| Wartenberg's syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Neurology |
Wartenberg's syndrome is a specific mononeuropathy, caused by entrapment of the superficial branch of the radial nerve. [1] Symptoms include numbness, tingling, and weakness of the posterior aspect of the thumb. Also called Cheiralgia paresthetica.[ citation needed ]
It is not to be confused with Wartenberg's migratory sensory neuropathy, Waardenburg syndrome, or Lateral medullary syndrome (known as Wallenberg's Syndrome). Also not to be confused with Wartenberg's sign, which relates to entrapment of the ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel.[ citation needed ]

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
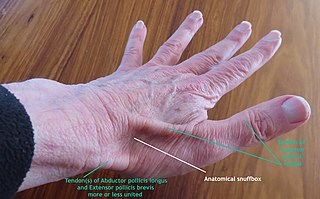
The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox or foveola radialis is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

Wrist drop is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles in the posterior compartment remain paralyzed.
Robert Wartenberg was a clinical neurologist and professor.

The suprascapular nerve is a mixed nerve that branches from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It is derived from the ventral rami of cervical nerves C5-C6. It provides motor innervation to the supraspinatus muscle, and the infraspinatus muscle.

In human anatomy, the supinator is a broad muscle in the posterior compartment of the forearm, curved around the upper third of the radius. Its function is to supinate the forearm.

The posterior interosseous nerve is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve. The nerve fibers originate from cervical segments C7 and C8 in the spinal column.

The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.

The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the Supinator, and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm. The deep branch provides motor function to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm, which is mostly the extensor muscles of the hand.

The superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third. It is a sensory nerve.

The bicipital aponeurosis is a broad aponeurosis of the biceps brachii, which is located in the cubital fossa of the elbow. It separates superficial from deep structures in much of the fossa.

The triangular interval is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: quadrangular space and triangular space.

Ulnar nerve entrapment is a condition where the ulnar nerve becomes physically trapped or pinched, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness, primarily affecting the little finger and ring finger of the hand. Entrapment may occur at any point from the spine at cervical vertebra C7 to the wrist; the most common point of entrapment is in the elbow. Prevention is mostly through correct posture and avoiding repetitive or constant strain. Treatment is usually conservative, including medication, activity modification, and exercise, but may sometimes include surgery. Prognosis is generally good, with mild to moderate symptoms often resolving spontaneously.

Arcade of Frohse, sometimes called the supinator arch, is the most superior part of the superficial layer of the supinator muscle, and is a fibrous arch over the posterior interosseous nerve.
Anterior interosseous syndrome is a medical condition in which damage to the anterior interosseous nerve (AIN), a distal motor and sensory branch of the median nerve, classically with severe weakness of the pincer movement of the thumb and index finger, and can cause transient pain in the wrist.

Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a trapped nerve, though this may also refer to nerve root compression. Its symptoms include pain, tingling, numbness and muscle weakness. The symptoms affect just one particular part of the body, depending on which nerve is affected. The diagnosis is largely clinical and can be confirmed with diagnostic nerve blocks. Occasionally imaging and electrophysiology studies aid in the diagnosis. Timely diagnosis is important as untreated chronic nerve compression may cause permanent damage. A surgical nerve decompression can relieve pressure on the nerve but cannot always reverse the physiological changes that occurred before treatment. Nerve injury by a single episode of physical trauma is in one sense an acute compression neuropathy but is not usually included under this heading, as chronic compression takes a unique pathophysiological course.

Cheiralgia paraesthetica is a neuropathy of the hand generally caused by compression or trauma to the superficial branch of the radial nerve. The area affected is typically on the back or side of the hand at the base of the thumb, near the anatomical snuffbox, but may extend up the back of the thumb and index finger and across the back of the hand. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, burning or pain. Since the nerve branch is sensory there is no motor impairment. It may be distinguished from de Quervain syndrome because it is not dependent on motion of the hand or fingers.
Wartenberg's sign is a neurological sign consisting of involuntary abduction of the fifth (little) finger, caused by unopposed action of the extensor digiti minimi.