This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(June 2021) |
The Warner Aircraft Corporation of Detroit, Michigan was the manufacturer of the Scarab family of radial engines for airplanes in 1928 through the early 1930s.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(June 2021) |
The Warner Aircraft Corporation of Detroit, Michigan was the manufacturer of the Scarab family of radial engines for airplanes in 1928 through the early 1930s.
The original name of the company was Aeronautical Industries Incorporated. [1] In October 1927 the company changed its name to the Warner Aircraft Corporation. In November 1927 the first Scarab radial engine was produced. The Scarab Junior was introduced in 1930. In 1933, the company designed and built a much larger radial engine, the Super Scarab. This was to be the last engine the company produced. Warner Aircraft was taken over by the Clinton Machine Company in 1950.
| Year | Name | Model | Military designation | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1927 | Scarab | R-420 | 125 hp | |
| 1930 | Scarab Junior | 90 hp | ||
| 1933 | Super Scarab 165 | SS-50 | R-500 | 165 hp |
| 1938 | Super Scarab 185 | SS-50A | R-550 | 185 hp |
Scarab may refer to:

The Monocoupe 90 was a two-seat, light cabin airplane built by Donald A. Luscombe for Monocoupe Aircraft. The first Monocoupe was built in an abandoned church in Davenport, Iowa, and first flew on April 1, 1927. Various models were in production until the late 1940s.
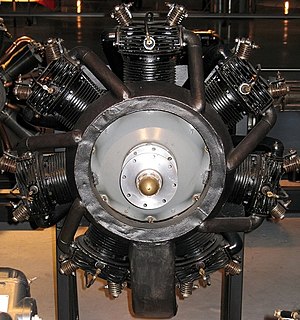
The Warner Scarab is an American seven-cylinder radial aircraft engine, that was manufactured by the Warner Aircraft Corporation of Detroit, Michigan in 1928 through to the early 1940s. In military service the engine was designated R-420.

The Cessna Airmaster, is a family of single-engined aircraft manufactured by the Cessna Aircraft Company. The Airmaster played an important role in the revitalization of Cessna in the 1930s after the crash of the aviation industry during the Great Depression.

The LeBlond radial engines, later produced under the name Ken-Royce, were a family of 3-cylinder, 5-cylinder and 7-cylinder, air-cooled radial engines for aircraft, built in the 1930s by the LeBlond Aircraft Engine Corporation until the operation was sold to Rearwin Airplanes in 1937 and renamed Ken-Royce Engines.
The Warner Scarab Junior was an American, five-cylinder, air-cooled, radial aero engine first produced in 1930. It was a scaled-down derivative of the seven-cylinder Warner Scarab, developing 90 hp (70 kW) against the Scarab's 110 hp (80 kW).

The Siemens-Halske Sh 13 was a five-cylinder air-cooled radial engine for aircraft produced in Germany in the 1920s and 1930s. First run in 1928, it was rated at 60 kW (80 hp).

The Culver Dart was a 1930s American two-seat light monoplane aircraft produced by the Dart Aircraft Company.

The Kinner R-5 is an American five cylinder radial engine for light general and sport aircraft of the 1930s.

The Kreider-Reisner Challenger was an American utility biplane aircraft designed and produced by the Kreider-Reisner Aircraft Company, which was later taken over by the Fairchild Aircraft Company.

The Fairchild 22 Model C7 was an American two-seat touring or training monoplane designed and built by the Kreider-Reisner division of the Fairchild Aircraft Corporation at Hagerstown, Maryland.

The Gee Bee Sportster was a family of sports aircraft built in the United States in the early 1930s by the Granville Brothers. They were low-wing strut- and wire-braced monoplanes of conventional, if short-coupled, design, with open cockpits and fixed, tailskid undercarriage.

The Ryan S-C (Sports-Coupe) was an American three-seat cabin monoplane designed and built by the Ryan Aeronautical Company. At least one was impressed into service with the United States Army Air Forces as the L-10.

The Luscombe Phantom was a 1930s American two-seat cabin monoplane and the first product of the Luscombe Aircraft Engineering Company.

The Rearwin Sportster is a 1930s American two-seat, high-winged, cabin monoplane designed and built by Rearwin Aircraft & Engines for sport/touring use.

The Monocoupe 110 Special was a United States sporting and racing aircraft of the 1930s and 1940s.

The Mohawk M1C was a 1920s American two or three-seat low-wing monoplane designed and built by Mohawk Aero Corporation of Minneapolis, Minnesota. One M1C was evaluated by the United States Army Air Corps in 1930 as the YPT-7 Pinto for use as a primary trainer.

The Kari-Keen 90 Sioux coupe was a two-seat cabin monoplane.

The Eastman E-2 Sea Rover, also called the Beasley-Eastman E-2 Sea Rover, was a light seaplane built in the late 1920s for business and shuttle use.

The Paramount Cabinaire was a 1920s designed cabin biplane, designed by Walter J. Carr and produced by the Paramount Aircraft Corporation. Only eight were completed before production ceased.