The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

Eleuthera refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of The Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incorporates the smaller Harbour Island. "Eleuthera" derives from the feminine form of the Greek adjective ἐλεύθερος (eleútheros), meaning "free". Known in the 17th century as Cigateo, it lies 80 km east of Nassau. It is long and thin—180 km long and in places little more than 1.6 km wide. Its eastern side faces the Atlantic Ocean, and its western side faces the Great Bahama Bank. The topography of the island varies from wide rolling pink sand beaches to large outcrops of ancient coral reefs, and its population is approximately 11,000. The principal economy of the island is tourism.

Cat Island is located in central Bahamas, and is one of its districts. Cat Island also has the nation's highest point, Mount Alvernia. It rises to 63 metres (207 ft) and is topped by a monastery called The Hermitage. This assembly of buildings was erected by the Franciscan "Brother Jerome".

Ragged Island is a 23 km2 (8.9 sq mi) island and district in the southern Bahamas. Ragged Island is part of the Jumentos Cays and Ragged Island Chain. The crescent-shaped chain measures over 180 km (110 mi) in length and includes cays known as Raccoon Cay, Hog Cay and Double-Breasted Cay. Island ownership is stated to have been granted to William George Lockhart some time in the 18th century. On 8 September 2017, Duncan Town took a direct hit from hurricane Irma.

Acklins is an island and district of the Bahamas.
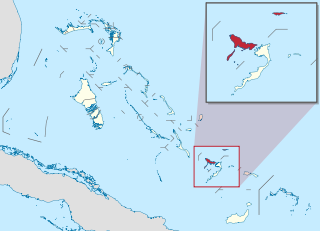
Crooked Island is an island and district, part of a group of Bahamian islands defining a large, shallow lagoon called the Bight of Acklins, of which the largest are Crooked Island in the north and Acklins in the south-east, and the smaller are Long Cay in the north-west, and Castle Island in the south.
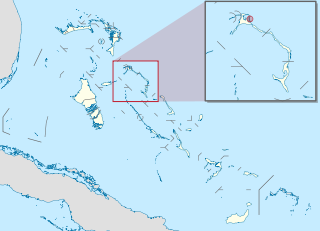
Harbour Island is an island and administrative district in the Bahamas and is located off the northeast coast of Eleuthera Island. It has a population of 1,762.

North Eleuthera is one of the districts of the Bahamas, on the island of Eleuthera. It has a population of 3,247.

South Eleuthera is one of the districts of the Bahamas, on the island of Eleuthera.

Spanish Wells is a district of the Bahamas. The settlement consists of a medium-sized town on the island of St. George's Cay 610 m (2,000 ft) wide by 2,860 m (9,380 ft) long, located approximately 500 m (1,600 ft) off the northern tip of Eleuthera island. According to the 2010 census, it has a population of 1,551 residents.
Dunmore Town is a town in the Bahamas. It has a population of 1,762.
Tarpum Bay is one of the larger settlements on the island of Eleuthera in the Bahamas. As of the 2010 census, Tarpum Bay had a population of 766. Initially named Glenelg after a British Secretary of State for War and the Colonies, the settlements name was changed to Tarpum Bay to reflect the tarpon fish that could be found there. Tarpum Bay is known for its vibrantly colored buildings and large waterside Anglican church. Local fishermen sell their catch daily at one of the two fishing docks.
Governor's Harbour is a principal settlement and administrative centre in Eleuthera in The Bahamas. It corresponds roughly to the centre of the former district of Central Eleuthera. Established by William Sayle and the Eleutherian Adventurers in 1648, it lays claim to being the beginning of the post-Lucayan Bahamas.
Rock Sound is a town and former district of the Bahamas. It corresponds roughly to the current district of South Eleuthera. At the 2010 census, the population was 961. As of 2012 it had a population of 1,075.
Florida Coastal Airlines (FCA) was an airline based in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA. It operated services between Florida and the Bahamas, Cuba, and Haiti.
Afro-Bahamians are an ethnicity originating in The Bahamas of predominantly or partial African descent. They are descendants of various African ethnic groups, many associated with the Bight of Biafra, Ghana, Songhai and Mali, the various Fula kingdoms, the Oyo Empire, and the Kingdom of Kongo. According to the 2010 Census, 92.7% of The Bahamas' population identifies as Black African descent.
White Bahamians are Bahamian citizens of European ancestry, most of whom trace their ancestry back to England, Scotland and Ireland. Bahamians of European descent are sometimes called "Conchs", a term that is also applied to people of White Bahamian descent in Florida. White Bahamians were a majority in the 18th century, but now constitute less than 5% of the Bahamian population. White Bahamians are largely concentrated in Eleuthera, the Abaco Islands, Long Island, and New Providence.

Georgianna Kathleen Symonette a Bahamian suffragist, was the founding chairwoman of the Women's Branch of the Progressive Liberal Party and founding member of the Women's Suffrage Movement. In 2012, The Bahamian government issued a series of postage stamps to honor the women who campaigned to gain universal adult suffrage. Symonette appeared on the 25 cent stamp.
Current Island is an island in the Bahamas, located in the district of North Eleuthera. The island had a population of 38 at the 2010 census. The island is separated from the island of North Eleuthera by a channel known as the Current Cut, which is a site used for diving.
Savannah Sound is a settlement of 204 people in Central Eleuthera, the Bahamas. Its chapel was built in 1809. Its high school is called Windermere.