
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
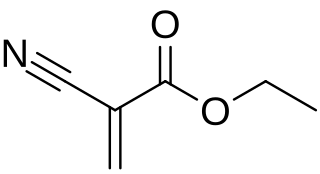
Cyanoacrylates are a family of strong fast-acting adhesives with industrial, medical, and household uses. They are derived from ethyl cyanoacrylate and related esters. The cyanoacrylate group in the monomer rapidly polymerizes in the presence of water to form long, strong chains. They have some minor toxicity.

Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One colour is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multi-coloured image or design.

Flexography is a form of printing process which utilizes a flexible relief plate. It is essentially a modern version of letterpress, evolved with high speed rotary functionality, which can be used for printing on almost any type of substrate, including plastic, metallic films, cellophane, and paper. It is widely used for printing on the non-porous substrates required for various types of food packaging.

Oriented strand board (OSB) is a type of engineered wood similar to particle board, formed by adding adhesives and then compressing layers of wood strands (flakes) in specific orientations. It was invented by Armin Elmendorf in California in 1963. OSB may have a rough and variegated surface with the individual strips of around 2.5 cm × 15 cm, lying unevenly across each other, and is produced in a variety of types and thicknesses.

A decal or transfer is a plastic, cloth, paper, or ceramic substrate that has printed on it a pattern or image that can be moved to another surface upon contact, usually with the aid of heat or water.

Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materials, such as plastic. A laminate is a permanently assembled object created using heat, pressure, welding, or adhesives. Various coating machines, machine presses and calendering equipment are used.

A sticker is a type of label: a piece of printed paper, plastic, vinyl, or other material with temporary or permanent pressure sensitive adhesive on one side. It can be used for decoration or for functional purposes, depending on the situation.

An adhesive label or sticky label is a small piece of paper designed to be affixed to any surface, typically by the action of a layer of adhesive on the front or back of the label. The term adhesive refers to a sticky substance, while something that is self-adhesive implies that it will stick without wetting or the application of glue to the product.

Flocking is the process of depositing many small fiber particles onto a surface. It can also refer to the texture produced by the process, or to any material used primarily for its flocked surface. Flocking of an article can be performed for the purpose of increasing its value in terms of the tactile sensation, aesthetics, color and appearance. It can also be performed for functional reasons including insulation, slip-or-grip friction, retention of a liquid film, and low reflectivity.

Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. When a material galls, some of it is pulled with the contacting surface, especially if there is a large amount of force compressing the surfaces together. Galling is caused by a combination of friction and adhesion between the surfaces, followed by slipping and tearing of crystal structure beneath the surface. This will generally leave some material stuck or even friction welded to the adjacent surface, whereas the galled material may appear gouged with balled-up or torn lumps of material stuck to its surface.

A label is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling.

Foamcore, foam board, or paper-faced foam board is a lightweight and easily cut material used for mounting of photographic prints, as backing for picture framing, for making scale models, and in painting. It consists of a board of polystyrene foam clad with an outer facing of paper on either side, typically white clay-coated paper or brown kraft paper.
Artificial hair integrations, more commonly known as hair extensions, hair weaves, and fake hair add length and fullness to human hair. Hair extensions are usually clipped, glued, or sewn on natural hair by incorporating additional human or synthetic hair. These methods include tape-in extensions, clip-in or clip-on extensions, micro/nano rings, fusion method, weaving method, and wigs.

Animal glue is an adhesive that is created by prolonged boiling of animal connective tissue in a process called rendering. In addition to being used as an adhesive it is used for coating and sizing, in decorative composition ornaments, and as a clarifying agent.
Adhesive bonding describes a wafer bonding technique with applying an intermediate layer to connect substrates of different types of materials. Those connections produced can be soluble or insoluble. The commercially available adhesive can be organic or inorganic and is deposited on one or both substrate surfaces. Adhesives, especially the well-established SU-8, and benzocyclobutene (BCB), are specialized for MEMS or electronic component production.

Postage stamp paper is the foundation or substrate of the postage stamp to which the ink for the stamp's design is applied to one side and the adhesive is applied to the other. The paper is not only the foundation of the stamp but it has also been incorporated into the stamp's design, has provided security against fraud and has aided in the automation of the postal delivery system.

A wall decal, also known as a wall sticker, wall tattoo, or wall vinyl, is a vinyl sticker that is affixed to a wall or other smooth surface for decoration and informational purposes. Wall decals are cut with vinyl cutting machines. Most decals use only one color, but some may have various images printed upon them.

A vinyl cutter is an entry level machine for making signs. Computer designed vector files with patterns and letters are directly cut on the roll of vinyl which is mounted and fed into the vinyl cutter through USB or serial cable. Vinyl cutters are mainly used to make signs, banners and advertisements. Advertisements seen on automobiles and vans are often made with vinyl cut letters. While these machines were designed for cutting vinyl, they can also cut through computer and specialty papers, as well as thicker items like thin sheets of magnet.

Pressure-sensitive tape, known also in various countries as PSA tape, adhesive tape, self-stick tape, sticky tape, Sellotape, or just tape, is an adhesive tape that will stick with application of pressure, without the need for a solvent or heat for activation. It can be used in the home, office, industry, and institutions for a wide variety of purposes.



















