). Jōetsu borders the Sea of Japan and is renowned for its abundance of snow, the annual cherry-blossom festival, sake and Koshihikari rice.
Nicola Hicks is an English sculptor, known for her works made using straw and plaster.
Tatsuo Miyajima is a Japanese sculptor and installation artist who lives in Moriya, in Ibaraki prefecture, Japan. His work frequently employs digital LED counters and is primarily concerned with the function and significance of time and space, especially within the context of Buddhist thought.
Kasa Jizō (笠地蔵) is a Japanese folk tale about an old couple whose generosity is rewarded by the bodhisattva Kṣitigarbha, whose name is Jizō in Japanese. The story is commonly handed down by parents to their children in order to instill moral values, as it is grounded in Buddhist thought. An alternative title, Kasako Jizō can be found in Iwate and Fukushima Prefectures. Its origins belong in the Tōhoku and Niigata regions, with the oldest dispensations coming from Hokuriku, as well as areas of Western Japan such as Hiroshima and Kumamoto Prefectures. Its precise origin, however, remains unknown.